Abstract
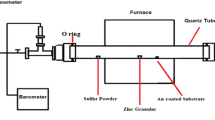
ZnO nanowires were grown by CVD process using both pure Zn powder and a mixture of ZnO and graphite powders as the Zn source, and the key factors controlling nanowire growth were identified. In both processes, the partial pressure of zinc vapor determines the prevailing growth morphology and is sensitive to the growth conditions. In the case of Zn powder as the source, the predominant growth mechanism is driven by self-catalyzed growth on the Si substrate, and in the case of a mixture of ZnO and graphite used as the source, the formation of ZnO nanowires is controlled by the vapor–liquid-solid mechanism, where the gold particles serve as catalyst.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Klingshirn, Phys. Stat. Sol. (b) 244, 3027 (2007)
C.H. Liu, J.A. Zapien, Y. Yao et al., Adv. Mater 15, 838 (2003)
Z.L. Wang, J.H. Song, Science 312, 242 (2006)
J. Liu, P. Fei, J. Zhou, R. Tummala, Z.L. Wang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 173105 (2008)
R. Könenkamp, R.C. Word, C. Schlegel, Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 6004 (2004)
A. Khan, M.E. Kordesch, Physica. E 33, 88 (2006)
Y. Dang, J. Wang, S.S. Fan, Nanotechnology 14, 738 (2003)
W. Mai, P. Gao, C. Lao, Z.L. Wu, A.K. Sood, D.L. Polla, M.B. Soprano, Chem. Phys. Lett. 460, 253 (2008)
T.W. Kim et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 3358 (2004)
J.B.K. Law, C.B. Boothroydb, J.T.L. Thong, J. Cryst. Growth 310, 2485 (2008)
R.F. Zhuo, H.T. Feng, Q. Liang et al., Phys. D Appl. Phys. 41, 185405 (2008)
H.J. Fan, R. Scholz, F.M. Kolb, M. Zacharias, Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 4142 (2004)
S. Ren, Y.F. Bai, J. Chen, S.Z. Deng, N.S. Xu, Q.B. Wu, S.H. Yang, Mater. Lett. 61, 666 (2007)
Z. Zhang, S.J. Wang, T. Yu, T. Wu, J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 17500 (2007)
F. Li, Z. Li, F. Jin, Phys. B 403, 664 (2008)
L.C. Campos, M. Tonezzer, A.S. Ferlauto, V. Grillo, Adv. Mater 20, 1499 (2008)
J.H. Song, X.D. Wang, E. Riedo, Z.L. Wang, J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 9869 (2005)
X.D. Wang, J.H. Song, Z.L. Wang, J. Mater Chem. 17, 711 (2007)
P. Yang, H. Yan, S. Mao, R. Russo, J. Johnson, R. Saykally, N. Morris, J. Pham, R. He, H.-J. Choi, Adv. Funct. Mater 12, 323 (2002)
H.J.T. Ellingham, J. Soc. Chem. Ind. 66, 125 (1944)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wan, H., Ruda, H.E. A study of the growth mechanism of CVD-grown ZnO nanowires. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 21, 1014–1019 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-010-0118-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-010-0118-7