Abstract
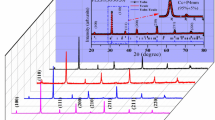
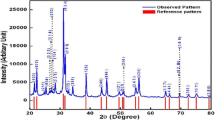
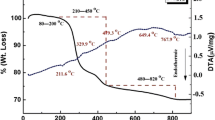
Polycrystalline samples of Mn-modified lead titanate (Pb Mn x Ti1−x O3 (PMT) with x = 0, 0.04, 0.07, 0.10) were prepared by a high-temperature solid-state reaction method. Calcination and sintering temperatures were optimized by thermal gravimetric analysis and repeated firing. Preliminary structural studies using an X-ray diffraction technique (at room temperature) suggest that compounds are formed in a single phase with tetragonal crystal system. Scanning electron micrographs show uniform grain distribution throughout the surface of the samples. Detailed studies of dielectric and impedance properties of the compounds in a wide range of temperature (35 °C–500 °C) and frequency range (1 kHz–1 MHz) exhibit that phase transition temperature of the PMT compounds depends on Mn concentration. The real and imaginary part of complex impedance plots exhibit semicircle(s) in the complex plane. The temperature dependent plots reveal the presence of both bulk and grain boundary effects at high-temperature. The bulk resistance of the material decreases with rise in temperatures. This exhibits a typical negative temperature coefficient of resistance behaviour of the material.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.H. Ahn, J.M. Triscone, J. Mannhart, Nature 424, 1015 (2003). doi:10.1038/nature01878
O. Auciello, J.F. Scott, R. Ramesh, Phys. Today 51, 22 (1998). doi:10.1063/1.882324
K. Dorr, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. (Berlin) 39, R125 (2006)
B.N. Mbenkum, N. Ashkenov, M. Schubert, M. Lorenz, H. Hochmuth, D. Michel, M. Grundmann, G. Wagner, Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 091904 (2005)
C. Chandler, C. Roger, M.H. Smith, Chem. Rev. 93, 1205 (1993). doi:10.1021/cr00019a015
W.C. Hendricks, S.B. Desu, C.H. Peng, Chem. Mater. 6, 1955 (1994). doi:10.1021/cm00047a011
J.S. Wright, L.F. Francis, J. Mater. Res. 8, 1712 (1993). doi:10.1557/JMR.1993.1712
D. Damjanovic, T.R. Gururaja, S.J. Jang, L.E. Cross, Am. Ceram. Soc. Bull. 66, 699 (1987)
B. Jimenez, J.M. Vicente, R. Jimenez, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 57, 389 (1996). doi:10.1016/0022-3697(95)00276-6
H. Takeuchi, S.E. Juomura, Y. Yamamoto, Y. Ito, J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 72, 1114 (1982). doi:10.1121/1.388319
S.Y. Chu, C.H. Chen, Sens. Actuators A Phys. 89, 210 (2001). doi:10.1016/S0924-4247(00)00536-7
POWD MULT: an interactive powder diffraction data interpretation and indexing programs v2.1, E. Wu School of Physical science, Hindess University of South Australia, Bedford Park, SA 5042, Australia
H.P. Klung, L.B. Alexander, X-ray diffraction procedures (Wiles, New York, 1974), pp. 687–689
B.D. Cullity, Elements of X-ray diffraction, 2nd edn. (Addison-Wesley, Philippines, 1978), pp. 281–285
M.E. Lines, A.M. Glass, Principles and applications of ferroelectrics and related materials (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1977), pp. 294–301
J.R. Macdonald, Impedance spectroscopy, emphasizing solid materials and systems, 2nd edn. (Wiley, Singapore, 1987), pp. 217–235
J. Maier, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 24, 1343 (2004)
Idem, Solid State Ion 157, 327 (2003)
D.C. Sinclair, A.R. West, J. Appl. Phys. 66, 3850 (1989)
I.M. Hodge, M.D. Ingram, A.R. West, J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 58, 429 (1975)
M.A.L. Nobre, S. Langfredi, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 62, 20 (1999)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shukla, A., Choudhary, R.N.P. & Thakur, A.K. Effect of Mn4+ substitution on thermal, structural, dielectric and impedance properties of lead titanate. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 20, 745–755 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-008-9797-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-008-9797-8