Abstract
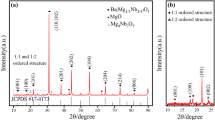
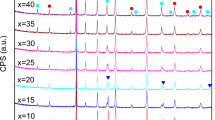
Ba0.6Sr0.4TiO3/Mg0.9Zn0.1O (BST/MZO) ceramic composites with different MZO contents were prepared by traditional ceramic process. The crystal structure, fracture surface morphology, and dielectric properties were systematically investigated. The results show that the BST/MZO ceramic composites possess diphase structure, dense, and uniform morphology. The composites have relatively low dielectric loss (in the order of 10−3) at microwave frequency. The ceramics all retain substantial tunability (more than 20% at 8 kV/mm DC field) and excellent dielectric strength (more than 19.5 kV/mm). The BST-50 wt% MZO sample has the optimal FOM value (about 256) and should be a better candidate for tunable microwave applications.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Kim, Y. Choi, M.G. Allen, J.S. Kenney, D. Kiesling, IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 50, 2903 (2002). doi:10.1109/TMTT.2002.805293
J. Nath, D. Ghosh, J. Maria, A.I. Kingon, W. Fathelbab, P.D. Franzon, IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 53, 2707 (2005). doi:10.1109/TMTT.2005.854196
D. Kuylenstierna, A. Vorobiev, P. Linnér, S. Gevorgian, IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 53, 2164 (2005). doi:10.1109/TMTT.2005.848805
J.B.L. Rao, D.P. Patel, P.K. Park, T.K. Dougherty, J.A. Zelik, D.S. Prior, A. Moffat, L.C. Sengupta, Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 720, 143 (2002)
L. Wu, S. Wu, F.C. Chang, Y.T. Shen, Y.C. Chen, J. Mater. Sci. 35, 5945 (2000). doi:10.1023/A:1026722206381
L.C. Sengupta, E. Ngo, S. Stowell, M. O’Day, R. Lancto, US Patent 5,486,491, 23 Jan 1996
L.C. Sengupta, US Patent 5,635,433, 3 Jun 1997
W. Chang, L.C. Sengupta, J. Appl. Phys. 92, 3941 (2002). doi:10.1063/1.1505669
L.C. Sengupta, S. Sengupta, Mater. Res. Innovat. 2, 278 (1999). doi:10.1007/s100190050098
X.H. Wang, W.Z. Lu, J. Liu, Y.L. Zhou, D.X. Zhou, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 26, 1981 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2005.09.092
E.R. Segnit, A.E. Holland, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 48, 409 (1965). doi:10.1111/j.1151-2916.1965.tb14778.x
S. Raghavan, J.P. Hajra, G.N.K. Iyengar, K.P. Abraham, Thermochim. Acta 189, 151 (1991). doi:10.1016/0040-6031(91)87109-A
J.Q. Qi, H.Y. Tian, Y. Wang, G.K.H. Pang, L.T. Li, H.L.W. Chan, J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 14006 (2005). doi:10.1021/jp051751w
H.Y. Tian, J.Q. Qi, Y. Wang, H.L.W. Chan, C.L. Choy, Prog. Solid State Chem. 33, 207 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.progsolidstchem.2005.11.019
G.H. Ning, X.P. Zhao, J. Li, Opt. Mater. 27, 1 (2004). doi:10.1016/j.optmat.2004.01.013
A.F. Devonshire, Adv. Phys. 3, 85 (1954). doi:10.1080/00018735400101173
K.M. Johnson, J. Appl. Phys. 33, 2826 (1962). doi:10.1063/1.1702558
R.H. Liang, X.L. Dong, Y. Chen, F. Cao, Y.L. Wang, Mater. Chem. Phys. 95, 222 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2005.06.015
J.W. Liou, B.S. Chiou, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 11, 645 (2000). doi:10.1023/A:1008949316917
B. Su, T.W. Button, J. Appl. Phys. 95, 1382 (2004). doi:10.1063/1.1636263
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, J., Dong, G., Wang, Y. et al. Microstructure and dielectric properties of BST/MZO ceramic composites for tunable microwave applications. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 20, 473–478 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-008-9754-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-008-9754-6