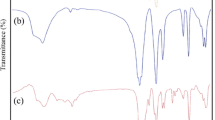
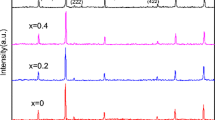
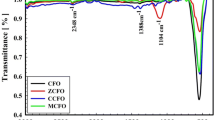
Abstract
A series of iron–cobalt alloy and cobalt–ferrite composites doped with La3+ (CoxFe1−x/CoyLazFe3−y−zO4) in which the Fe–Co alloy has either a bcc or a fcc structure and the oxide is a spinel phase, have been synthesized by using the disproportionation of Fe (OH)2 and the reduction of Co (II) by Fe0 in a concentrated and hot KOH solution. when x ≤ 0.1, the structures of the FexCo1−x alloy and cobalt–ferrite are fcc structure; and when x ≥ 0.25, the structures of the FexCo1−x alloy is bcc structure. The fcc structure of alloy is favored for [KOH] close to 9 N, Co(II)/Fe(II) ratios between 0.5 and 0.9 and short reaction time of synthesis. And the bcc structure of the alloy is favored for [KOH] close to 1 N, Co(II)/Fe(II) ratios between 0.1 and 0.5 and long reaction time of synthesis. A low [KOH] favors nucleation leading to octahedral of 1 µm. And [KOH] of 9–12 N favors particle growth. The metal occurs in square particles of 100–150 nm included within the spinel. Powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), thermal gravity analysis (TGA) and different thermal analysis (DTA), scanning electron microscope (SEM), transmission electron micrograph (TEM) and vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) were employed characterize the crystallite sizes, structure, morphology and magnetic properties of the composites. And the effect of the Co(II)/Fe (II) ratio (0 ≤ Co/Fe ≤ 1), concentration of KOH, reaction time and substitution Fe3+ ions by La3+ ions on structure, magnetic properties of the composites were investigated.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.B. Yang, S.K. Malik, X.D. Zhou, M.S. Kim, W.B. Yelon, W.J. James, H.U. Anderson, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 38, 1215 (2005). doi:10.1088/0022-3727/38/8/019
H. Zeng, J. Li, J.P. Liu, Z.L. Wang, S. Sun, Nature 420, 395 (2002). doi:10.1038/nature01208
E. Bonetti, L. Del Bianco, S. Signoretti, P. Tiberto, J. Appl. Phys. 89, 1806 (2001). doi:10.1063/1.1339855
J. Ding, W.F. Miao, R. Street, P.G. McCormick, Scr. Mater. 35, 1307 (1996). doi:10.1016/1359-6462(96)00306-5
F.C.C. Moura, M.H. Araujo, R.C.C. Costa, J.D. Fabris, J.D. Ardisson, W.A.A. Macedo, R.M. Lago, Chemosphere 60, 1118 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.12.076
B.D. Cullity, Introduction to magnetic materials. (Addison-Wesley, Reading, 1972)
Y. Ying-Chang, K. Lin-Shu, S. Shu-He, G. Dong-mei, J. Appl. Phys. 63, 3702 (1988). doi:10.1063/1.340667
H.-S. Li, B.-P. Hu, J.M.D. Coey, Solid State Commun. 66, 133 (1988). doi:10.1016/0038-1098(88)90797-1
N. Rezlesu, E. Rezlescu, C. Pasnicu, M.L. Craus, J. Phys. 6, 5707 (1994)
N. Rezlesu, E. Rezlescu, C. Pasnicu, M.L. Craus, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 136, 319 (1994). doi:10.1016/0304-8853(94)00309-2
N. Rezlesu, E. Rezlescu, P.D. Popa, L. Rezlescu, J. Alloys Compd. 275–277, 657 (1998). doi:10.1016/S0925-8388(98)00413-7
A.G. Evans, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 105–106, 65 (1988). doi:10.1016/0025-5416(88)90481-8
C. Estournès, N. Cornu, J.L. Guille, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 170, 287 (1994). doi:10.1016/0022-3093(94)90058-2
Ch. Laurent, J.J. Demai, A. Rousset, K.R. Kannan, C.N.R. Rao, J. Mater. Res. 9, 229 (1994). doi:10.1557/JMR.1994.0229
P. Matteazi, G. Le Caer, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 75, 2749 (1992). doi:10.1111/j.1151-2916.1992.tb05499.x
S. Lakamp, A. Malas, I. Riera, G. Pourroy, P. Poix, J.L. Dormann, J.M. Greneche, Eur. J. Solid State Inorg. Chem. 32, 159–168 (1995)
J.C. Tamegni-Noubeyo, T. Bouakham, G. Pourroy, Eur. J. Solid State Inorg. Chem. 37, 210–217 (1998)
C.G. Shull, M.K. Wilkinson, Phys. Rev. 97, 304 (1955). doi:10.1103/PhysRev.97.304
M.Z. Dang, D.G. Rancourt, Phys. Rev. B 53, 2291 (1996). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.53.2291
R.M. Bozorth, Ferromagnetism. (Van Norstrand, NewYork, 1951), p. 15
D.L.L. Pelecky, R.D. Rieke, Chem. Mater. 38, 1770 (1996). doi:10.1021/cm960077f
L. Néel, J. Phys. Radium 15, 225 (1954). doi:10.1051/jphysrad:01954001504022500
D.A. Dimitrov, G.M. Wysin, Phys. Rev. B 50, 3077 (1994). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.50.3077
R.H. Kodoma, A.E. Berkowitz, Phys. Rev. B 59, 6321 (1999). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.59.6321
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Cui, Y., Yang, X. et al. Hydrothermal synthesis and magnetic properties of CoxFe1−x/CoyLazFe3−y−zO4 composites. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 20, 425–432 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-008-9746-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-008-9746-6