Abstract
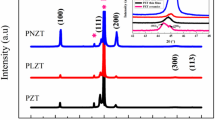
A series of Pb(1+x)TiO3/PbZr0.3Ti0.7O3/Pb(1+x)TiO3 (PTO/PZT/PTO) and PbZr0.3Ti0.7O3 (PZT) thin films were prepared by a sol–gel method. Different excess Pb content (x) (x = 0, 0.05, 0.10, 0.15, 0.20) were added to the PbTiO3 (PTO) precursors to investigate their effect on ferroelectric and fatigue properties of the PTO/PZT/PTO thin films. X-ray diffraction results show that the crystallization behavior of the PTO/PZT/PTO thin films is greatly affected by the excess Pb content (x) in PTO precursors. Topographic images show that the PTO/PZT/PTO thin films with excess Pb content x = 0.10 appears the densest and the most uniform grain size surface morphology. The ferroelectric and fatigue properties of the films correlate straightforwardly to the crystallization behaviors and excess Pb content (x) in the PTO precursors. The excess Pb content (x) in the PTO layers which acts as a nucleation site or seeding layer for PZT films affects the crystallization of the PTO layer and ultimately affects the perovskite phase formation of the PZT films. With the proper excess Pb content (x = 0.10–0.15) in the PTO precursors, the pure perovskite structure PTO/PZT/PTO thin films, with dense, void-free, and uniform fine grain size are obtained, and a well-saturated hysteresis loop with higher remnant polarization is achieved. Using an appropriate Pb content, the fatigue has been avoided by controlling the inter-diffusion and surface volatilization.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Ramesh, S. Aggarwal, O. Auciello, Mater. Sci. Eng. 32, 191 (2001)
M. Dawber, K.M. Rabe, J.F. Scott, Rev. Mod. Phys. 77, 1083 (2005)
K. Kim, Y.J. Song, Microelectron. Reliab. 43, 385 (2003)
D.-S. Yoon, J.S. Roh, S.-M. Lee, H.K. Baik, Prog. Mater. Sci. 48, 275 (2003)
H.-H. Parka, I.-S. Jina, D.-H. Kima, T.S. Kimb, Thin Solid Films 332, 300 (1998)
Y. Park, K.W. Jeong, J.T. Song, Mater. Lett. 56, 481 (2002)
Z. Song, J. Gao, X. Zhu, L. Wang, X. Fu, C. Lin, J. Mater. Sci. 36, 4285 (2001)
J.-K. Yang, W.S. Kim, H.-H. Park, Thin Solid Films 377/378, 739 (2000)
E. Cattan, G. Velu, B. Jaber, D. Remiens, B. Thierry, Appl. Phys. Lett. 70, 1718 (1997)
J. Cheng, W. Zhu, N. Li, L.E. Cross, J. Appl. Phys. 91, 5997 (2002)
W. Liu, J.S. Ko, W. Zhu, Thin Solid Films 371, 254 (2000)
C.J. Kim, Y.K. Lee, K.M. Lee, I. Chung, Proceedings of the 2000 12th IEEE International Symposium on Applications of Ferroelectrics, July 21–22, 2001, p. 925
K.H. Yoon, J.H. Shin, J.H. Park, D.H. Kang, J. Appl. Phys. 83, 3626 (1998)
Q.-Y. Shao, A.-D. Li, Y.-F. Tang, H.-Q. Ling, N.-B. Ming, Mater. Chem. Phys. 75, 207 (2002)
D. Bao, S.K. Lee, X. Zhu, M. Alexe, D. Hesse, Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 082906 (2005)
H. Doi, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 33, 5159 (1994)
K. Tokita, M. Aratani, H. Funakubo, Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 4122 (2003)
F.F.C. Duval, R.A. Dorey, R.H. Haigh, R.W. Whatmore, Thin Solid Films 444, 235 (2003)
W. Gong, J.-F. Li, X. Chu, Z. Gui, L. Li, Acta. Mater. 52, 2787 (2004)
Y.K. Wang, T.Y. Tseng, P. Lin, Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 3790 (2002)
C.W. Law, K.Y. Tong, J.H. Li, K. Li, M.C. Poon, Thin Solid Films 354, 162 (1999)
G. Asano, H. Morioka, H. Funakubo, Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 5506 (2003)
T.-L. Ren, L.-T. Zhang, X.-N. Wang, J.-S. Liu, L.-T. Liu, Z.-J. Li, Integr Ferroelectr 46, 47 (2002)
T.-L. Ren, L.-T. Zhang, L.-T. Liu, Z.-J. Li, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 40, 2363 (2001)
T.-L. Ren, L.-T. Zhang, L.-T. Liu, Z.-J. Li, Integr. Ferroelectr. 39, 1165 (2001)
K.-S. Liu, T.-F. Tseng, I.-N. Lin, Appl. Phys. Lett. 72, 1182 (1998)
K. Niwa, Y. Kotaka, M. Tomotani, H. Ashida, Y. Goto, S. Otani, Acta Mater. 48, 4755 (2000)
Y.-C. Lai, Y.S. Gong, C. Lee, Mater. Chem. Phys. 51, 147 (1997)
L. Wang, J. Yu, Y. Wang, J. Gao, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 17, 509 (2006)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the Key Research Plan of National Nature Science Foundation of China, No. 90407023.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Yu, J., Wang, Y. et al. Effect of excess Pb in PbTiO3 precursors on ferroelectric and fatigue property of sol–gel derived PbTiO3/PbZr0.3Ti0.7O3/PbTiO3 thin films. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 19, 1191–1196 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-007-9524-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-007-9524-x