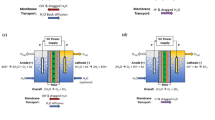
Abstract
The PDA/PEI modification technology is commonly employed to improve the resistance to membrane fouling of polymeric membranes used in the treatment of oily wastewater. Nevertheless, the surface characteristics of membrane materials frequently restrict the implementation of the modification technique in terms of both the amount and speed of deposition. The hydrophobic membranes, such as PVDF and PTFE, have a surface with very low surface free energy and only inert functional groups. This surface is not suitable for the deposition of PDA/PEI. This study utilized plasma etching treatment to break the C–H and C–F bonds on the surface of the PVDF membrane, resulting in the introduction of oxygen-containing functional groups. During the deposition process, the PDA/PEI exhibited a tendency to chemically connect to material surfaces that included oxygen-containing functional groups, such as –OH, by processes such as hydrogen bonding. During the modification procedure, the etched membrane experienced an increase in the mass of PDA/PEI deposition and the strength of interfacial bonding. As a result, the modified membrane acquired improved hydrophilicity and anti-fouling performance. In summary, this study offers useful insights for improving the surface properties of hydrophobic polymeric membranes to prevent membrane fouling.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mao X, Wang Y, Yan X et al (2023) A review of superwetting membranes and nanofibers for efficient oil/water separation. J Mater Sci 58:3–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-07945-8
Wang X, Xiao C, Chen M, Liu H, Zhang F, Luo W (2019) Design of a novel PVDF-HFP/GE tubular nanofiber membranes for ultrafast and continuous oil/water separation. J Mater Sci 54:13810–13820. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-019-03798-w
Gao Y, Qi Y, Wang S, Zhou X, Lyu L, Jin G (2022) Superhydrophobic polyphenylene sulfide fiber paper with nanofiber network-like structure prepared via regulation of TIPS process for oil/water separation. J Mater Sci 57:20531–20542. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-07944-9
Gao N, Wang L, Zhang Y, Liang F, Fan Y (2022) Modified ceramic membrane with pH/ethanol induced switchable superwettability for antifouling separation of oil-in-acidic water emulsions. Sep Purif Technol 293:121022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.121022
Castel C, Favre E (2018) Membrane separations and energy efficiency. J Membr Sci 548:345–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2017.11.035
Zsirai T, Qiblawey H, A-Marri MJ, Judd S (2016) The impact of mechanical shear on membrane flux and energy demand. J Membr Sci 516:56–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2016.06.010
Zhang W, Shi Z, Zhang F, Liu X, Jin J, Jiang L (2013) Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic PVDF membranes for effective separation of water-in-oil emulsions with high flux. Adv Mater 25:2071–2076. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201204520
Gopi S, Kargl R, Kleinschek KS, Pius A, Thomas S (2018) Chitin nanowhisker—inspired electrospun PVDF membrane for enhanced oil–water separation. J Environ Manage 228:249–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.09.039
Yang X, Sun H, Pal A, Bai Y, Shao L (2018) Biomimetic silicification on membrane surface for highly efficient treatments of both oil-in-water emulsion and protein wastewater. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:29982–29991. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b09218
Yang X, Yan L, Wu Y, Liu Y, Shao L (2019) Biomimetic hydrophilization engineering on membrane surface for highly-efficient water purification. J Membr Sci 589:117223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2019.117223
Miller DJ, Dreyer DR, Bielawski CW, Paul DR, Freeman BD (2017) Surface modification of water purification membranes. Angew Chem Int Edit 56:4662–4711. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201601509
Wen Y, Yang X, Li Y, Yan L, Sun P, Shao L (2024) Hydrogel/mineral-integrated interface for synergistic antifouling membrane. Sep Purif Technol 340:126775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2024.126775
Zhao C, Ye Y, Chen X, Da X, Qiu M, Fan Y (2022) Charged modified tight ceramic ultrafiltration membranes for treatment of cationic dye wastewater. Chin J Chem Eng 41:267–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2021.11.007
Lee XJ, Show PL, Katsuda T, Chen W-H, Chang J-S (2018) Surface grafting techniques on the improvement of membrane bioreactor: state-of-the-art advances. Bioresour Technol 269:489–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.08.090
Zhang DY, Hao Q, Liu J, Shi YS, Zhu J, Su L, Wang Y (2018) Antifouling polyimide membrane with grafted silver nanoparticles and zwitterion. Sep Purif Technol 192:230–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.10.018
Low SC, Ng QH, Tan LS (2019) Study of magnetic-responsive nanoparticle on the membrane surface as a membrane antifouling surface coating. J Polym Res 26:70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-019-1734-4
Yu Q, Zhou L, Su Y, Wu H, You X, Shen J, Zhang R, Jiang Z (2019) Assembly of self-cleaning perfluoroalkyl coating on separation membrane surface. Appl Surf Sci 496:143674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.143674
Dahi A, Fatyeyeva K, Langevin D, Chappey C, Poncin-Epaillard F, Marais S (2017) Effect of cold plasma surface treatment on the properties of supported ionic liquid membranes. Sep Purif Technol 187:127–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.05.055
Vo TS, Vo TTBC (2022) Surface characterization of polyimide and polyethylene terephthalate membranes toward plasma and UV treatments. Prog Nat Sci 32:314–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnsc.2022.03.010
Gao N, Wang L, Hu X, Liu H (2023) Mussel-inspired in-situ metallization of nano-Ag on ceramic membrane for catalytic degradation of dye wastewater. J Alloy Compd 955:170191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.170191
Wang L, Gao N, Han F, Mao Y, Tian J (2023) Immobilization of nano-Cu on ceramic membrane by dopamine assisted flowing synthesis for enhanced catalysis. Sep Purif Technol 326:124781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2023.124781
Gao N, Fan W, Xu Z-K (2020) Ceramic membrane with protein-resistant surface via dopamine/diglycolamine co-deposition. Sep Purif Technol 234:116135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.116135
Yang H-C, Waldman RZ, Wu M-B, Hou J, Chen L, Darling SB, Xu Z-K (2018) Dopamine: Just the right medicine for membranes. Adv Funct Mater 28:1705327. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201705327
Zhao C, Yu X, Da X, Qiu M, Chen X, Fan Y (2021) Fabrication of a charged PDA/PEI/Al2O3 composite nanofiltration membrane for desalination at high temperatures. Sep Purif Technol 263:118388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.118388
Yang S-J, Zou L-Y, Liu C et al (2020) Codeposition of levodopa and polyethyleneimine: reaction mechanism and coating construction. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:54094–54103. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c16142
Zin G, Wu J, Rezzadori K, Petrus JCC, Di Luccio M, Li Q (2019) Modification of hydrophobic commercial PVDF microfiltration membranes into superhydrophilic membranes by the mussel-inspired method with dopamine and polyethyleneimine. Sep Purif Technol 212:641–649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.10.014
Luan W, Nie C, Chen X, Tang Z, Qiu M, Fan Y (2022) Effective construction of anti-fouling zwitterion-functionalized ceramic membranes for separation of oil-in-water emulsion based on PDA/PEI co-deposition. J Environ Chem Eng 10:108396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.108396
Lv Y, Du Y, Qiu W-Z, Xu Z-K (2017) Nanocomposite membranes via the codeposition of polydopamine/polyethylenimine with silica nanoparticles for enhanced mechanical strength and high water permeability. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:2966–2972. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b13761
Lv Y, Du Y, Chen Z-X, Qiu W-Z, Xu Z-K (2018) Nanocomposite membranes of polydopamine/electropositive nanoparticles/polyethyleneimine for nanofiltration. J Membr Sci 545:99–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2017.09.066
Zhang W, Liao Z, Meng X, Ai Niwaer AE, Wang H, Li X, Liu D, Zuo F (2020) Fast coating of hydrophobic upconversion nanoparticles by NaIO4-induced polymerization of dopamine: Positively charged surfaces and in situ deposition of Au nanoparticles. Appl Surf Sci 527:146821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.146821
Jiang J, Zhu L, Zhu L, Zhu B, Xu Y (2011) Surface Characteristics of a self-polymerized dopamine coating deposited on hydrophobic polymer films. Langmuir 27:14180–14187. https://doi.org/10.1021/la202877k
Kim Y, You A, Kim D, Bisht H, Heo Y, Hong D, Kim M, Kang SM (2022) Effect of N-Methylation on dopamine surface chemistry. Langmuir 38:6404–6410. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.2c00513
Lv Y, Yang S-J, Du Y, Yang H-C, Xu Z-K (2018) Co-deposition Kinetics of polydopamine/polyethyleneimine coatings: effects of solution composition and substrate surface. Langmuir 34:13123–13131. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b02454
Lee H, Scherer NF, Messersmith PB (2006) Single-molecule mechanics of mussel adhesion. P Natl A Sci 103:12999–13003. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0605552103
Luo C, Liu Q (2017) Oxidant-Induced high-efficient mussel-inspired modification on PVDF membrane with superhydrophilicity and underwater superoleophobicity characteristics for oil/water separation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:8297–8307. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b16206
Liao P, You L, Zheng WJ, Zou W, Yan J, Yang H, Yang F (2022) Self-cleaning expanded polytetrafluoroethylene-based hybrid membrane for water filtration. RSC Adv 12:13228–13234. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2RA01026G
Gryta M (2021) Surface modification of polypropylene membrane by helium plasma treatment for membrane distillation. J Membr Sci 628:119265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2021.119265
Zhang Y, Ma J, Shao L (2020) Ultra-thin trinity coating enabled by competitive reactions for unparalleled molecular separation. J Mater Chem A 8:5078–5085. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9TA12670H
Li Y, Yang X, Yan L, Dang G, Sun P, Nxumalo EN, Mamba BB, Shao L (2024) Engineering activated mineralized antifouling membranes via interface segregation tailoring. J Membr Sci 696:122526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2024.122526
Sringari SS, Raja VK (2023) Treatment of food processing industries wastewater using a novel Fuller’s earth clay-based tubular ceramic membrane. Water Sci Technol 88:2533–2546. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2023.374
Ding D, Mao H, Chen X, Qiu M, Fan Y (2018) Underwater superoleophobic-underoil superhydrophobic Janus ceramic membrane with its switchable separation in oil/water emulsions. J Membr Sci 565:303–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2018.08.035
Zhang R, Su Y, Zhao X, Li Y, Zhao J, Jiang Z (2014) A novel positively charged composite nanofiltration membrane prepared by bio-inspired adhesion of polydopamine and surface grafting of poly(ethylene imine). J Membr Sci 470:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2014.07.006
Yang X, Sun P, Wen Y et al (2024) Protein-activated atomic layer deposition for robust crude-oil-repellent hierarchical nano-armored membranes. Sci Bull 69:218–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2023.12.001
Hu X, Ke Y, Zhang M, Niu H, Wu D, Zhao L (2021) Understanding the self-polymerization mechanism of dopamine by molecular simulation and applying dopamine surface modification to improve the interfacial adhesion of polyimide fibers with epoxy resin matrix. High Perform Polym 33:601–614. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954008320988332
Chen X, Zou D, Lin Y, Zhang W, Qiu M, Fan Y (2018) Enhanced performance arising from low-temperature preparation of α-alumina membranes via titania doping assisted sol-gel method. J Membr Sci 559:19–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2018.04.032
Gu Q, Ng TCA, Zhang L, Lyu Z, Zhang Z, Ng HY, Wang J (2020) Interfacial diffusion assisted chemical deposition (ID-CD) for confined surface modification of alumina microfiltration membranes toward high-flux and anti-fouling. Sep Purif Technol 235:116177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.116177
Xiong Z, He Z, Mahmud S, Yang Y, Zhou L, Hu C, Zhao S (2020) Simple Amphoteric Charge Strategy to Reinforce Superhydrophilic Polyvinylidene Fluoride Membrane for Highly Efficient Separation of Various Surfactant-Stabilized Oil-in-Water Emulsions. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:47018–47028. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c13508
Li R, Li J, Rao L, Lin H, Shen L, Xu Y, Chen J, Liao B-Q (2021) Inkjet printing of dopamine followed by UV light irradiation to modify mussel-inspired PVDF membrane for efficient oil-water separation. J Membr Sci 619:118790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2020.118790
da Silva AFV, Della Rocca DG, Moreira RFPM, Oliveira JV, Ambrosi A, Di Luccio M (2024) Synergistic effects of PVDF membrane surface functionalization with polydopamine and titanium dioxide for enhanced oil/water separation and photocatalytic behavior. J Environ Chem Eng 12:111854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2023.111854
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Open Fund Project of Chenguang High Performance Fluorine Material Innovation Center (SCFZ2204) and Innovation and Entrepreneurship Projects for College Students (CX2023048).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Stephen Eichhorn.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, C., Yang, G. & Luo, Q. Plasma etching assisted fabrication of PDA/PEI modified PVDF membranes for oil/water emulsion separation. J Mater Sci 59, 9165–9181 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-024-09766-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-024-09766-3