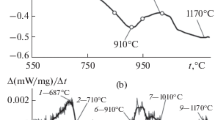
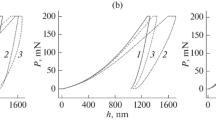
Abstract
Although vanadium is used in many alloys as an alloying element, the binary Ti–V system has been studied very poorly. In particular, the effect of heat treatment in combination with high-pressure torsion (HPT) has not been studied at all for this system. The Ti-2 wt%V alloy was pre-annealed at three temperatures in two different regions of the Ti–V phase diagram, namely at 400 °C (α phase), 700 °C (α phase) and 1000 °C (β phase). The as-cast state was also investigated. After annealing and quenching, all four samples contained only the α/α′ phase. After the HPT, the ω-phase appeared in the material. Its portion increased from 70 to 76% with an increase in the pre-annealing temperature, but the as-cast sample had after HPT the largest proportion of ωTi phase of 86%. The values of nanohardness (H) and Young’s modulus (E) after HPT were measured. H increased from 5.1 ± 0.1 to 6.4 ± 0.1 GPa with increasing pre-annealing temperature. The steady-state value of torsion torque during HPT also increases from 1533 to 2094 N m. However, the E value remained almost unchanged at 147 ± 3 GPa. The microhardness of the samples after HPT increased by about two times compared to the annealed samples.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All necessary data are in the text of this paper.
References
Donachie Jr MJ (2000) Titanium: A technical guide, 2nd ed. ASM International: Materials Park, OH. 1–280
Boyer R, Collings EW, Welsch G (1994) Materials properties handbook: titanium alloys, ASM International, Materials Park, OH. 1–310
Straumal BB, Kilmametov AR, Ivanisenko Yu, Gornakova AS, Mazilkin AA, Kriegel MJ, Fabrichnaya OB, Baretzky B, Hahn H (2015) Phase transformations in Ti–Fe alloys induced by high pressure torsion. Adv Eng Mater 17:1835–1841. https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.201500143
Kutsar AR, Pavlovskii MN, Komissarov VV (1982) The observation of two-wave configuration of shock wave in titanium. JETP Lett 35:108–112
Sikka SK, Vohra YK, Chidambaram R (1982) Omega phase in materials. Prog Mater Sci 27:245–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/0079-6425(82)90002-0
Jamieson JC (1963) Crystal structures of titanium, zirconium, and hafnium at high pressures. Science 140:72–73. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.140.3562.72
Hickman BS (1969) The formation of omega phase in Ti and Zr alloys: a review. J Mater Sci 4:554–563. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00550217
Panigrahi A, Bönisch M, Waitz T, Schafler E, Calin M, Eckert J, Skrotzki W, Zehetbauer M (2015) Phase transformations and mechanical properties of biocompatible Ti–16.1Nb processed by severe plastic deformation. J Alloys Compd 628:434–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.12.159
Dai N, Zhang LC, Zhang J, Zhang X, Ni Q, Chen Y, Wu M, Yang C (2016) Distinction in corrosion resistance of selective laser melted Ti-6Al-4V alloy on different planes. Corr Sci. 111:703–710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prostr.2020.10.092
Murray JL (1987) Phase diagrams of binary titanium alloys, 2nd ed. ASM International, Metals Park, Ohio, 1–250
Hong K-M, Shin YC (2016) Analysis of microstructure and mechanical properties change in laser welding of Ti6Al4V with a multiphysics prediction model. J Mater Proc Technol 237:420–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2016.06.034
Yang J, Yu H, Yin J, Gao M, Wang Z, Zeng X (2016) Formation and control of martensite in Ti-6Al-4V alloy produced by selective laser melting. Mater Design 108:308–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.06.117
Zhao P, Fu L, Chen H (2016) Low cycle fatigue properties of linear friction welded joint of TC11 and TC17 titanium alloys. J Alloys Compd 675:248–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.03.113
Usikov MP, Zilbershtein VA (1973) The orientation relationship between the α- and ω-phases of titanium and zirconium. Phys Status Sol A 19:53–58. https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa.2210190103
Xia H, Parthasarathy G, Luo H, Vohra YK, Ruoff AL (1990) Crystal structures of group IVa metals at ultrahigh pressures. Phys Rev B 42:6736–6738. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.42.6736
Zhang J, Zhao Y, Hixson RS, Gray GT III, Wang L, Wataru U, Saito H, Hattori T (2008) Experimental constraints on the phase diagram of titanium metal. J Phys Chem Sol 69:2559–2563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2008.05.016
Vohra YK, Sikka SK, Vaidya SN, Chidambaram R (1977) Impurity effects and reaction kinetics of the pressure-induced α → ω transformation in Ti. J Phys Chem Sol 38:1293–1296. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3697(77)90031-2
Errandonea D, Meng Y, Somayazulu M, Häusermann D (2005) Pressure-induced α → ω transition in titanium metal: a systematic study of the effects of uniaxial stress. Physica B 355:116–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2004.10.030
Velisavljevic N, MacLeod S, Cynn H (2012) Titanium alloys at extreme pressure conditions. In: Amin N (ed) Titanium alloys—towards achieving enhanced properties for diversified applications. InTech. 67–86. https://doi.org/10.5772/36038
Trinkle DR, Hennig RG, Srinivasan SG, Hatch DM, Jones MD, Stokes HT, Albers RC, Wilkins JW (2003) New mechanism for the α to ω martensitic transformation in pure titanium. Phys Rev Lett 91:025701. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.91.025701
Dobromyslov AV, Elkin VA (2001) Martensitic transformation and metastable β-phase in binary titanium alloys with d-metals of 4–6 periods. Scripta Mater 44:905–910. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6462(00)00694-1
Dobromyslov AV, Elkin VA (2006) The orthorhombic α″-phase in binary titanium-base alloys with d-metals of V-VIII groups. Mater Sci Eng A 438:324–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2006.02.086
Edalati K, Matsubara E, Horita Z (2009) Processing pure Ti by high-pressure torsion in wide ranges of pressures and strain. Metal Mater Trans A 40:2079–2086. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-009-9890-5
Islamgaliev RK, Kazyhanov VU, Shestakova LO, Sharafutdinov AV, Valiev RZ (2008) Microstructure and mechanical properties of titanium (grade 4) processed by high-pressure torsion. Mater Sci Eng A 493:190–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2007.08.084
Sergueeva AV, Stolyarov VV, Valiev RZ, Mukherjee AK (2001) Advanced mechanical properties of pure titanium with ultrafine grained structure. Scripta Mater 45:747–752. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6462(01)01089-2
Valiev RZ, Sergueeva AV, Mukherjee AK (2003) The effect of annealing on tensile deformation behavior of nanostructured SPD titanium. Scripta Mater 49:669–674. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6462(03)00395-6
Todaka I, Sasaki J, Moto T, Umemoto M (2008) Bulk submicrocrystalline ω-Ti produced by high-pressure torsion straining. Scripta Mater 59:615–618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2008.05.015
Todaka I, Umemoto M, Yamazaki A, Sasaki J, Tsuchiya K (2008) Effect of strain path in high-pressure torsion process on hardening in commercial purity titanium. Mater Trans 49:47–53. https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.ME200714
Ivanisenko Y, Kilmametov A, Rösner H, Valiev RZ (2008) Evidence of α→ ω phase transition in titanium after high pressure torsion. Int J Mater Res 99:36–41. https://doi.org/10.3139/146.101606
Valiev RZ (2004) Nanostructuring of metals by severe plastic deformation for advanced properties. Nature Mater Res 3:511–516. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1180
Valiev RZ, Alexandrov IV, Zhu YT, Lowe TC (2002) Paradox of strength and ductility in metals processed by severe plastic deformation. J Mater Res 17:5–8. https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2002.0002
Edalati K, Horita Z, Mine Y (2010) High-pressure torsion of hafnium. Mater Sci Eng A 527:2136–2141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2009.11.060
Zhilyaev AP, Sabirov I, González-Doncela G, Molina-Aldareguía J, Srinivasarao B, Pérez-Prado MT (2011) Effect of Nb additions on the microstructure, thermal stability and mechanical behavior of high pressure Zr phases under ambient conditions. Mater Sci Eng A 528:3496–3505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2011.01.062
Nosova GI (1968) Phase transformations in titanium alloys, 1st ed. Metallurgy. 1–180
Zwicker U (1974) Titan und titanlegierungen, 1st ed. Springer-Verlag. 1–511
Ilyin AA, Kolachev BA, Polkin IS (2009) Titanium alloys, 1st ed. VILS-MATI, 520
Massalski TB, Murray JL, Bennett LH, Baker H (1986) Binary alloy phase diagrams. Am Soc Metals, Metals Park, Ohio 2:2384–2386
Murray JL (1981) The Ti–V (titanium-vanadium) system. Bull alloy ph diagr, Cent Mater Res 2:48–55
Hu B, Sridar S, Hao L, Xiong W (2020) A new thermodynamic modeling of the Ti–V system including the metastable ω phase. Interme 122:106791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2020.106791
Campos-Quirós A, Cubero-Sesín JM, Edalati K (2020) Synthesis of nanostructured biomaterials by high-pressure torsion: effect of niobium content on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-Nb alloys. Mater Sci Eng A 795:139972. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2020.139972
Cvijović-Alagić I, Rakin M, Laketić S, Zagorac D (2020) Microstructural study of Ti45Nb alloy before and after HPT processing using experimental and ab initio data mining approach. Mater Charact 169:110635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2020.110635
Edalati K, Daio T, Lee S, Horita Z, Nishizaki T, Akune T, Sasaki T (2014) High strength and superconductivity in nanostructured niobium–titanium alloy by high-pressure torsion and annealing: significance of elemental decomposition and supersaturation. Acta Mater 80:149–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2014.07.065
Korneva A, Straumal B, Kilmametov A, Kopacz S, Szczerba M, Cios G, Chulist R (2022) Phase transitions and mechanical behavior of Ti–3 wt% Nb alloy after high pressure torsion and low-temperature annealing. Mater Sci Eng A 857:144096. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2022.144096
Deng G, Bhattacharjee T, Chong Y, Zheng R, Bai Y, Shibata A, Tsuji N (2020) Influence of Fe addition in CP titanium on phase transformation, microstructure and mechanical properties during high pressure torsion. J Alloys Compd 822:153604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.153604
Gornakova AS, Straumal BB, Mazilkin AA, Afonikova NS, Karpov MI, Novikova EA, Tyurin AI (2021) Phase composition, nanohardness and Young’s modulus in Ti-Fe alloys after heat treatment and high pressure torsion. Metals 11:1657. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11101657
Straumal BB, Kilmametov AR, Ivanisenko Y, Mazilkin AA, Valiev RZ, Afonikova NS, Hahn H (2018) Diffusive and displacive phase transitions in Ti–Fe and Ti–Co alloys under high pressure torsion. J Alloys Compd 735:2281–2286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.11.317
Kilmametov A, Ivanisenko Y, Straumal BB, Mazilkin AA, Gornakova AS, Kriegel MJ, Hahn H (2017) Transformations of α’martensite in Ti–Fe alloys under high pressure torsion. Scripta Mater 136:46–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2017.04.010
Janeček M, Čížek J, Stráský J, Václavová K, Hruška P, Polyakova V, Semenova I (2014) Microstructure evolution in solution treated Ti15Mo alloy processed by high pressure torsion. Mater Charact 98:233–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2014.10.024
Meenakshi KS, Kumar SA (2022) Corrosion resistant behaviour of titanium–Molybdenum alloy in sulphuric acid environment. Mater Today Procs 65:3282–3287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.05.389
Kerber M, Waitz T, Matsuda M (2023) Structural changes of TiPt high-temperature shape memory alloys induced by high pressure torsion. J Alloys Compd 935:168037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.168037
Oliver WC, Pharr GM (1992) An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J Mater Res 7:1564–1583. https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.1992.1564
Oliver WC, Pharr GM (2004) Measurement of hardness and elastic modulus by instrumented indentation: advances in understanding and refinements to methodology. J Mater Res 19:3–20. https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2004.19.1.3
Oliver WC, Pharr GM (2010) Nanoindentation in materials research: past, present, and future. MRS Bull 35:897–907. https://doi.org/10.1557/mrs2010.717
Kilmametov A, Ivanisenko Yu, Mazilkin AA, Straumal BB, Gornakova AS, Fabrichnaya OB, Kriegel MJ, Rafaja D, Hahn H (2018) The α → ω and β → ω phase transformations in Ti–Fe alloys under high-pressure torsion. Acta Mater 144:337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2017.10.051
Korneva A, Straumal BB, Kilmametov AR, Gondek Ł, Wierzbicka-Miernik A, Lityńska-Dobrzyńska L, Chulist R, Cios G, Zięba P (2021) The α ↔ ω phase transformations and thermal stability of Ti–Co alloy treated by high pressure torsion. Mater Charact 80:110937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2021.110937
Korneva A, Straumal B, Gornakova A, Kilmametov A, Gondek Ł, Lityńska-Dobrzyńska L, Chulist R, Pomorska M, Zięba P (2022) Formation and thermal stability of ω-phase in Ti–Nb and Ti–Mo alloys subjected to HPT. Materials 15:4136. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15124136
Korneva A, Straumal B, Kilmametov A, Lityńska-Dobrzyńska L, Chulist R, Gondek Ł, Zięba P (2022) The phase transformations induced by high-pressure torsion in Ti–Nb-based alloys. Microsc Microanal 28:946. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1431927621012277
Huang Y, Mortier S, Pereira PHR, Bazarnik P, Lewandowska M, Langdon TG (2017) Thermal stability and mechanical properties of HPT processed CP–Ti. In: IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater Sci Eng. 194:012012. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/194/1/012012
Zayed EM, Shazly M, El-Sabbagh A, El-Mahallawy NA (2023) Deformation behavior and properties of severe plastic deformation techniques for bulk materials: a review. Heliyon 9:e16700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16700
Atefi S, Parsa MH, Ahmadkhaniha D, Zanella C, Jafarian HR (2022) A study on microstructure development and mechanical properties of pure copper subjected to severe plastic deformation by the ECAP-conform process. J Mater Res Technol 21:1614–1629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.09.103
Edalati K, Horita Z (2016) A review on high-pressure torsion (HPT) from 1935 to 1988. Mater Sci Eng A 652:325–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2015.11.074
Jiang B, Men D, Emura S, Tsuchiya K (2023) Microstructural response and mechanical properties of α-precipitated Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-3Cr alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. J Mater Res Technol 23:564–576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2023.01.047
Sun K, Sun B, Yi X, Yaqian Y, Meng X, Gao Z, Cai W (2022) The microstructure and martensitic transformation of Ti-13 V-3Al light weight shape memory alloy deformed by high-pressure torsion. J Alloys Compd 895:162612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.162612
Shahmir H, Langdon TG (2016) Characteristics of the allotropic phase transformation in titanium processed by high-pressure torsion using different rotation speeds. Mater Sci Eng A 667:293–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.05.001
Chen W, Xu J, Liu D, Bao J, Sabbaghianrad S, Shan D, Langdon TG (2020) Microstructural evolution and microhardness variations in pure titanium processed by high-pressure torsion. Adv Eng Mater 22:1901462. https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.201901462
Acknowledgements
We express our deep gratitude to Dr. Askar Kilmametov for conducting HPT tests as well as to the Research Center for Collective Use “Materials Science and Metallurgy” of NUST MISIS.
Funding
This research was funded by the Russian Ministry of Science and Higher Education (contract no. 075-15-2023-609 Grant no. 13.2251.21.0224).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization was done by GSD and ASG; methodology was done by EAN and ASG; software was done by NSA, AK and AIT; validation was done by NSA, AK and AIT; formal analysis was done by AIT and EAN; investigation was done by NSA and GSD; resources were done by EAN, AK, and BBS; data curation was done by ASG and GSD; writing—original draft preparation was done by ASG and GSD; writing—review and editing was done by AIT and BBS; visualization was done by AK, AIT, and EAN; supervision was done by GSD; project administration was done by NSA and ASG; funding acquisition was done by BBS. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interests or competing interests exist.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Megumi Kawasaki.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Davdian, G.S., Gornakova, A.S., Straumal, B.B. et al. Effect of pre-annealing on the formation of the ω-phase in the Ti-2 wt%V alloy after high-pressure torsion. J Mater Sci 59, 5771–5786 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-024-09395-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-024-09395-w