Abstract
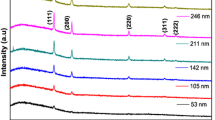
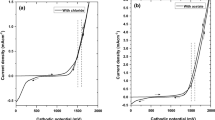
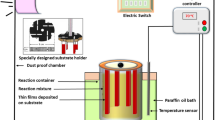
Cadmium oxide (CdO) is a much-studied wide gap semiconductor with an inherent high mobility of > 100 cm2/Vs, high electron concentration of > 1021 cm−3 and a wide optical transparency window of > 1800 nm. These unique properties make CdO a potential transparent conductor for full spectrum photovoltaics. However, in order to achieve optimum material properties for optoelectronic applications, CdO was grown by vacuum-based physical or chemical vapor deposition methods. In this work, we explored the application of a low-cost sol-gel spin coating method to achieve highly conducting and transparent CdO thin films doped with 0–10% In (CdO:In). We find that while as-grown CdO:In films are nanocrystalline/amorphous with a high resistivity of ~ 1 Ω-cm, polycrystalline and highly conducting films can be obtained after optimized annealing at ≥ 400 °C. However, the electron concentration n saturates at ~ 5 × 1020 cm−3 for In concentration > 5% (or NIn ~ 1.9 × 1021 cm−3). This low activation of In may be attributed to the high density of native defects and/or impurities incorporated in the sol-gel process. With 5% In doping, we obtained a low resistivity of ρ ~ 2.5 × 10–4 Ω-cm and a high mobility μ ~ 50 cm2/Vs. These values of σ and µ are better than those reported for other TCOs synthesized by solution processes and comparable to conventional commercial TCOs grown by physical vapor deposition methods. Benefiting from their high mobility, these sol-gel CdO:In films are optically transparent over a wide spectral range up to λ > 1800 nm, making them promising as transparent conductors for optoelectronic devices utilizing the infrared photons.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ginley DS, Perkins JD (2010) Transparent conductors. Handbook of transparent conductors. Springer, New York, pp 1–25
Ellmer K (2012) Past achievements and future challenges in the development of optically transparent electrodes. Nat Photonics 6:809–817. https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2012.282
Dixon SC, Scanlon DO, Carmalt CJ, Parkin IP (2016) n-Type doped transparent conducting binary oxides: an overview. J Mater Chem C 4:6946–6961. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TC01881E
Morales-Masis M, Wolf SD, Woods-Robinson R, Ager JW, Ballif C (2017) Transparent electrodes for efficient optoelectronics. Adv Electron Mater 3(5):1600529. https://doi.org/10.1002/aelm.201600
Granqvist CG (2007) Transparent conductors as solar energy materials: a panoramic review. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 91(17):1529–1598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2007.04.031
Delahoy AE, Guo SY (2011) Transparent conducting oxides for photovoltaics. In: Luque A, Hegedus S (eds) Handbook of photovoltaic science and engineering. Wiley, Chichester, pp 716–796
Tahar RBH, Ban T, Ohya Y, Takahashi Y (1998) Tin doped indium oxide thin films: Electrical properties. J Appl Phys 83(5):2631–2645. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.367025
Shigesato Y (2010) Based TCOs. Handbook of transparent conductors. Springer, New York, pp 149–170
Kykyneshi R, Zeng J, Cann DP (2010) Transparent conducting oxides based on tin oxide. Handbook of transparent conductors. Springer, New York, pp 171–192
Fukano T, Motohiro T, Hashizume H (2005) Enhanced carrier densities in indium tin oxide films covered with nanoparticles of fluorine-doped tin oxide for transparent conducting electrodes. Jpn J Appl Phys 44:8747–8752. https://doi.org/10.1143/JJAP.44.8747
Yu KM, Mayer MA, Speaks DT, He HC, Zhao RY, Hsu L, Mao SS, Haller EE, Walukiewicz W (2012) Ideal transparent conductors for full spectrum photovoltaics. J Appl Phys 111:123505. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4729563
Exarhos GJ, Zhou XD (2007) Discovery-based design of transparent conducting oxide films. Thin Solid Films 515:7025–7052. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2007.03.014
Coutts TJ, Young DL, Li X, Mulligan WP, Wu X (2000) Search for improved transparent conducting oxides: a fundamental investigation of CdO, Cd2SnO4, and Zn2SnO4. J Vac Sci Technol A 18(6):2646–2660. https://doi.org/10.1116/1.1290371
Tahar RBH, Ban T, Ohya Y, Takahashi Y (1998) Tin doped indium oxide thin films: electrical properties. J Appl Phys 83:2631–2645. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.367025
Keszler DA, Anderson JT, Meyers ST (2009) Oxide dielectric films for active electronics. In: Mitzi DB (ed) Solution processing of inorganic materials. Wiley, New Jersey, pp 109–130
Nadarajah A, Carnes ME, Kast MG, Johnson DW, Boettcher SW (2013) Aqueous solution processing of f-doped sno2 transparent conducting oxide films using a reactive tin(II) hydroxide nitrate nanoscale cluster. Chem Mater 25:4080–4087. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm402424c
Chen ZX, Li WC, Li R, Zhang YF, Xu GQ, Cheng HS (2013) Fabrication of highly transparent and conductive indium-tin oxide thin films with a high figure of merit via solution processing. Langmuir 29(45):13836–13842. https://doi.org/10.1021/la4033282
Seki S, Sawada Y, Ogawa M, Yamamoto M, Kagota Y, Shida A, Ide M (2003) Highly conducting indium-tin-oxide transparent films prepared by dip-coating with an indium carboxylate salt. Surf Coat Technol 169–170:525–527. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0257-8972(03)00170-1
Speaks DT, Mayer MA, Yu KM, Mao SS, Haller EE, Walukiewicz W (2010) Fermi level stabilization energy in cadmium oxide. J Appl Phys 107(11):113706. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3428444
Chen GB, Yu KM, Reichertz LA, Walukiewicz W (2013) Material properties of Cd1−xMgxO alloys synthesized by radio frequency sputtering. Appl Phys Lett 103(4):041902. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4816326
Piper LFJ, Colakerol L, King PDC, Schleife A, Zúñiga-Pérez J, Glans P-A, Learmonth T, Federov A, Veal TD, Fuchs F, Muñoz-Sanjosé V, Bechstedt F, McConville CF, Smith KE (2008) Observation of quantized subband states and evidence for surface electron accumulation in CdO from angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy. Phys Rev B 78(16):165127. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.78.165127
Yu KM, Detert DM, Chen G, Zhu W, Liu CP, Grankowska S, Dubon OD, Hsu L, Walukiewicz W (2016) Defects and properties of cadmium oxide based transparent conductors. J Appl Phys 119:181501. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4948236
Wang L, Yang Y, Jin S, Marks TJ (2006) MgO(100) template layer for CdO thin film growth: Strategies to enhance microstructural crystallinity and charge carrier mobility. Appl Phys Lett 88(16):162115. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2195093
Yang Y, Jin S, Medvedeva JE, Ireland JR, Metz AW, Ni J, Hersam MC, Freeman AJ, Marks TJ (2005) CdO as the archetypical transparent conducting oxide. Systematics of dopant ionic radius and electronic structure effects on charge transport and band structure. J Am Chem Soc 127(24):8796–8804. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja051272a
Jin S, Yang Y, Medvedeva JE, Wang L, Li SY, Cortes N, Ireland JR, Metz AW, Ni J, Hersam MC, Freeman AJ, Marks TJ (2008) Tuning the properties of transparent oxide conductors. Dopant ion size and electronic structure effects on CDO-based transparent conducting oxides. Ga- and In-doped CdO thin films grown by MOCVD. Chem Mater 20(1):220–230. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm702588m
Liu CP, Foo Y, Kamruzzaman M, Ho CY, Zapien JA, Zhu W, Li YJ, Walukiewicz W, Yu KM (2016) Effect of free carriers on the optical properties of doped CdO for full-spectrum photovoltaics. Phys Rev Appl 6:064018. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevApplied.6.064018
Gupta PK, Ghosh K, Patel R, Mishra SR, Kahol PK (2009) Preparation and characterization of highly conducting and transparent Al doped CdO thin films by pulsed laser deposition. Curr Appl Phys 9:673–677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2008.06.004
Jin S, Yang Y, Medvedeva JE, Ireland JR, Metz AW, Ni J, Kannewurf CR, Freeman AJ, Marks TJ (2004) Dopant ion size and electronic structure effects on transparent conducting oxides SC-doped CDO thin films grown by MOCVD. J Am Chem Soc 126(42):13787–13793. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0467925
Kelley KP, Sachet E, Shelton CT, Maria J-P (2017) High mobility yttrium doped cadmium oxide thin films. Appl Phys Lett Mater 5(7):076105. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4993799
Zhu YK, Mendelsberg RJ, ZhuHan JQJ, Anders A (2013) Transparent and conductive indium doped cadmium oxide thin films prepared by pulsed filtered cathodic arc deposition. Appl Surf Sci 265:738–744. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.11.096
Le NM, Lee B-T (2018) Investigation of material properties and defect behavior in In-doped CdO films. Appl Surf Sci 451:218–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.04.221
Liu CP, Ho CY, Kwok CK, Guo PF, Hossain MK, Zapien JA, Yu KM (2017) High mobility transparent amorphous CdO-In2O3 alloy films synthesized at room temperature. Appl Phys Lett 111:072108. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4989889
Ali HM, Mohamed HA, Wakkad MM, Hasaneen MF (2007) Properties of transparent conducting oxides formed from CdO alloyed with In2O3. Thin Solid Films 515(5):3024–3029. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2006.06.037
Yan M, LaneKannewurf MCR, Chang RPH (2001) Highly conductive epitaxial CdO thin films prepared by pulsed laser deposition. Appl Phys Lett 78(16):2342–2344. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1365410
Zheng BJ, Lian JS, Zhao L, Jiang Q (2010) Optical and electrical properties of In-doped CdO thin films fabricated by pulse laser deposition. Appl Surf Sci 256(9):2910–2914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2009.11.049
Aksoy S, Caglar Y, Ilican S, Caglar M (2009) Effect of heat treatment on physical properties of CdO films deposited by sol–gel method. Int J Hydrogen Energy 34(12):5191–5195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2008.09.057
Flores MA, Castanedo R, Torres G, Zelaya O (2009) Optical, electrical and structural properties of indium-doped cadmium oxide films obtained by the sol–gel technique. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 93(1):28–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2008.02.006
Kumaravel R, Ramamurthi K, Krishnakumar V (2010) Effect of indium doping in CdO thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis technique. J Phys Chem Solids 71(11):1545–1549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2010.07.021
Gurumurugan K, Mangalaraj D, Narayandass SK, Sekar K, Vallabhan CPG (1994) Characterization of transparent conducting CdO films deposited by spray-pyrolysis. Semicond Sci Technol 9(10):1827–1832. https://doi.org/10.1088/0268-1242/9/10/013
Kose S, Atay F, Bilgin V, Akyuz I (2009) In doped CdO films: electrical, optical, structural and surface properties. Int J Hydrogen Energy 34(12):5260–5266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2008.11.110
Körber C, Krishnakumar V, Klein A, Panaccione G, Torelli P, Walsh A, Da Silva JLF, Wei S-H, Egdell RG, Payne DJ (2010) Electronic structure of In2O3 and Sn-doped In2O3 by hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopy. Phys Rev B 81(16):165207. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.81.165207
Flores MA, Castanedo R, Torres G, Zelaya O (2009) Optical, electrical and structural properties of indium-doped cadmium oxide films obtained by the sol–gel technique. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 93:28–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2008.02.006
King PDC, Veal TD, Schleife A, Zúñiga-Pérez J, Martel B, Jefferson PH, Fuchs F, Muñoz-Sanjosé V, Bechstedt F, McConville CF (2009) Valence-band electronic structure of CdO, ZnO, and MgO from x-ray photoemission spectroscopy and quasi-particle-corrected density-functional theory calculations. Phys Rev B 79:205205. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.79.205205
Park SY, Song JH, Lee CK, Son BG, Lee CK, Kim HJ, Choi R, Choi YJ, Kim UK, Hwang CS, Kim HJ (2013) Improvement in photo-bias stability of high-mobility indium zinc oxide thin-film transistors by oxygen high-pressure annealing. IEEE Electron Device Lett 34(7):894–896. https://doi.org/10.1109/LED.2013.225
Burbano M, Scanlon DO, Watson GW (2011) Source of conductivity and doping limits in CdO from hybrid density functional theory. J Am Chem Soc 133(38):15065–15072. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja204639y
Lee SY, Park BO (2005) Electrical and optical properties of In2O3-ZnO thin films prepared by sol-gel method. Thin Solid Films 484:184–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2005.03.007
Dong L, Zhu GS, Xu HR, Jiang XP, Zhang XY, Zhao YY, Yan DL, Yuan L, Yu AB (2019) Preparation of indium tin oxide (ITO) thin film with (400) preferred orientation by sol–gel spin coating method. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30:8047–8054. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01126-1
Vishwanath SK, Cho KY, Kim J (2016) Polymer-assisted solution processing of Mo-doped indium oxide thin films: high-mobility and carrier scattering mechanisms. J Phys D Appl Phys 49:155501. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/49/15/155501
Deokate RJ, Salunkhe SV, Agawane GL, Pawar BS, Pawar SM, Rajpure KY, Moholkar AV, Kim JH (2010) Structural, optical and electrical properties of chemically sprayed nanosized gallium doped CdO thin films. J Alloy Compd 496(1–2):357–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.01.150
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the General Research Fund of the Research Grants Council of Hong Kong SAR, China, under project no. CityU 11267516 and CityU SGP 9380076.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: N. Ravishankar.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwok, C.K.G., Yu, K.M. Highly transparent and conducting In doped CdO synthesized by sol-gel solution processing. J Mater Sci 56, 12607–12619 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-021-06087-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-021-06087-7