Abstract
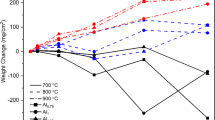
This work studied the high-temperature oxidation resistance properties of Mg alloys with Gd and Ca. The oxidation property of Mg-3.5Gd-xCa (x = 0, 0.5, 1.0 and 3.0 wt%) alloys followed parabolic oxidation kinetics at 500 °C. A stable oxide film was formed on the alloy surface and limited further oxidation. The oxide film was composed of Gd2O3, MgO and MgCO3 for Mg-3.5Gd and was mainly CaO and CaCO3 with increasing Ca content for Mg-3.5Gd-xCa alloys. The high oxidation affinity of Ca caused it to be oxidized preferentially and the fast diffusion of Ca in Mg alloys provided a source for the continuous oxidation of Ca at the surface. The parabolic rate constant, grains size and surface roughness of the oxide film increased with the increasing Ca content in Mg-3.5Gd-xCa alloy. The understanding of multi-element alloying on the oxidation behavior of Mg alloy is helpful for the design of multi-element oxidation-resistant Mg alloys.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw/processed data required to reproduce these findings are available on request.
References
Luo A, Pekguleryuz MO (1994) Cast magnesium alloys for elevated temperature applications. J Mater Sci 29:5259–5271. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01171534
Chen T, Yuan Y, Wu J, Liu T, Chen X, Tang A, Pan F (2019) Alloy design strategies of the native anti-corrosion magnesium alloy. In: Joshi V, Jordon J, Orlov D, Neelameggham N (eds) Magnesium Technology 2019. The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society 2019. Springer, pp 169–173
Zhao X, Ning Z, Li Z, Zou W, Li B, He K, Cao F, Sun J, Luo A (2018) In-mold oxidation behavior of Mg-4.32Y-2.83Nd-0.41Zr alloy. J Mater Sci 53:11091–11103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2271-y
Yang L, Jiang Q, Zheng M, Hou B, Li Y (2016) Corrosion behavior of Mg-8Li-3Zn-Al alloy in neutral 3.5% NaCl solution. J Magn Alloys 4:22–26
Zhao J, Jiang B, Yuan Y, Tang A, Sheng H, Yang T, Huang G, Zhang D, Pan F (2020) Influence of Zn addition on the microstructure, tensile properties and work-hardening behavior of Mg-1Gd alloy. Mat Sci Eng A 772:1–8
Fan J, Yang C, Han G, Fang S, Yang W, Xu B (2011) Oxidation behavior of ignition-proof magnesium alloys with rare earth addition. J Alloys Compd 509:2137–2142
Chen T, Xiong X, Yuan Y, Tang A, Li D, Atrens A, Pan F (2020) Effect of steels on the purity of molten Mg alloys. Adv Eng Mater 8:1–8
Tan Q, Mo N, Jiang B, Pan F, Atrens A, Zhang M (2017) Combined influence of Be and Ca on improving the high-temperature oxidation resistance of the magnesium alloy Mg-9Al-1Zn. Corros Sci 122:1–11
Zhao J, Jiang B, Yuan Y, Tang A, Wang Q, Yang T, Huang G, Zhang D, Pan F (2020) Influence of Ca and Zn synergistic alloying on the microstructure, tensile properties and strain hardening of Mg-1Gd alloy. Mat Sci Eng A 785:1–12
Czerwinski F (2015) The reactive element effect on high-temperature oxidation of magnesium. Int Mater Rev 60:264–296
Luo A (2004) Recent magnesium alloy development for elevated temperature applications. Int Mater Rev 49:13–30
Mirak A, Davidson C, Taylor J (2014) Characterisation of fresh surface films formed on molten Mg-Nd alloy protected by different atmospheres. Appl Surf Sci 301:91–98
Fan J, Yang G, Zhou Y, Wei Y, Xu B (2009) Selective oxidation and the third-element effect on the oxidation of Mg-Y alloys at high temperatures. Metall Mater Trans A Phys Metall Mater Sci 40:2184–2189
Wang X, Zeng X, Zhou Y (2008) Early oxidation behaviors of Mg–Y alloys at high temperatures. J Alloys Compd 460:368–374
Wang X, Zeng X, Wu G (2007) The effect of Y-ion implantation on the oxidation of AZ31 magnesium alloy. Mater Lett 61:968–970
Inoue S, Yamasaki M, Kawamura Y (2019) Oxidation behavior and incombustibility of molten Mg-Zn-Y alloys with Ca and Be addition. Corros Sci 149:133–143
Seong J, Kim W (2015) Mg-Ca binary alloy sheets with Ca contents of ≤1wt.% with high corrosion resistance and high toughness. Corros Sci 98:372–381
Zhou N, Zhang Z, Dong J, Jin L, Ding W (2013) Selective oxidation behavior of an ignition-proof Mg-Y-Ca-Ce alloy. J Rare Earth 31:1003–1008
Ha S, Yoon Y, Kim B, Lee T, Lim S, Kim S (2017) Precipitation of oxide particles in surface mixed layer of Al–Mg alloys with a trace of Ca during oxidation. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 17:8232–8235
Lee T, Kim H, So M, Lee J, Kim S, Park W, Kim W, Lim S (2015) Microstructural evaluation of oxide layers in CaO-added Mg alloys. J Alloys Compd 635:5–10
Zhang Y, Wu G, Liu W, Zhang L, Pang S, Ding W (2015) Microstructure and mechanical properties of rheo-squeeze casting AZ91-Ca magnesium alloy prepared by gas bubbling process. Mater Des 67:1–8
Li M, Chen Q, Zhang W (2011) Corrosion behavior in SBF for titania coatings on Mg–Ca alloy. J Mater Sci 46:2365–2369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-5083-2
You B, Park W, Chung I (2000) The effect of calcium additions on the oxidation behavior in magnesium alloys. Scr Mater 42:1089–1094
Choi B, You B, Park I (2006) Characterization of protective oxide layers formed on molten AZ91 alloy containing Ca and Be. Met Mater Int 12:63–67
You B, Park W, Chung I (2001) The effect of calcium addition to magnesium on the microstructure and compositional changes of oxide film formed at high temperature. Mater Trans 42:1139–1141
Kielbus A, Rzychon T, Przeliorz R (2011) Oxidation behaviour of WE54 and Elektron 21 magnesium alloys. Defect Diffus Forum 312:483–488
Cheng S, Yang G, Fan J (2009) Effect of Ca and Y additions on oxidation behavior of AZ91 alloy at elevated temperatures. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 19:299–304
He S, Zeng X, Peng L (2006) Precipitation in a Mg-10Gd-3Y-0.4Zr (wt.%) alloy during isothermal ageing at 250 °C. J Alloys Compd 421:0–313
Hu Y, Deng J, Zhao C (2011) Microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg–Gd–Zr alloys with low gadolinium contents. J Mater Sci 46:5838-5846. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-011-5540-6
Xu C, Zheng M, Xu S (2012) Microstructure and mechanical properties of rolled sheets of Mg–Gd–Y–Zn–Zr alloy: as-cast versus as-homogenized. J Alloys Compd. 528:0–44
Xu C, Nakata T, Oh-Ishi K (2017) Improving creep property of Mg–Gd–Zn alloy via trace Ca addition. Scripta Mater 139:34–38
Mo N, Mccarroll I, Tan Q (2019) Understanding solid solution strengthening at elevated temperatures in a creep-resistant Mg-Gd-Ca alloy. Acta Mater 181:185–199
Mo N, Tan Q, Jiang B (2017) Stress-relaxation behavior of Magnesium-3Gadolinium-2Calcium-based alloys at elevated temperatures. Metall Mater Trans A 48:5710–5716
Nie J, Gao X, Zhu S (2005) Enhanced age hardening response and creep resistance of Mg–Gd alloys containing Zn. Scripta Mater 53:1049–1053
López M, Múnez C, Carboneras M, Rodrigo P, Escalera M, Otero E (2010) Influence of temperature on oxidation behaviour of ZE41 magnesium alloy. J Alloys Compd 491:131–136
Steinbrück M, Große M (2015) Deviations from the parabolic kinetics during oxidation of zirconium alloys. In: Comstock B, Barberis P (eds) Zirconium in the nuclear industry, vol 17. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, pp 979–1001
Nguyen Q, Gupta M, Srivatsan T (2009) On the role of nano-alumina particulate reinforcements in enhancing the oxidation resistance of magnesium alloy AZ31B. Mater Sci Eng A 500:233–237
Kofstad P (1988) High temperature corrosion. Elsevier Applied Science Publishers Ltd, New York
Tan Q, Atrens A, Mo N, Zhang M (2016) Oxidation of magnesium alloys at elevated temperatures in air: a review. Corros Sci 112:734–759
Czerwinski F (2002) The oxidation behaviour of an AZ91D magnesium alloy at high temperatures. Acta Mater 50:2639–2654
Tan Q, Yin Y, Mo N, Zhang M, Atrens A (2019) Recent understanding of the oxidation and burning of magnesium alloys. Surf Innov 7:71–92
Czerwinski F (2004) The early stage oxidation and evaporation of Mg-9%Al-1%Zn alloy. Corros Sci 46:377–386
Combronde J, Brebec G (1971) Anisotropie d’autodiffusion du magnesium. Acta Metall 19:1393–1399
Zhou B, Shang S, Wang Y, Liu Z (2016) Diffusion coefficients of alloying elements in dilute Mg alloys: a comprehensive first-principles study. Acta Mater 103:573–586
Zhong W, Zhao J (2017) First experimental measurement of calcium diffusion in magnesium using novel liquid-solid diffusion couples and forward-simulation analysis. Scr Mater 127:92–96
Ganeshan S, Hector L, Liu Z (2011) First-principles calculations of impurity diffusion coefficients in dilute Mg alloys using the 8-frequency model. Acta Mater 59:3214–3228
Das S, Kang Y, Ha T, Jung I (2014) Thermodynamic modeling and diffusion kinetic experiments of binary Mg-Gd and Mg-Y systems. Acta Mater 71:164–175
Huang W, Zhang K, Kang M, Yuan H, Lei J, Yuan F (2013) Diffusion behaviors of Y, Gd, Nd in pure magnesium. Special Cast Nonferrous Alloy 33:845–847
Zhong W, Zhao J (2019) Measurements of diffusion coefficients of Ce, Gd and Mn in Mg. Materialia. 7:100353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtla.2019.100353
Kohiki S, Ohmura T, Kusao K (1983) A new charge-correction method in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. J Electron Spectros Relat Phenomena 28:229–237
Chuang T, Chang L (2013) To mitigate airborne molecular contamination through ultra-pure air system. Build Environ 59:153–163
Lobert J, Srivastava R, Belanger F (2018) Airborne molecular contamination: formation, impact, measurement and removal of nitrous acid (HNO2). Conference: 2018 29th Annual SEMI Advanced Semiconductor Manufacturing Conference (ASMC) 180–185
Yu X, Jiang B, Yang H (2015) High temperature oxidation behavior of Mg-Y-Sn, Mg-Y, Mg-Sn alloys and its effect on corrosion property. Appl Surf Sci 353:1013–1022
Bak S, LEE D, (2009) Effect of Y and Y2O3 on oxidation of AZ91D Mg alloys between 400 °C and 500 °C. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 19:871–874
Li W, Zhou H, Zhou W, Li W, Wang M (2007) Effect of cooling rate on ignition point of AZ91D-0.98 wt% Ce magnesium alloy. Mater Lett 61:2772–2774
Song Y, Han E, Dong K (2013) Microstructure and protection characteristics of the naturally formed oxide films on Mg-xZn alloys. Corros Sci 72:133–143
Min X, Du W, Xue F, Sun Y (2002) Analysis of EET on Ca increasing the melting point of Mg17Al12 phase. Chinese Sci Bull 47:1082–1086
Sakamoto M, Akiyama S, Ogi K (1997) Suppression of ignition and burning of molten Mg alloys by Ca bearing stable oxide film. J Mater Sci Lett 16:1048–1050
Sosulnikov M, Teterin Y (1992) X-ray photoelectron studies of Ca, Sr and Ba and their oxides and carbonates. J Electron Spectros Relat Phenomena 59:111–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/0368-2048(92)85002-O
Hanawa T, Ota M (1991) Calcium phosphate naturally formed on titanium in electrolyte solution. Biomaterials 12:767–774
Christie A, Lee J, Sutherland I, Walls J (1983) An XPS study of ion-induced compositional changes with group II and group IV compounds. Appl Surf Sci 15:224–237
Inoue Y, Yasumori I (1981) Catalysis by alkaline earth metal oxides. III. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic study of catalytically active MgO, CaO, and BaO surfaces. Bull Chem Soc Jpn 54:1505–1510
Raiser D, Deville J (1991) Study of XPS photoemission of some gadolinium compounds. J Electron Spectros Relat Phenomena 51:91–97
Chen J, Song Y, Shan D, Han E (2012) Study of the in-situ growth mechanism of Mg–Al hydrotalcite conversion film on AZ31 magnesium alloy. Corros Sci 63:148–158
Saini S, Kumar S, Barman R (2016) Oxidation study of Mg-Li-Al based alloy. Mater Today Proc 3:3035–3044
Liang Y, Che Y (1993) Handbook of inorganic thermodynamics data (in China). North-East University Pres, Shenyang
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51971044, 51971040 and U1910213), the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing (cstc2019yszx-jcyjX0004), the Qinghai Provincial Science and Technology Key Program (2018-GX-A1) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2020CDJDPT001). The authors also thank Karlsruhe Nano Micro Facility (KNMF), and Institute for Applied Materials (IAM) of Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) provided the characterizations. Fellowship from KIT for research guest stay of author Prof. Yuan Yuan during preparing this manuscript is greatly acknowledged. Fruitful discussion with Dr. Martin Steinbruke, KIT, during the second revision process is appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Avinash Dongare.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Yuan, Y., Yu, X. et al. The high-temperature oxidation resistance properties of magnesium alloys alloyed with Gd and Ca. J Mater Sci 56, 8745–8761 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-05758-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-05758-1