Abstract
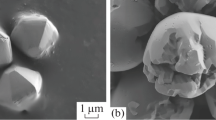
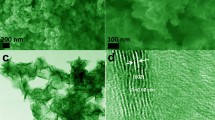
FeOCl-MoS2 was synthesized via calcination, which possessed excellent adsorption performance for methyl orange (MO). The characterization results showed that the FeOCl-MoS2 was formed between MoS2 and FeOCl phases, while a remarkable improvement in specific surface area and porosity was obtained in comparison with pure FeOCl and MoS2. The adsorption experiment results showed that the adsorption capacity of MO dye at 25 °C could reach 1615.11 mg/g. In addition, the pseudo-second-order kinetic model (R2 > 0.99) has a good applicability to describe the adsorption of MO onto FeOCl-MoS2. Langmuir isotherm model (R2 > 0.99) can describe the adsorption process well, proving that the adsorption is surface-controlled monolayer adsorption. Thermodynamic analyses showed the adsorption is an exothermic process and has spontaneity in nature. The adsorption of MO onto FeOCl-MoS2 is attributed to electrostatic interaction. In particular, the adsorption capacity could still reach 82.1% of the initial adsorption capacity by alkali washing after five cycles. Hence, this study reveals that FeOCl-MoS2 could be a high-efficient adsorbent for dyes removal from wastewaters.
Graphical abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dang T-D, Banerjee AN, Tran Q-T, Roy S (2016) Fast degradation of dyes in water using manganese-oxide-coated diatomite for environmental remediation. J Phys Chem Solids 98:50–58
Kafshgari LA, Ghorbani M, Azizi A (2017) Fabrication and investigation of MnFe2O4/MWCNTs nanocomposite by hydrothermal technique and adsorption of cationic and anionic dyes. Appl Surf Sci 419:70–83
Xing M, Xu W, Dong C, Bai Y, Zeng J, Zhou Y, Zhang J, Yin Y (2018) Metal sulfides as excellent co-catalysts for H2O2 decomposition in advanced oxidation processes. Chem 4:1359–1372
Jing C, Xu B, Lin H, Luo B, Chen S (2012) Chemical etching preparation of BiOI/BiOBr heterostructures with enhanced photocatalytic properties for organic dye removal. Chem Eng J 185–186:91–99
Li J, Hu M, Pei H, Ma X, Yan F, Dlamini DS, Cui Z, He B, Li J (2020) Matsuyama H, Improved water permeability and structural stability in a polysulfone-grafted graphene oxide composite membrane used for dye separation. J Membrane Sci 595:117547
Wang T, Wu H, Zhao S, Zhang W, Tahir M, Wang Z, Wang J (2020) Interfacial polymerized and pore-variable covalent organic framework composite membrane for dye separation. Chem Eng J 384:123347
Hassan MM, Carr CM (2018) A critical review on recent advancements of the removal of reactive dyes from dyehouse effluent by ion-exchange adsorbents. Chemosphere 209:201–219
Kaur K, Jindal R (2019) Comparative study on the behaviour of Chitosan-Gelatin based Hydrogel and nanocomposite ion exchanger synthesized under microwave conditions towards photocatalytic removal of cationic dyes. Carbohyd Polym 207:398–410
Li X, Jin X, Zhao N, Angelidaki I, Zhang Y (2017) Novel bio-electro-Fenton technology for azo dye wastewater treatment using microbial reverse-electrodialysis electrolysis cell. Bioresource Technol 228:322–329
Liang S, Zhang B, Shi J, Wang T, Zhang L, Wang Z, Chen C (2018) Improved decolorization of dye wastewater in an electrochemical system powered by microbial fuel cells and intensified by micro-electrolysis. Bioelectrochemistry 124:112–118
Qiang T, Song Y, Zhao J, Li J (2019) Controlled incorporation homogeneous Ti-doped SBA-15 for improving methylene blue adsorption capacity. J Alloy Compd 770:792–802
Zhu J, Wang Y, Liu J, Zhang Y (2014) Facile one-pot synthesis of novel spherical zeolite-reduced graphene oxide composites for cationic dye adsorption. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:13711–13717
Lee HS, Min S-W, Chang Y-G, Park MK, Nam T, Kim H, Kim JH, Ryu S, Im S (2012) MoS2 nanosheet phototransistors with thickness-modulated optical energy gap. Nano Lett 12:3695–3700
Na L, Kim P, Ji HK, Ye JH, Lee CJ (2014) Large-area atomically thin MoS2 nanosheets prepared using electrochemical exfoliation. ACS Nano 8:6902
Shi Y, Wan Y, Liu R, Tu B, Zhao D (2007) Synthesis of highly ordered mesoporous crystalline WS2 and MoS2 via a high-temperature reductive sulfuration route. J Am Chem Soc 129:9522–9531
Skrabalak SE, Suslick KS (2005) Porous MoS2 synthesized by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. J Am Chem Soc 127:9990–9991
Yang C, Cheng J, Chen Y, Hu Y (2017) Enhanced adsorption performance of MoS2 nanosheet-coated MIL-101 hybrids for the removal of aqueous rhodamine B. J Colloid Interf Sci 504:39–47
Komarneni M, Sand A, Burghaus U (2009) Adsorption of thiophene on inorganic MoS2 fullerene-like nanoparticles. Catal Lett 129:66–70
Chao Y, Zhu W, Wu X, Hou F, Xun S, Wu P, Ji H, Xu H, Li H (2014) Application of graphene-like layered molybdenum disulfide and its excellent adsorption behavior for doxycycline antibiotic. Chem Eng J 243:60–67
Wu Y, Su M, Chen J, Xu Z, Tang J, Chang X, Chen D (2019) Superior adsorption of methyl orange by h-MoS2 microspheres: Isotherm, kinetics, and thermodynamic studies. Dyes Pigments 170:107591
Qiao X, Hu F, Tian F, Hou D, Li D (2016) Equilibrium and kinetic studies on MB adsorption by ultrathin 2D MoS2 nanosheets. Rsc Adv 6:11631–11636
Qiao X, Hu F, Hou D, Li D (2016) PEG assisted hydrothermal synthesis of hierarchical MoS2 microspheres with excellent adsorption behavior. Mater Lett 169:241–245
Wang X, Ding J, Yao S, Wu X, Feng Q, Wang Z, Geng B (2014) High supercapacitor and adsorption behaviors of flower-like MoS2 nanostructures. J Mater Chem A 2:15958–15963
Kanamaru F, Shimada M, Koizumi M, Takano M, Takada T (1973) Mössbauer effect of FeOCl-pyridine complex. J Solid State Chem 7:297–299
Jarrige I, Cai Y, Shieh S, Ishii H, Hiraoka N, Karna S, Li W-H (2010) Charge transfer in FeOCl intercalation compounds and its pressure dependence: an X-ray spectroscopic study. Phys Rev B 82:165121
Sun M, Zucker I, Davenport DM, Zhou X, Qu J, Elimelech M (2018) Reactive, self-cleaning ultrafiltration membrane functionalized with iron oxychloride nanocatalysts. Environ Sci Technol 52:8674–8683
Yang X, Xu X, Xu X, Xu J, Wang H, Semiat R, Han Y (2016) Modeling and kinetics study of Bisphenol A (BPA) degradation over an FeOCl/SiO2 Fenton-like catalyst. Catal Today 276:85–96
Ai L, Zeng Y, Jiang J (2014) Hierarchical porous BiOI architectures: facile microwave nonaqueous synthesis, characterization and application in the removal of Congo red from aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 235:331–339
Eda G, Yamaguchi H, Voiry D, Fujita T, Chen M, Chhowalla M (2011) Photoluminescence from chemically exfoliated MoS2. Nano Lett 11:5111–5116
Qu S, Li C, Sun X, Wang J, Luo H, Wang S, Ta J, Li D (2019) Enhancement of peroxymonosulfate activation and utilization efficiency via iron oxychloride nanosheets in visible light. Sep Purif Technol 224:132–141
De Faria D, Venâncio Silva S, De Oliveira M (1997) Raman microspectroscopy of some iron oxides and oxyhydroxides. J Raman Spectrosc 28:873–878
Thommes M, Kaneko K, Neimark AV, Olivier JP, Rodriguez-Reinoso F, Rouquerol J, Sing KS (2015) Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl Chem 87:1051–1069
Sharma YC, Upadhyay SN (2009) Removal of a cationic dye from wastewaters by adsorption on activated carbon developed from coconut coir. Energ Fuel 23:2983–2988
Du X, Wang C, Liu J, Zhao X, Zhong J, Li Y, Li J, Wang P (2017) Extensive and selective adsorption of ZIF-67 towards organic dyes: performance and mechanism. J Colloid Interf Sci 506:437–441
Elsherbiny AS, El-Hefnawy ME, Gemeay AH (2017) Linker impact on the adsorption capacity of polyaspartate/montmorillonite composites towards methyl blue removal. Chem Eng J 315:142–151
Tahir MA, Bhatti HN, Iqbal M (2016) Solar red and brittle blue direct dyes adsorption onto eucalyptus angophoroides bark: equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamic studies. J Environ Chem Eng 4:2431–2439
Zhang B, Dong Z, Sun D, Wu T, Li Y (2017) Enhanced adsorption capacity of dyes by surfactant-modified layered double hydroxides from aqueous solution. J Ind Eng Chem 49:208–218
Fu J, Chen Z, Wang M, Liu S, Zhang J, Zhang J, Han R, Xu Q (2015) Adsorption of methylene blue by a high-efficiency adsorbent (polydopamine microspheres): kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamics and mechanism analysis. Chem Eng J 259:53–61
Lan C, Bo B (2013) Equilibrium, kinetic, thermodynamic, and in situ regeneration studies about methylene blue adsorption by the raspberry-like TiO2@yeast microspheres. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:15568–15577
Kumara AJ, Singha RP, Fua D, Namasivayamb C (2017) Comparison of physical-and chemical-activated Jatropha curcas husk carbon as an adsorbent for the adsorption of reactive red 2 from aqueous solution. Desalin Water Treat 95:308–318
Abdi J, Vossoughi M, Mahmoodi NM, Alemzadeh I (2017) Synthesis of metal-organic framework hybrid nanocomposites based on GO and CNT with high adsorption capacity for dye removal. Chem Eng J 326:1145–1158
Ahmad S, Khalid N, Daud M (2002) Adsorption studies of lead on lateritic minerals from aqueous media. Sep Sci Technol 37:343–362
Darwish A, RashadAL-Aoh MHA (2019) Methyl orange adsorption comparison on nanoparticles: Isotherm, kinetics, and thermodynamic studies. Dyes Pigments 160:563–571
Ahmad A, Razali MH, Mamat M, Mehamod FSB, Amin KAM (2017) Adsorption of methyl orange by synthesized and functionalized-CNTs with 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane loaded TiO2 nanocomposites. Chemosphere 168:474–482
Chen Y, Jing C, Zhang X, Jiang D, Liu X, Dong B, Feng L, Li S, Zhang Y (2019) Acid-salt treated CoAl layered double hydroxide nanosheets with enhanced adsorption capacity of methyl orange dye. J Colloid Interf Sci 548:100–109
Zaghouane-Boudiaf H, Boutahala M, Arab L (2012) Removal of methyl orange from aqueous solution by uncalcined and calcined MgNiAl layered double hydroxides (LDHs). Chem Eng J 187:142–149
Morimoto K, Tamura K, Iyi N, Ye J, Yamada H (2011) Adsorption and photodegradation properties of anionic dyes by layered double hydroxides. J Phys Chem Solids 72:1037–1045
Mandal S, Tichit D, Lerner DA, Marcotte N (2009) Azoic dye hosted in layered double hydroxide: physicochemical characterization of the intercalated materials. Langmuir 25:10980–10986
Chen H, Zhao J, Wu J, Dai G (2011) Isotherm, thermodynamic, kinetics and adsorption mechanism studies of methyl orange by surfactant modified silkworm exuviae. J Hazard Mater 192:246–254
Lafi R, Hafiane A (2016) Removal of methyl orange (MO) from aqueous solution using cationic surfactants modified coffee waste (MCWs). J Taiwan Inst Chem E 58:424–433
Kyzas GZ, Lazaridis NK, Mitropoulos AC (2012) Removal of dyes from aqueous solutions with untreated coffee residues as potential low-cost adsorbents: equilibrium, reuse and thermodynamic approach. Chem Eng J 189:148–159
Haque E, Jun JW, Jhung SH (2011) Adsorptive removal of methyl orange and methylene blue from aqueous solution with a metal-organic framework material, iron terephthalate (MOF-235). J Hazard Mater 185:507–511
Deng Y, Zhao Y, Wang P, Yao Z, Zhang X, Sun W (2017) Coordination polymers with 1, 3-bis (1-imidazolyl)-5-(imidazol-1-ylmethyl) benzene and biphenyl-4,4′-dicarboxylate ligands: selective adsorption of gas and dye molecules. Micropor Mesopor Mat 241:192–201
Tella AC, Olawale MD, Neuburger M, Obaleye JA (2017) Synthesis and crystal structure of Cd-based metal-organic framework for removal of methyl-orange from aqueous solution. J Solid State Chem 255:157–166
Auta M, Hameed BH (2014) Chitosan–clay composite as highly effective and low-cost adsorbent for batch and fixed-bed adsorption of methylene blue. Chem Eng J 237:352–361
Mahmoodi NM, Hayati B, Arami M, Mazaheri F (2010) Single and binary system dye removal from colored textile wastewater by a dendrimer as a polymeric nanoarchitecture: equilibrium and kinetics. J Chem Eng Data 55:4660–4668
Ajmal M, Rao RAK, Ahmad R, Ahmad J (2000) Adsorption studies on Citrus reticulata (fruit peel of orange): removal and recovery of Ni (II) from electroplating wastewater. J Hazard Mater 79:117–131
Soha S, Naz C, Zeinab MS (2018) Synthesis of MoS2/MnFe2O4 nanocomposite with highly efficient catalytic performance in visible light photo-Fenton-like process. J Photochem Photobiol, A 367:420–428
Zhang B, Chen M, Li D, Xu H, Xia D (2019) Quantitative investigation into the enhancing utilization efficiency of H2O2 catalyzed by FeOCl under visible light. J Photochem Photobiol, A 386:112072
Acknowledgements
The research was partially supported by China Petroleum and Chemical Industry Federation Scientific Research Developing Projects (318024-5 and 319005-7) and Changzhou University Scientific Research Starting Foundation (18020311).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Chris Cornelius.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Zhang, W., Mao, L. et al. Synthesis of FeOCl-MoS2 with excellent adsorption performance for methyl orange. J Mater Sci 56, 6704–6718 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-05715-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-05715-y