Abstract
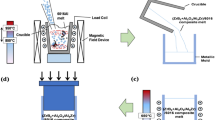
The in situ Mg2Si nanoparticles (Mg2Sip)-reinforced AZ91D composites were fabricated by powder thixoforming that involved introduction of Si nanoparticles (Sip) by ball milling followed by partial remelting and thixoforming. The results indicated that Sip can be homogeneously dispersed on the surface of AZ91D powders, while they will be clustered when their amount exceeded 0.91 vol%. The thixoformed microstructure of the composites consisted of spheroidal primary α-Mg particles, intergranular secondary solidified structures (SSS) and in situ Mg2Sip that dispersed in the SSS. The tensile strength and elongation of Mg2Sip/AZ91D composites increased with the increased content of Mg2Sip, but the improved degree in the mechanical properties was reduced when its content exceeded 3vol%. The 4.5 vol.%Mg2Sip/AZ91D composite has the excellent mechanical properties, achieving an ultimate tensile strength (UTS) of 288 MPa, yield strength (YS) of 205 MPa and elongation (ɛf) of 6.9%, which were increased by 50% and 48.6% and decreased by 9.2%, respectively, compared to those of the AZ91D alloy. The strong Mg2Sip/Mg interfacial bonding and homogeneously distributed Mg2Sip were beneficial to activating the combined strengthening effects of thermal mismatch and Orowan mechanisms, improving the mechanical properties of the Mg2Sip/AZ91D composites. However, the Mg2Sip clustering degraded the strength of the composites with higher Mg2Sip content.
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Trojanová Z, Gärtnerová V, Jäger A, Námešný A, Chalupová M, Palček P, Lukáč P (2009) Mechanical and fracture properties of an AZ91 magnesium alloy reinforced by Si and SiC particles. Compos Sci Technol 69:2256–2264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2009.06.016
Zhang JH, Liu SJ, Wu RZ, Hou LG, Zhang ML (2018) Recent developments in high-strength Mg-RE-based alloys: focusing on Mg-Gd and Mg-Y systems. J Magnes Alloy 6:277–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jma.2018.08.001
Li RG, Li HR, Zhao DY, Dai YQ, Fang DQ, Zhang JH, Zong L, Sun J (2020) High strength commercial AZ91D alloy with a uniformly fine-grained structure processed by conventional extrusion. Mater Sci Eng A 780:139193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2020.139193
Chen LY, Xu JQ, Choi HJ, Pozuelo M, Ma XL, Bhowmick S, Yang J-M, Mathaudhu S, Li XC (2015) Processing and properties of magnesium containing a dense uniform dispersion of nanoparticles. Nature 528:539–543. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature16445
Li C, Wu YY, Li H, Liu XF (2011) Morphological evolution and growth mechanism of primary Mg 2 Si phase in Al–Mg 2 Si alloys. Acta Mater 59:1058–1067
Zhang WL, Li XF, Ding DY, Gao P (2019) Effect of modification treatment on the microstructure and tensile properties of Mg2Si/AZ91 composites in-situ synthesized by incorporating silica fume. J Mater Process Technol 267:308–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.12.031
Wang HX, Zhou B, Zhao YT, Zhou KK, Cheng WL, Liang W (2014) Effect of Si addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of ECAPed Mg–15Al alloy. Mater Sci Eng A 589:119–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2013.09.075
Liu JA, Zhang LR, Liu SJ, Han ZW, Dong ZQ (2020) Effect of Si content on microstructure and compressive properties of open-cell Mg composite foams reinforced by in-situ Mg2Si compounds. Mater Charact 159:110045. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2019.110045
Wang M, Xiao DH, Liu WS (2017) Effect of Si addition on microstructure and properties of magnesium alloys with high Al and Zn contents. Vacuum 141:144–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2017.04.005
Farahany S, Ghandvar H, Nordin NA, Ourdjini A, Idris MH (2016) Effect of primary and eutectic Mg2Si crystal modifications on the mechanical properties and sliding wear behaviour of an Al–20Mg2Si–2Cu–xBi composite. J Mater Sci Technol 32:1083–1097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2016.01.014
Lu L, Thong KK, Gupta M (2003) Mg-based composite reinforced by Mg2Si. Compos Sci Technol 63:627–632. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0266-3538(02)00203-8
Zeng F, Cai Q, Liu XJ, Yao YW, Zhuo FL, Gao Q, Xie Y, Wang YJ (2017) Fabrication and mechanical properties of mesoporous silica nanoparticles reinforced magnesium matrix composite. J Alloys Compd 728:413–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.09.043
Li PB, Chen TJ, Qin H (2016) Effects of mold temperature on the microstructure and tensile properties of SiCp/2024 Al-based composites fabricated via powder thixoforming. Mater Des 112:34–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.09.049
Zhou MY, Ren LB, Fan LL, Tun KS, Gupta M, Zhang YWX, Lu TH, Quan GF (2019) Achieving ultra-high strength and good ductility in AZ61 alloy composites containing hybrid micron SiC and carbon nanotubes reinforcements. Mater Sci Eng A 768:138447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2019.138447
Chen TJ, Hao Y, Sun J (2004) Microstructural evolution of predeformed SiCp/ZA27 composites during partial remelting. Metall Mater Trans A 35:2073–2085. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-004-0156-y
Yao X, Zhang Z, Zheng YF, Kong C, Quadir MZ, Liang JM, Chen YH, Munroe P, Zhang DL (2017) Effects of SiC nanoparticle content on the microstructure and tensile mechanical properties of ultrafine grained AA6063-SiCnp nanocomposites fabricated by powder metallurgy. J Mater Sci Technol 33:1023–1030. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2016.09.022
Li CD, Wang XJ, Liu WQ, Wu K, Shi HL, Ding C, Hu XS, Zheng MY (2014) Microstructure and strengthening mechanism of carbon nanotubes reinforced magnesium matrix composite. Mater Sci Eng A 597:264–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2014.01.008
Salasel AR, Abbasi A, Barri N, Mirzadeh H, Emamy M, Malekan M (2019) Effect of Si and Ni on microstructure and mechanical properties of in-situ magnesium-based composites in the as-cast and extruded conditions. Mater Chem Phys 232:305–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.04.079
Lu JW, Dong LL, Liu Y, Fu YQ, Zhang W, Du Y, Zhang YS, Zhao YQ (2020) Simultaneously enhancing the strength and ductility in titanium matrix composites via discontinuous network structure. Compos Part A 136:105971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2020.105971
Torabi Parizi M, Ebrahimi GR, Ezatpour HR (2019) Effect of graphene nanoplatelets content on the microstructural and mechanical properties of AZ80 magnesium alloy. Mater Sci Eng A 742:373–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.11.025
Amirkhanlou S, Rahimian M, Ketabchi M, Parvin N, Yaghinali P, Carreño F (2016) Strengthening mechanisms in nanostructured Al/SiCp composite manufactured by accumulative press bonding. Metall Mater Trans A 47:5136–5145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-016-3666-5
Yuan QH, Zeng XS, Liu YB, Luo L, Wu JB, Wang YC, Zhou GH (2016) Microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ91 alloy reinforced by carbon nanotubes coated with MgO. Carbon 96:843–855. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2015.10.018
Sajjadi SA, Ezatpour HR, Torabi Parizi M (2012) Comparison of microstructure and mechanical properties of A356 aluminum alloy/Al2O3 composites fabricated by stir and compo-casting processes. Mater Des 34:106–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2011.07.037
Goh CS, Wei J, Lee LC, Gupta M (2007) Properties and deformation behaviour of Mg–Y2O3 nanocomposites. Acta Mater 55:5115–5121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2007.05.032
Du X, Du WB, Wang ZH, Liu K, Li SB (2018) Ultra-high strengthening efficiency of graphene nanoplatelets reinforced magnesium matrix composites. Mater Sci Eng A 711:633–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.11.040
Li C, Wu YY, Li H, Liu XF (2011) Morphological evolution and growth mechanism of primary Mg2Si phase in Al–Mg2Si alloys. Acta Mater 59:1058–1067. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2010.10.036
Zhang Z, Chen DL (2006) Consideration of orowan strengthening effect in particulate-reinforced metal matrix nanocomposites: a model for predicting their yield strength. Scr Mater 54:1321–1326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2005.12.017
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support by the Science and Technology Project for Young Talents of Ningxia (Grant No. TJGC2019042) and the Basic Scientific Fund of Ningxia University (Grant No.NGY2018009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Naiqin Zhao.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, P., Yang, H., Tan, W. et al. Effect of in situ Mg2Sip contents on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg2Sip/AZ91D composites. J Mater Sci 56, 6799–6813 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-05693-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-05693-1