Abstract
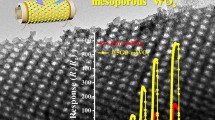
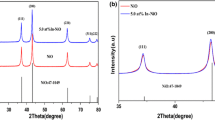
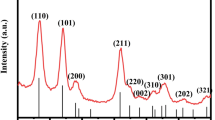
The sensing performance of a mixed-potential NH3 sensor is dependent on the microstructure of its electrode, which can be optimized to enhance the adsorption and diffusion of target gases. Mesoporous tungsten trioxide was prepared using an effective hard template method and applied as a sensitive electrode in a yttria-stabilized zirconia electrolyte-based mixed-potential NH3 gas sensor. The NH3 detection of the sensor was investigated in a temperature range of 250–650 °C. The sensor exhibited a much better NH3 sensing performance than another sensor based on commercial bulk WO3 under the same conditions. Furthermore, the NH3 sensor based on mesoporous WO3 exhibited a logarithmic response to the NH3 concentration (30–250 ppm). To investigate this response, the specialized microstructure of mesoporous WO3 was observed by transmission electron microscopy. Specifically, the high surface area and well-defined mesopores of the material significantly contributed to the excellent sensing performance. This report provides the first demonstration of the excellent response and sensitivity of an NH3 sensor based on mesoporous WO3 at low temperatures (250–400 °C).
Graphical Abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SE:
-
Sensing electrode
- TPB:
-
Triple-phase boundary
- TPD:
-
Temperature-programmed desorption
- YSZ:
-
Yttria-stabilized zirconia
- XRD:
-
X-ray diffraction
- TCD:
-
Thermal conductivity detector
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscope
- EDS:
-
Energy-dispersive spectrometer
- BET:
-
Brunauer–Emmett–Teller
- BJH:
-
Barrett–Joyner–Halenda
References
Meng W, Wang L, Li Y et al (2018a) Enhanced sensing performance of mixed potential ammonia gas sensor based on Bi0.95Ni0.05VO3.975 by silver. Sensors Actuators B Chem 259:668–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.12.120
Timmer B, Olthuis W, van den Berg A (2005) Ammonia sensors and their applications—a review. Sensors Actuators B Chem 107:666–677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2004.11.054
Liu IP, Chang C-H, Chou TC, Lin K-W (2019) Ammonia sensing performance of a platinum nanoparticle-decorated tungsten trioxide gas sensor. Sensors Actuators B Chem 291:148–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.04.046
Zeb S, Peng X, Yuan G et al (2020) Controllable synthesis of ultrathin WO3 nanotubes and nanowires with excellent gas sensing performance. Sensors Actuators B Chem 305:127435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.127435
Xu Y, Lou C, Zheng L et al (2020) Highly sensitive and selective detection of acetone based on platinum sensitized porous tungsten oxide nanospheres. Sensors Actuators B Chem 307:127616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.127616
Yin F, Li Y, Yue W et al (2020) Sn3O4/rGO heterostructure as a material for formaldehyde gas sensor with a wide detecting range and low operating temperature. Sensors Actuators B Chem 312:127954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.127954
Zhou P, Shen Y, Lu W et al (2020) Highly selective NO2 chemiresistive gas sensor based on hierarchical In2O3 microflowers grown on clinoptilolite substrates. J Alloys Compd 828:154395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154395
Ashraf MA, Liu Z, Peng W, Parsaee Z (2019) Design, preparation and evaluation of a high performance sensor for formaldehyde based on a novel hybride nonocomposite ZnWO3/rGO. Anal Chim Acta 1051:120–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.11.014
Mounasamy V, Mani GK, Ponnusamy D et al (2020) Investigation on CH4 sensing characteristics of hierarchical V2O5 nanoflowers operated at relatively low temperature using chemiresistive approach. Anal Chim Acta 1106:148–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.01.060
Yang B, Wang C, Xiao R et al (2019) High NH3 selectivity of NiFe2O4 sensing electrode for potentiometric sensor at elevated temperature. Anal Chim Acta 1089:165–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.09.006
Li X, Dai L, Meng W et al (2019a) A novel mixed-potential type NH3 sensor based on Ag nanoparticles decorated AgNbO3 sensing electrode synthesized by demixing method. Sensors Actuators B Chem 301:127146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.127146
Liu T, Li W, Zhang Y et al (2019) Acetone sensing with a mixed potential sensor based on Ce0.8Gd0.2O1.95 solid electrolyte and Sr2MMoO6 (M: Fe, Mg, Ni) sensing electrode. Sensors Actuators B Chem 284:751–758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.12.136
Bhardwaj A, Hong J, Kim I-H et al (2019) Effects of electronic probe’s architecture on the sensing performance of mixed-potential based NOX sensor. Sensors Actuators B Chem 282:426–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.11.099
Liu F, Li S, He J et al (2019) Highly selective and stable mixed-potential type gas sensor based on stabilized zirconia and Cd2V2O7 sensing electrode for NH3 detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem 279:213–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.09.024
Liu T, Li L, Yang X et al (2019) Mixed potential type acetone sensor based on Ce0.8Gd0.2O1.95 and Bi0.5La0.5FeO3 sensing electrode used for the detection of diabetic ketosis. Sensors Actuators B Chem 296:126688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.126688
Liu F, Wang J, You R et al (2020) YSZ-based solid electrolyte type sensor utilizing ZnMoO4 sensing electrode for fast detection of ppb-level H2S. Sensors Actuators B Chem 302:127205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.127205
Wang C, Liu A, Yang X et al (2019) YSZ-based mixed-potential type highly sensitive acetylene sensor based on porous SnO2/Zn2SnO4 as sensing electrode. Sensors Actuators B Chem 293:166–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.05.006
Bhardwaj A, Kim I, Hong J et al (2019) Transition metal oxide (Ni Co, Fe)-tin oxide nanocomposite sensing electrodes for a mixed-potential based NO2 sensor. Sensors Actuators B Chem 284:534–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.01.003
Liu F, He J, Yang Z et al (2018) The mixed potential type gas sensor based on stabilized zirconia and molybdate MMoO4 (M: Ni, Co and Zn) sensing electrode aiming at detecting triethylamine. Sensors Actuators B Chem 267:430–437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.04.044
Bhardwaj A, Kumar A, Sim U et al (2020a) Synergistic enhancement in the sensing performance of a mixed-potential NH3 sensor using SnO2@CuFe2O4 sensing electrode. Sensors Actuators B Chem 308:127748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.127748
Ritter T, Hagen G, Lattus J, Moos R (2018) Solid state mixed-potential sensors as direct conversion sensors for automotive catalysts. Sensors Actuators B Chem 255:3025–3032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.09.126
Li X, Liu Y, Dai L et al (2019a) Mixed-potential type NH3 sensor based on La10Si5.5Al0.5O27 electrolyte and CuV2O6 sensing electrode. Sensors Actuators B Chem 294:206–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.05.040
Meng W, Wang L, Li Y et al (2019) Mixed-potential type NH3 sensor based on CoWO4-PdO sensing electrode prepared by self-demixing. Electrochim Acta 321:134668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2019.134668
Hao X, Liu T, Li W et al (2020) Mixed potential gas phase sensor using YSZ solid electrolyte and spinel-type oxides AMn2O4(A = Co, Zn and Cd) sensing electrodes. Sensors Actuators B Chem 302:127206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.127206
Wang J, Wang C, Liu A et al (2019) High-response mixed-potential type planar YSZ-based NO2 sensor coupled with CoTiO3 sensing electrode. Sensors Actuators B Chem 287:185–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.02.005
Li X, Dai L, He Z et al (2019a) Enhancing NH3 sensing performance of mixed potential type sensors by chemical exsolution of Ag nanoparticle on AgNbO3 sensing electrode. Sensors Actuators B Chem 298:126854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.126854
Wang L, Meng W, He Z et al (2018a) Enhanced selective performance of mixed potential ammonia gas sensor by Au nanoparticles decorated CeVO4 sensing electrode. Sensors Actuators B Chem 272:219–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.05.156
Lee I, Jung B, Park J et al (2013) Mixed potential NH3 sensor with LaCoO3 reference electrode. Sensors Actuators B Chem 176:966–970. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2012.09.009
Schönauer D, Wiesner K, Fleischer M, Moos R (2009) Selective mixed potential ammonia exhaust gas sensor. Sensors Actuators B Chem 140:585–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2009.04.064
Liu F, Sun R, Guan Y et al (2015) Mixed-potential type NH3 sensor based on stabilized zirconia and Ni3V2O8 sensing electrode. Sensors Actuators B Chem 210:795–802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.01.043
Li X, Wang C, Wang B et al (2016) Effects of sintering temperature on the NH3 sensing properties of Mg2Cu0.25Fe1O3.75 electrode for YSZ-based potentiometric NH3 sensor. Ceram Int 42:2214–2220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.10.013
Wang C, Li X, Yuan Y et al (2017) Effects of sintering temperature on sensing properties of V2O5-WO3-TiO2 electrode for potentiometric ammonia sensor. Sensors Actuators B Chem 241:268–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.09.117
Li T, Shen Y, Zhao S et al (2020) Synthesis and in-situ noble metal modification of WO3•0.33H2O nanorods from a tungsten-containing mineral for enhancing NH3 sensing performance. Chinese Chem Lett 31:2037–2040. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2020.01.024
Van TN, Hung CM, Van DN et al (2017) Bilayer SnO2–WO3 nanofilms for enhanced NH3 gas sensing performance. Mater Sci Eng B Solid-State Mater Adv Technol 224:163–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2017.08.004
Van Duy N, Hoa ND, Dat NT et al (2016) Ammonia-gas-sensing characteristics of WO3/carbon nanotubes nanocomposites: effect of nanotube content and sensing mechanism. Sci Adv Mater 8:524–533. https://doi.org/10.1166/sam.2016.2716
Amer MS, Ghanem MA, Al-Mayouf AM (2020) Hydroxide ion oxidation using low-symmetry mesoporous titanium dioxide (lsm-TiO2) electrode. J Electroanal Chem 871:114268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2020.114268
Amer MS, Arunachalam P, Al-Mayouf AM et al (2019) Mesoporous tungsten trioxide photoanodes modified with nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots for enhanced oxygen evolution photo-reaction. Nanomaterials 9:1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9101502
Prasad AK, Kubinski DJ, Gouma PI (2003) Comparison of sol–gel and ion beam deposited MoO3 thin film gas sensors for selective ammonia detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem 93:25–30
Yuan Y, Wang B, Wang C et al (2017) Effects of CoFe2O4 electrode microstructure on the sensing properties for mixed potential NH3 sensor. Sensors Actuators B Chem 239:462–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.07.171
Marquis BT, Vetelino JF (2001) A semiconducting metal oxide sensor array for the detection of NOx and NH3. Sensors Actuators B Chem 77:100–110
Zhan S, Zhang H, Zhang Y et al (2017) Efficient NH3-SCR removal of NOx with highly ordered mesoporous WO3(χ)-CeO2 at low temperatures. Appl Catal B 203:199–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.10.010
Ramanavičius S, Petrulevičiene M, Juodkazyte J et al (2020) Selectivity of tungsten oxide synthesized by sol-gel method towards some volatile organic compounds and gaseous materials in a broad range of temperatures. Materials (Basel) 13:523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13030523
Li X, Dai L, He Z et al (2019b) Enhancing NH3 sensing performance of mixed potential type sensors by chemical exsolution of Ag nanoparticle on AgNbO3 sensing electrode. Sensors Actuators, B Chem 298:3–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.126854
Zhao D, Feng J, Huo Q et al (1998) Triblock copolymer syntheses of mesoporous silica with periodic 50 to 300 angstrom pores. Science 279(80):548–552
Zheng X, Zhang C, Xia J et al (2019a) Sensing properties of amperometric ppb-level NO2 sensor based on sodium ion conductor with sensing electrodes comprising different WO3 nanostructures. J Mater Sci 54:5311–5320. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-03189-7
Zheng X, Zhang C, Xia J et al (2019b) Mesoporous tungsten oxide electrodes for YSZ-based mixed potential sensors to detect NO2 in the sub ppm-range. Sensors Actuators B Chem 284:575–581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.01.016
Zhang J, Zhang C, Xia J et al (2017) Mixed-potential NH3 sensor based on Ce0.8Gd0.2O1.9 solid electrolyte. Sensors Actuators B Chem 249:76–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.04.035
Li X, Dai L, Meng W et al (2019b) A novel mixed-potential type NH3 sensor based on Ag nanoparticles decorated AgNbO3 sensing electrode synthesized by demixing method. Sensors Actuators, B Chem 301:127146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.127146
Wang C, Yang B, Xu J et al (2019) Effects of CeVO4 electrode morphology and oxygen content on ammonia sensing properties for potentiometric sensor. Sensors Actuators, B Chem 299:126863. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.126863
Wang L, Meng W, He Z et al (2018b) Enhanced selective performance of mixed potential ammonia gas sensor by Au nanoparticles decorated CeVO4 sensing electrode. Sensors Actuators, B Chem 272:219–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.05.156
Meng W, Wang L, Li Y et al (2018b) Enhanced sensing performance of mixed potential ammonia gas sensor based on Bi0.95Ni0.05VO3.975 by silver. Sensors Actuators, B Chem 259:668–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.12.120
Meng W, Dai L, Li Y et al (2020) Mixed potential NH3 sensor based on La995K005Si5Al1O2645 electrolyte and Ag doped BiVO4 sensing electrode. Sensors Actuators, B Chem 316:128206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.128206
Li X, Liu Y, Dai L et al (2019b) Mixed-potential type NH3 sensor based on La10Si5.5Al0.5O27 electrolyte and CuV2O6 sensing electrode. Sensors Actuators, B Chem 294:206–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.05.040
Wang C, Yang B, Liu H et al (2020) Potentiometric ammonia sensor with InVO4 sensing electrode. Sensors Actuators, B Chem 316:128140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.128140
Bhardwaj A, Kumar A, Bae H et al (2020) Surface decorated spinel-oxide electrodes for mixed-potential ammonia sensor: Performance and DRT analysis. J Hazard Mater 396:122601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122601
Bhardwaj A, Kumar A, Sim U et al (2020b) Synergistic enhancement in the sensing performance of a mixed-potential NH3 sensor using SnO2@CuFe2O4 sensing electrode. Sensors Actuators, B Chem 308:127748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.127748
Fergus JW (2010) Sensing mechanism of non-equilibrium solid-electrolyte-based chemical sensors. J Solid State Electrochem 15:971–984. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-010-1046-4
Schonauer-Kamin D, Fleischer M, Moos R (2013) Half-cell potential analysis of an ammonia sensor with the electrochemical cell Au | YSZ | Au, V2O5-WO3-TiO2. Sensors (Basel) 13:4760–4780. https://doi.org/10.3390/s130404760
Meloni D, Martin D, Guisnet M (2001) Acidic and catalytic properties of H-MCM-22 zeolites: 2. n -Heptane cracking: activity, selectivity and deactivation by coking. Appl Catal A Gen 215:67–79
Zhang X, Cheng D, Chen F, Zhan X (2018) The role of external acidity of hierarchical ZSM-5 zeolites in n-heptane catalytic cracking. ChemCatChem 10:2655–2663. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201800086
Yoo J, Chatterjee S, Van Assche FM, Wachsman ED (2007) Influence of adsorption and catalytic reaction on sensing properties of a potentiometric La2CuO4/YSZ/Pt sensor. J Electrochem Soc 154:J190. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2731305
Bouazizi N, Ouargli R, Nousir S et al (2015) Properties of SBA-15 modified by iron nanoparticles as potential hydrogen adsorbents and sensors. J Phys Chem Solids 77:172–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2014.10.011
Wang J, Yang J, Han N et al (2017) Highly sensitive and selective ethanol and acetone gas sensors based on modified ZnO nanomaterials. Mater Des 121:69–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.02.048
Wang H, Qu Z, Xie H et al (2016) Insight into the mesoporous FexCe1−xO2−δ catalysts for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3: Regulable structure and activity. J Catal 338:56–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2016.02.009
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No. ZR2019BEM036), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51808328), and Major Scientific and Technological Innovation Project of Shandong (Nos. 2018CXGC1406, 2019JZZY010457 and 2019JZZY020309).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
This manuscript has not been published or presented elsewhere in part or in entirety and is not under consideration by another journal. We have read and understood your journal’s policies, and we believe that neither the manuscript nor the study violates any of these. There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Yaroslava Yingling.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Zhang, C., Zheng, X. et al. Mesoporous tungsten trioxide for highly sensitive and selective detection of ammonia. J Mater Sci 56, 4172–4183 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-05534-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-05534-1