Abstract
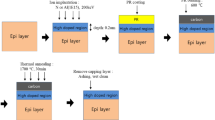
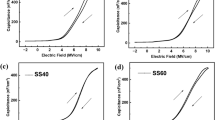
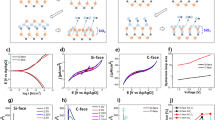
In this study, the thermal oxidation rate of oxygen ion (O+) implanted 4H–silicon carbide (SiC) was investigated. And the critical breakdown electric field (Ebreakdown) and capacitance–voltage (CV) curve of the grown oxide (SiO2) film were also evaluated. It is found that the thermal SiO2 growth rate on 4H–SiC (0001) face was significantly improved by O+ implantation. Ebreakdown test results showed that the unconsumed amorphous and damaged crystalline layer under the grown SiO2 contained defects leading to an inferior critical breakdown field. Thus, in order to obtain a high-quality SiO2 film, the oxidation process should be designed delicately so that the damaged layer by implantation could be fully consumed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mouli GRC et al (2017) Design and comparison of a 10-kW interleaved boost converter for PV application using Si and SiC devices. IEEE J Emerg Sel Topics Power Electron 5(2):610–623
Ding XF et al (2017) Comprehensive comparison between silicon carbide MOSFETs and silicon IGBTs based traction systems for electric vehicles. Appl Energy 194:626–634
Gurpinar E, Castellazzi A (2016) Single-phase T-type inverter performance benchmark using Si IGBTs, SiC MOSFETs, and GaN HEMTs. IEEE Trans Power Electron 31(10):7148–7160
Hazra S et al (2016) High switching performance of 1700-V, 50-A SiC power MOSFET over Si IGBT/BiMOSFET for advanced power conversion applications. IEEE Trans Power Electron 31(7):4742–4754
Šimonka V et al (2016) Growth rates of dry thermal oxidation of 4H–silicon carbide. J Appl Phys 120(13):135705
Nakano Y et al (2012) 690 V, 1.00 mΩcm2 4H–SiC double-trench MOSFETs. Mater Sci Forum 717–720:1069–1072
Kyoung S et al (2018) Designing 4H–SiC P-shielding trench gate MOSFET to optimize on–off electrical characteristics. Solid-State Electron 140:23–28
Alok D, Baliga BJ (1997) Kinetics of enhanced thermal oxidation of silicon carbide using amorphization by ion implantation. J Electrochem Soc 144(3):1135–1137
Alok D, Baliga BJ, Mclarty PK (1994) Thermal-oxidation of 6H–silicon carbide at enhanced growth rates. IEEE Electron Device Lett 15(10):424–426
Poggi A et al (2005) Oxidation kinetics of ion-amorphized (0001) 6H–SiC: competition between oxidation and recrystallization processes. Appl Phys Lett 86(12):121907
Radtke C, Baumvol IJR, Stedile FC (2002) Effects of ion irradiation in the thermal oxidation of SiC. Phys Rev B. 66(15):155437
Poggi A et al (2004) Low temperature oxidation of SiC preamorphized by ion implantation. J Appl Phys 95(11):6119–6123
Makhtari A et al (2001) Oxidation of ion implanted silicon carbide. Mater Sci Semicond Process 4(4):345–349
Yoneda T, et al. (1998) Dose dependence of the enhancement of thermal oxidation for 6H–SiC by 30 keV O-18(+) and Ne-20(+) irradiation. Jpn J Appl Phys Part 1-Regular Papers Brief Communications & Review Papers, 37(11):6262–6265
Tseng Y-H, Lin C-Y, Tsui B-Y (2017) Characterization of LOCOS field oxide on 4H–SiC formed by Ar preamorphization ion implantation. IEEE Electron Device Lett 38(6):798–801
Leclerc S et al (2005) Swelling of SiC under helium implantation. J Appl Phys 98(11):113506
Musumeci P et al (1996) Optical properties of defects in ion implanted silicon carbide probed at λ = 633 nm. Appl Phys Lett 69(4):468–470
Knaup JM et al (2005) Theoretical study of the mechanism of dry oxidation of 4H–SiC. Phys Rev B 71(23):235321
Knaup JM et al (2005) Defects in SiO2 as the possible origin of near interface traps in the SiC/SiO2 system: a systematic theoretical study. Phys Rev B 72(11):115323
Cheng G-D et al (2017) PL and ESR study for defect centers in 4H–SiC induced by oxygen ion implantation. Nucl Sci Tech 28(8):105
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by The National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFB0400400) and the CAS Key Technology Talent Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, M., Zhang, S., Yang, X. et al. Enhancing oxidation rate of 4H–SiC by oxygen ion implantation. J Mater Sci 54, 1147–1152 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2921-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2921-0