Abstract
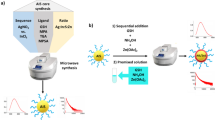
Boron nitride quantum dots (BNQDs), as promising metal-free quantum dots with unique photoelectric properties, have been controllably fabricated by a facile and high-efficiency microwave irradiation technique in this work. Though a number of attempts have been reported so far, it remains challenging to explore an effective approach to synthesize high-quality BNQDs with uniform size, well dispersion and high quantum yield (QY). Microwave irradiation strategy is identified as an advanced and beneficial method not only for high-efficiency energy inputting but also time-saving in comparison with the reported solvothermal process. Encouragingly, the particle size and QY of BNQDs can be well controlled by adjusting microwave reaction temperature as well as duration time. The average diameter of the as-prepared blue luminescent BNQDs ranges from 1.98 to 7.05 nm with QY up to 23.44%. Furthermore, attributed to the unique nanostructure, quantum confinement effect, and high dielectric loss, the as-prepared BNQDs exhibits an optimal reflection loss of −19.6 dB at 8.9 GHz with a broad effective absorption bandwidth of 5.02 GHz in the frequency range of 2–18 GHz, demonstrating as potential microwave absorption material in electromagnetic interference field.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dubertret B, Skourides P, Norris DJ, Noireaux V, Brivanlou AH, Libchaber A (2002) In vivo imaging of quantum dots encapsulated in phospholipid micelles. Science 298(5599):1759–1762
Bao L, Liu C, Zhang ZL, Pang DW (2015) Photoluminescence-tunable carbon nanodots: surface-state energy-gap tuning. Adv Mater 27(10):1663–1667
Bloom BP, Mendis MN, Wierzbinski E, Waldeck DH (2016) Eliminating fermi-level pinning in PbS quantum dots using an alumina interfacial layer. J Mater Chem C 4(4):704–712
Bu X, Zhou Y, Zhang T, He M (2014) Preparation of optically active substituted polyacetylene@CdSe quantum dots composites and their application for low infrared emissivity. J Mater Sci 49(20):7133–7142. doi:10.1007/s10853-014-8421-y
Mirnajafizadeh F, Wang F, Reece P, Stride JA (2016) Synthesis of type-II CdSe(S)/Fe2O3 core/shell quantum dots: the effect of shell on the properties of core/shell quantum dots. J Mater Sci 51(11):5252–5258. doi:10.1007/s10853-016-9828-4
Bu X, Zhou Y, He M, Chen Z, Zhang T (2013) Bioinspired, direct synthesis of aqueous CdSe quantum dots for high-sensitive copper(II) ion detection. Dalton Trans 42(43):15411–15420
Singh S, Kumari R, Chakraborty A, Hussain S, Singh MK, Das P (2016) Melamine-DNA encoded periodicity of quantum dot arrays. J Colloid Interface Sci 461:45–49
Moura I, de Sa A, Abreu AS, Oliveira M, Machado AV (2016) Morphology, optical, and electric properties of polymer-quantum dots nanocomposites: effect of polymeric matrix. J Mater Sci 51(18):8699–8710. doi:10.1007/s10853-016-0129-8
Xie Z, Du Q, Wu Y, Hao X, Liu C (2016) Full-band UV shielding and highly daylight luminescent silane-functionalized graphene quantum dot nanofluids and their arbitrary polymerized hybrid gel glasses. J Mater Chem C 4(41):9879–9886
Tang L, Ji R, Cao X, Lin J, Jiang H, Li X, Teng KS, Luk CM, Zeng S, Hao J, Lau SP (2012) Deep ultraviolet photoluminescence of water-soluble self-passivated graphene quantum dots. ACS Nano 6(6):5102–5110
Zhu SJ, Meng QN, Wang L, Zhang JH, Song YB, Jin H, Zhang K, Sun HC, Wang HY, Yang B (2013) Highly photoluminescent carbon dots for multicolor patterning, sensors, and bioimaging. Angew Chem Int Ed 52(14):3953–3957
Sathish M, Mitani S, Tomai T, Honma I (2014) Supercritical fluid assisted synthesis of N-doped graphene nanosheets and their capacitance behavior in ionic liquid and aqueous electrolytes. J Mater Chem A 2(13):4731–4738
Li Y, Zhao Y, Cheng H, Hu Y, Shi G, Dai L, Qu L (2012) Nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots with oxygen-rich functional groups. J Am Chem Soc 134(1):15–18
Bandyopadhyay A, Yamijala SSRKC, Pati SK (2013) Tuning the electronic and optical properties of graphene and boron-nitride quantum dots by molecular charge-transfer interactions: a theoretical study. Phys Chem Chem Phys 15(33):13881–13887
Qu L-H, Zhang J-M, Xu K-W (2013) First-principles study of single-layer C-terminated BN quantum dots. Phys E Low Dimens Syst Nanostructures 53:115–119
Wang H, Maiyalagan T, Wang X (2012) Review on recent progress in nitrogen-doped graphene: synthesis, characterization, and its potential applications. Acs Catal 2(5):781–794
Zhang J, Xie W, Xu X, Zhang S, Zhao J (2016) Structural and electronic properties of interfaces in graphene and hexagonal boron nitride lateral heterostructures. Chem Mater 28(14):5022–5028
Zhou XJ, Zhang Y, Wang C, Wu XC, Yang YQ, Zheng B, Wu HX, Guo SW, Zhang JY (2012) Photo-fenton reaction of graphene oxide: a new strategy to prepare graphene quantum dots for DNA cleavage. ACS Nano 6(8):6592–6599
Wu X, Guo S, Zhang J (2016) Auigraphene quantum dots/ferroferric oxide composites as catalysts for the solvent-free oxidation of alcohols. Mater Lett 183:227–231
Yu T, Wang F, Xu Y, Ma L, Pi X, Yang D (2016) Graphene coupled with silicon quantum dots for high-performance bulk-silicon-based schottky-junction photodetectors. Adv Mater 28(24):4912–4919
Lin L, Xu Y, Zhang S, Ross IM, Ong ACM, Allwood DA (2014) Fabrication and luminescence of monolayered boron nitride quantum dots. Small 10(1):60–65
Li H, Tay RY, Tsang SH, Zhen X, Teo EHT (2015) Controllable synthesis of highly luminescent boron nitride quantum dots. Small 11(48):6491–6499
Lei Z, Xu S, Wan J, Wu P (2015) Facile preparation and multifunctional applications of boron nitride quantum dots. Nanoscale 7(45):18902–18907
Bilecka I, Niederberger M (2010) Microwave chemistry for inorganic nanomaterials synthesis. Nanoscale 2(8):1358–1374
Li L-L, Ji J, Fei R, Wang C-Z, Lu Q, Zhang J-R, Jiang L-P, Zhu J-J (2012) A facile microwave avenue to electrochemiluminescent two-color graphene quantum dots. Adv Func Mater 22(14):2971–2979
Zhu G, Pan L, Xu T, Zhao Q, Lu B, Sun Z (2011) Microwave assisted CdSe quantum dot deposition on TiO2 films for dye-sensitized solar cells. Nanoscale 3(5):2188–2193
Washington AL II, Strouse GF (2009) Microwave synthetic route for highly emissive TOP/TOP-S passivated CdS quantum dots. Chem Mater 21(15):3586–3592
Xuan TT, Wang XJ, Zhu G, Li HL, Pan LK, Sun Z (2013) One-step microwave-assisted synthesis of water soluble CdSe quantum dots for white light-emitting diodes with excellent color rendering. J Alloys Compd 558:105–108
Fitzmorris RC, Oleksak RP, Zhou Z, Mangum BD, Kurtin JN, Herman GS (2015) Structural and optical characterization of CuInS2 quantum dots synthesized by microwave-assisted continuous flow methods. J Nanoparticle Res 17(7):319
Afrasiabi R, Sugunan A, Shahid R, Toprak MS, Muhammed M Microwave mediated synthesis of semiconductor quantum dots. In: Lourdudoss S, Marcinkevicius S, Kataria H (eds) Physica Status solidi C: current topics in solid state physics, vol 9, No 72012, pp 1551–1556
Zhu Y, Murali S, Stoller MD, Velamakanni A, Piner RD, Ruoff RS (2010) Microwave assisted exfoliation and reduction of graphite oxide for ultracapacitors. Carbon 48(7):2118–2122
Chen W, Yan L, Bangal PR (2010) Preparation of graphene by the rapid and mild thermal reduction of graphene oxide induced by microwaves. Carbon 48(4):1146–1152
Li Y, Hu Y, Zhao Y, Shi G, Deng L, Hou Y, Qu L (2011) An electrochemical avenue to green-luminescent graphene quantum dots as potential electron-acceptors for photovoltaics. Adv Mater 23(6):776–780
Thangasamy P, Santhanam M, Sathish M (2016) Supercritical fluid facilitated disintegration of hexagonal boron nitride nanosheets to quantum dots and its application in cells imaging. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(29):18647–18651
Mahule TS, Srinivasu VV, Das J (2016) Observation of low field microwave absorption in co-doped ZnO system. Solid State Commun 243:60–64
Huang TY, He M, Zhou YM, Li SW, Ding BB, Pan WL, Huang S, Tong Y (2016) Solvothermal synthesis of flower-like CoS hollow microspheres with excellent microwave absorption properties. RSC Adv 6(102):100392–100400
Tan KH, Ahmad R, Johan MR (2013) Electromagnetic and microwave absorbing properties of amorphous carbon nanotube-cadmium selenide quantum dot hybrids. Mater Chem Phys 139(1):66–72
Sun D, Zou Q, Wang Y, Wang Y, Jiang W, Li F (2014) Controllable synthesis of porous Fe3O4@ZnO sphere decorated graphene for extraordinary electromagnetic wave absorption. Nanoscale 6(12):6557–6562
Che RC, Peng LM, Duan XF, Chen Q, Liang XL (2004) Microwave absorption enhancement and complex permittivity and permeability of Fe encapsulated within carbon nanotubes. Adv Mater 16(5):401–405
Zhang K, Gao X, Zhang Q, Li T, Chen X (2017) Pitch carbon coating graphene/carbon nanotubes lightweight composite and their excellent microwave absorption capacity. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 28(2):1352–1358
Rubrice K, Castel X, Himdi M, Parneix P (2016) Dielectric characteristics and microwave absorption of graphene composite materials. Materials 9(10):825
Sun G, Dong B, Cao M, Wei B, Hu C (2011) Hierarchical dendrite-like magnetic materials of Fe3O4, gamma-Fe2O3, and Fe with high performance of microwave absorption. Chem Mater 23(6):1587–1593
Zou CW, Yao YD, Wei ND, Gong YC, Fu WD, Wang M, Jiang L, Liao XM, Yin GF, Huang ZB, Chen XC (2015) Electromagnetic wave absorption properties of mesoporous Fe3O4/C nanocomposites. Compos B Eng 77:209–214
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the financial supports of National Natural Science Foundation of China (51673040, 21306023, 21676056 and 21376051), The Prospective Joint Research Project of Jiangsu Province (BY2016076-01), The Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (3207046302), and The Fund Project for Transformation of Scientific and Technological Achievements of Jiangsu Province of China (BA2016105).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, L., Zhou, Y., He, M. et al. Facile microwave approach to controllable boron nitride quantum dots. J Mater Sci 52, 13522–13532 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1395-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1395-9