Abstract
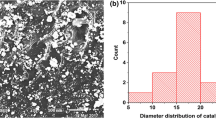
The influence of catalyst particle size on the formation and diameter of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) is investigated. Ferrocene catalyst with an average diameter of 19.7, 21.4, 23.6 and 27.0 µm is used for the growth of CNTs by a cost-effective and facile method using microwave oven. Morphological observations by transmission electron microscopy and field emission scanning electron microscopy reveal consistently that smaller catalyst diameter generates CNTs with smaller diameter. Raman spectroscopy indicates that the full width at half maximum of G-, D- and 2D-bands decreases gradually with increasing CNTs diameter; meanwhile, G-band/D-band intensity ratio is found to be sensitive to crystal defects, showing a drop for CNTs diameter in the range 25–40 nm then followed by a slight increase for higher diameters. This may be associated with CNTs curvature and strain which developed along tube walls. X-ray diffraction analysis demonstrates an increase in d (002) interlayer spacing with decreasing CNTs diameter. Furthermore, CNTs diameter is found to be inversely proportional to (002) linewidth. Finally, the energy band gap estimated from UV–NIR–Vis measurements increases slightly with CNTs diameter, 5.69–5.84 eV.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Köhler AR, Som C, Helland A, Gottschalk F (2008) Studying the potential release of carbon nanotubes throughout the application life cycle. J Clean Prod 16(8):927–937
Prasek J, Drbohlavova J, Chomoucka J, Hubalek J, Jasek O, Adam V, Kizek R (2011) Methods for carbon nanotubes synthesis—review. J Mater Chem 21(40):15872–15884
Zhang X, Liu Z (2012) Recent advances in microwave initiated synthesis of nanocarbon materials. Nanoscale 4(3):707–714
Xie H, Poyraz S, Thu M, Liu Y, Snyder EY, Smith JW, Zhang X (2014) Microwave-assisted fabrication of carbon nanotubes decorated polymeric nano-medical platforms for simultaneous drug delivery and magnetic resonance imaging. RSC Adv 4(11):5649–5652
Jones D, Lelyveld T, Mavrofidis S, Kingman S, Miles N (2002) Microwave heating applications in environmental engineering—a review. Resour Conserv Recycl 34(2):75–90
Liu Z, Wang J, Kushvaha V, Poyraz S, Tippur H, Park S, Kim M, Liu Y, Bar J, Chen H (2011) Poptube approach for ultrafast carbon nanotube growth. Chem Commun 47(35):9912–9914
Poyraz S, Liu Z, Liu Y, Zhang X (2013) Devulcanization of scrap ground tire rubber and successive carbon nanotube growth by microwave irradiation. Curr Org Chem 17(20):2243–2248
Poyraz S, Zhang L, Schroder A, Zhang X (2015) Ultrafast microwave welding/reinforcing approach at the interface of thermoplastic materials. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(40):22469–22477
Liu Z, Zhang L, Poyraz S, Smith J, Kushvaha V, Tippur H, Zhang X (2014) An ultrafast microwave approach towards multi-component and multi-dimensional nanomaterials. RSC Adv 4(18):9308–9313
Odom TW, Huang J-L, Kim P, Lieber CM (1998) Atomic structure and electronic properties of single-walled carbon nanotubes. Nature 391(6662):62–64
Cabria I, Mintmire J, White C (2003) Metallic and semiconducting narrow carbon nanotubes. Phys Rev B 67(12):121406
Cheung CL, Kurtz A, Park H, Lieber CM (2002) Diameter-controlled synthesis of carbon nanotubes. J Phys Chem B 106(10):2429–2433
Nasibulin AG, Pikhitsa PV, Jiang H, Kauppinen EI (2005) Correlation between catalyst particle and single-walled carbon nanotube diameters. Carbon 43(11):2251–2257
Ago H, Komatsu T, Ohshima S, Kuriki Y, Yumura M (2000) Dispersion of metal nanoparticles for aligned carbon nanotube arrays. Appl Phys Lett 77(1):79–81
Schäffel F, Kramberger C, Rümmeli MH, Grimm D, Mohn E, Gemming T, Pichler T, Rellinghaus B, Büchner B, Schultz L (2007) Nanoengineered catalyst particles as a key for tailor-made carbon nanotubes. Chem Mater 19(20):5006–5009
Antunes E, Lobo A, Corat E, Trava-Airoldi V (2007) Influence of diameter in the Raman spectra of aligned multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Carbon 45(5):913–921
Singh DK, Iyer P, Giri P (2010) Diameter dependence of interwall separation and strain in multiwalled carbon nanotubes probed by X-ray diffraction and Raman scattering studies. Diam Relat Mater 19(10):1281–1288
Mondal A, Agrawal D, Upadhyaya A (2008) Microwave heating of pure copper powder with different particle size and porosity. In: Global congress on microwave energy application, Japan
Bai X, Li D, Wang Y, Liang J (2005) Effects of temperature and catalyst concentration on the growth of aligned carbon nanotubes. Tsinghua Sci Technol 10(6):729–735
Shamsudin M, Asli N, Abdullah S, Yahya S, Rusop M (2012) Effect of synthesis temperature on the growth iron-filled carbon nanotubes as evidenced by structural, micro-raman, and thermogravimetric analyses. Adv Condens Matter Phys 2012:1–7
Tuinstra F, Koenig J (1970) Characterization of graphite fiber surfaces with Raman spectroscopy. J Compos Mater 4(4):492–499
Ebbesen T, Takada T (1995) Topological and sp 3 defect structures in nanotubes. Carbon 33(7):973–978
Reznik D, Olk C, Neumann D, Copley J (1995) X-ray powder diffraction from carbon nanotubes and nanoparticles. Phys Rev B 52(1):116
Davis JA, Leckie JO (1978) Surface ionization and complexation at the oxide/water interface II. Surface properties of amorphous iron oxyhydroxide and adsorption of metal ions. J Colloid Interface Sci 67(1):90–107
Liu M, Cowley JM (1994) Structures of carbon nanotubes studied by HRTEM and nanodiffraction. Ultramicroscopy 53(4):333–342
Kiang C-H, Endo M, Ajayan P, Dresselhaus G, Dresselhaus M (1998) Size effects in carbon nanotubes. Phys Rev Lett 81(9):1869
Maciel IO, Anderson N, Pimenta MA, Hartschuh A, Qian H, Terrones M, Terrones H, Campos-Delgado J, Rao AM, Novotny L (2008) Electron and phonon renormalization near charged defects in carbon nanotubes. Nat Mater 7(11):878–883
Butler M (1977) Photoelectrolysis and physical properties of the semiconducting electrode WO2. J Appl Phys 48(5):1914–1920
Collins PG, Arnold MS, Avouris P (2001) Engineering carbon nanotubes and nanotube circuits using electrical breakdown. Science 292(5517):706–709
Avouris P (2002) Carbon nanotube electronics. Chem Phys 281(2):429–445
Guo G, Chu K, Wang D-S, Duan C-G (2004) Linear and nonlinear optical properties of carbon nanotubes from first-principles calculations. Phys Rev B 69(20):205416
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the Department of Physics at Universiti Sains Malaysia for the help and support for the achievement of this research project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Algadri, N.A., Hassan, Z., Ibrahim, K. et al. Effect of ferrocene catalyst particle size on structural and morphological characteristics of carbon nanotubes grown by microwave oven. J Mater Sci 52, 12772–12782 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1381-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1381-2