Abstract
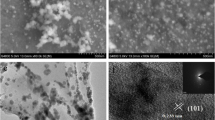
A three-dimensional (3D) nickel oxide (NiO) catalytic electrode was fabricated by annealing Ni2(L-asp)2bipy MOF membrane and was subsequently applied for electrochemical glucose sensor. This 3D self-supported MOF membrane precursor provided uniform and porous architecture, and it was used for fabricating 3D NiO electrode in the first time. The SEM and XRD data showed that the NiO was evenly distributed on Ni mesh and complete transformation from Ni2(L-asp)2bipy to NiO. This catalytic electrode, using a chronoamperometric approach, demonstrated linear range up to 400 μM with high sensitivity of 478.9 μA mM−1 cm−2 and low limit of detection of 4.34 μM. Uric acid, urea and ascorbic acid showed negligible interferences to the detection of glucose. The excellent performance of this electrode was attributed to the uniformly distributed NiO on the Ni substrate, direct electron transformation from Ni substrate to electrochemical active NiO and the porosity of such electrode design.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Park S, Boo H, Chung TD (2006) Electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensors. Anal Chim Acta 556:46–57
Toghill KE, Compton RG (2010) Electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensors: a perspective and an evaluation. Int J Electrochem Sci 5:1246–1301
Niu XH, Li X, Pan JM, He YF, Qiu FX, Yan YS (2016) Recent advances in non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensors based on non-precious transition metal materials: opportunities and challenges. Rsc Adv 6:84893–84905
Ensafi AA, Ahmadi N, Rezaei B (2017) Nickel nanoparticles supported on porous silicon flour, application as a non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensor. Sens Actuators B Chem 239:807–815
Garcia-Garcia FJ, Salazar P, Yubero F, Gonzalez-Elipe AR (2016) Non-enzymatic Glucose electrochemical sensor made of porous NiO thin films prepared by reactive magnetron sputtering at oblique angles. Electrochim Acta 201:38–44
Khedekar VV, Bhanage BM (2016) Simple electrochemical synthesis of cuprous oxide nanoparticles and their application as a non-enzymatic glucose sensor. J Electrochem Soc 163:B248–B251
Mahmoudian MR, Basirun WJ, Woi PM, Sookhakian M, Yousefi R, Ghadimi H, Alias Y (2016) Synthesis and characterization of Co3O4 ultra-nanosheets and Co3O4 ultra-nanosheet-Ni(OH)(2) as non-enzymatic electrochemical sensors for glucose detection. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 59:500–508
Wang D, Cai D, Huang H, Liu B, Wang L, Liu Y, Li H, Wang Y, Li Q, Wang T (2015) Non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensor based on NiMoO4 nanorods. Nanotechnology 26:145501
Deng Z, Long H, Wei Q, Yu Z, Zhou B, Wang Y, Zhang L, Li S, Ma L, Xie Y, Min J (2017) High-performance non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on nickel-microcrystalline graphite-boron doped diamond complex electrode. Sens Actuators B Chem 242:825–834
Wang L, Lu X, Wen C, Xie Y, Miao L, Chen S, Li H, Li P, Song Y (2015) One-step synthesis of Pt–NiO nanoplate array/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites for nonenzymatic glucose sensing. J Mater Chem A 3:608–616
Wang L, Zhang Y, Yu J, He J, Yang H, Ye Y, Song Y (2017) A green and simple strategy to prepare graphene foam-like three-dimensional porous carbon/Ni nanoparticles for glucose sensing. Sens Actuators B Chem 239:172–179
Song Y, Liu H, Tan H, Xu F, Jia J, Zhang L, Li Z, Wang L (2014) pH-switchable electrochemical sensing platform based on chitosan-reduced graphene oxide/concanavalin a layer for assay of glucose and urea. Anal Chem 86:1980–1987
Song Y, Lu X, Li Y, Guo Q, Chen S, Mao L, Hou H, Wang L (2016) Nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes supported by macroporous carbon as an efficient enzymatic biosensing platform for glucose. Anal Chem 88:1371–1377
Wang L, Zhang Q, Chen S, Xu F, Chen S, Jia J, Tan H, Hou H, Song Y (2014) Electrochemical sensing and biosensing platform based on biomass-derived macroporous carbon materials. Anal Chem 86:1414–1421
Adatoz E, Avci AK, Keskin S (2015) Opportunities and challenges of MOF-based membranes in gas separations. Sep Purif Technol 152:207–237
Zhang Y, Feng X, Yuan S, Zhou J, Wang B (2016) Challenges and recent advances in MOF-polymer composite membranes for gas separation. Inorg Chem Front 3:896–909
Hou C, Xu Q, Yin L, Hu X (2012) Metal-organic framework templated synthesis of Co3O4 nanoparticles for direct glucose and H2O2 detection. Analyst 137:5803–5808
Zhou E, Zhang Y, Li Y, He X (2014) Cu(II)-based MOF immobilized on multiwalled carbon nanotubes: synthesis and application for nonenzymatic detection of hydrogen peroxide with high sensitivity. Electroanalysis 26:2526–2533
Wu D, Xu Z, Zhang T, Shao Y, Xi P, Li H, Xu C (2016) Cu2O/CuO@rGO heterostructure derived from metal-organic-frameworks as an advanced electrocatalyst for non-enzymatic electrochemical H2O2 sensor. RSC Adv 6:103116–103123
Wang L, Yang H, He J, Zhang Y, Yu J, Song Y (2016) Cu-hemin metal-organic-frameworks/chitosan-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites with peroxidase-like bioactivity for electrochemical sensing. Electrochim Acta 213:691–697
Shi L, Zhu X, Liu T, Zhao H, Lan M (2016) Encapsulating Cu nanoparticles into metal-organic frameworks for nonenzymatic glucose sensing. Sens Actuators B Chem 227:583–590
Kang Z, Xue M, Fan L, Huang L, Guo L, Wei G, Chen B, Qiu S (2014) Highly selective sieving of small gas molecules by using an ultra-microporous metal-organic framework membrane. Energy Environ Sci 7:4053–4060
Wang S, Wang C, Wei G, Xiao H, An N, Zhou Y, An C, Zhang J (2016) Non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on facial hydrothermal synthesized NiO nanosheets loaded on glassy carbon electrode. Colloids Surf A 509:252–258
Medway SL, Lucas CA, Kowal A, Nichols RJ, Johnson D (2006) In situ studies of the oxidation of nickel electrodes in alkaline solution. J Electroanal Chem 587:172–181
Xu K, Huang X, Liu Q, Zou R, Li W, Liu X, Li S, Yang J, Hu J (2014) Understanding the effect of polypyrrole and poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) on enhancing the supercapacitor performance of NiCo2O4 electrodes. J Mater Chem A 2:16731–16739
Zhao Y, Wang Q, Bian T, Yu H, Fan H, Zhou C, Wu LZ, Tung CH, O’Hare D, Zhang T (2015) Ni3+ doped monolayer layered double hydroxide nanosheets as efficient electrodes for supercapacitors. Nanoscale 7:7168–7173
Gao S, Liao F, Ma S, Zhu L, Shao M (2015) Network-like mesoporous NiCo2O4 grown on carbon cloth for high-performance pseudocapacitors. J Mater Chem A 3:16520–16527
Parveen N, Cho MH (2016) Self-assembled 3D flower-like nickel hydroxide nanostructures and their supercapacitor applications. Sci Rep 6:27318
Zeng G, Li W, Ci S, Jia J, Wen Z (2016) Highly dispersed NiO nanoparticles decorating graphene nanosheets for non-enzymatic glucose sensor and biofuel cell. Sci Rep 6:36454
Yang J, Yu J-H, Rudi Strickler J, Chang W-J, Gunasekaran S (2013) Nickel nanoparticle–chitosan-reduced graphene oxide-modified screen-printed electrodes for enzyme-free glucose sensing in portable microfluidic devices. Biosens Bioelectron 47:530–538
Shamsipur M, Najafi M, Hosseini M-RM (2010) Highly improved electrooxidation of glucose at a nickel(II) oxide/multi-walled carbon nanotube modified glassy carbon electrode. Bioelectrochemistry 77:120–124
Xu J, Xu N, Zhang X, Xu P, Gao B, Peng X, Mooni S, Li Y, Fu J, Huo K (2017) Phase separation induced rhizobia-like Ni nanoparticles and TiO2 nanowires composite arrays for enzyme-free glucose sensor. Sens Actuators B Chem 244:38–46
Ghanbari K, Babaei Z (2016) Fabrication and characterization of non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on ternary NiO/CuO/polyaniline nanocomposite. Anal Biochem 498:37–46
Long M, Tan L, Liu H, He Z, Tang A (2014) Novel helical TiO2 nanotube arrays modified by Cu2O for enzyme-free glucose oxidation. Biosens Bioelectron 59:243–250
Li Y, Zhong Y, Zhang Y, Weng W, Li S (2015) Carbon quantum dots/octahedral Cu2O nanocomposites for non-enzymatic glucose and hydrogen peroxide amperometric sensor. Sens Actuators B Chem 206:735–743
Balamurugan J, Thanh TD, Karthikeyan G, Kim NH, Lee JH (2017) A novel hierarchical 3D N-Co-CNT@NG nanocomposite electrode for non enzymatic glucose and hydrogen peroxide sensing applications. Biosens Bioelectron 89:970–977
Nontawong N, Amatatongchai M, Jarujamrus P, Tamuang S, Chairam S (2017) Non-enzymatic glucose sensors for sensitive amperometric detection based on simple method of nickel nanoparticles decorated on magnetite carbon nanotubes modified glassy carbon electrode. Int J Electrochem Sci 12:1362–1376
Krebs HA (1950) Chemical composition of blood plasma and serum. Annu Rev Biochem 19:409–430
Acknowledgements
The authors thank for the financial supports provided by National Natural Science Foundation of China (21501198).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Li, J., Wang, S. et al. From MOF membrane to 3D electrode: a new approach toward an electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose biosensor. J Mater Sci 52, 12089–12097 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1349-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1349-2