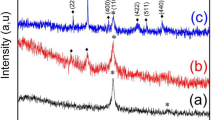
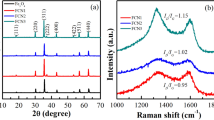
Abstract
The three-layer core–shell–shell γ-Fe2O3–SiO2–poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) nanocomposite has been successfully synthesized by a facile chemical process followed by a detailed investigation of morphology, composition, electromagnetic, and microwave absorption properties. The electrical conductivity of γ-Fe2O3–SiO2–PEDOT nanocomposites was as high as 3.34 S cm−1, and the saturation magnetization was in the range of 1–7 emu g−1. The minimum reflection loss reached −27.5 dB at 13.8 GHz with a matching layer thickness of 2.0 mm and an effective absorption bandwidth (< −10 dB) of about 4.1 GHz (12.0–16.1 GHz). The excellent microwave absorbing performance of this nanocomposite is due to proper impedance matching and the synergistic interaction of dielectric loss, the magnetic loss, and core–shell microstructure. Moreover, the electromagnetic and microwave absorbing properties of γ-Fe2O3–SiO2–PEDOT nanocomposites can be regulated by changing the dosage of functionalized γ-Fe2O3–SiO2.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Melvin GJH, Ni QQ, Suzuki Y et al (2014) Microwave-absorbing properties of silver nanoparticle/carbon nanotube hybrid nanocomposites. J Mater Sci 49(14):5199–5207
He Q, Yuan T, Zhang X et al (2014) Electromagnetic field absorbing polypropylene nanocomposites with tuned permittivity and permeability by nanoiron and carbon nanotubes. J Phys Chem C 118(42):24784–24796
Sun H, Che R, You X et al (2014) Cross-stacking aligned carbon-nanotube films to tune microwave absorption frequencies and increase absorption intensities. Adv Mater 26(48):8120–8125
Zhao T, Hou C, Zhang H et al (2014) Electromagnetic wave absorbing properties of amorphous carbon nanotubes. Sci Rep 4:5619–5625
Li Y, Chen G, Li Q et al (2011) Facile synthesis, magnetic and microwave absorption properties of Fe3O4/polypyrrole core/shell nanocomposite. J Alloy Compd 509(10):4104–4107
Benykhlef S, Bekhoukh A, Berenguer R et al (2016) PANI-derived polymer/Al2O3 nanocomposites: synthesis, characterization, and electrochemical studies. Colloid Polym Sci 294(12):1877–1885
Chouli F, Radja I, Morallon E et al (2015) A novel conducting nanocomposite obtained by p anisidine and aniline with titanium (IV) oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and electrochemical properties. Polym Compos. doi:10.1002/pc.23837
Radja I, Djelad H, Morallon E (2015) Characterization and electrochemical properties of conducting nanocomposites synthesized from p-anisidine and aniline with titanium carbide by chemical oxidative method. Synth Met 202:25–32
Zhou W, Hu X, Bai X et al (2011) Synthesis and electromagnetic, microwave absorbing properties of core–shell Fe3O4–poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) microspheres. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 3(10):3839–3845
Dong XL, Zhang XF, Huang H et al (2008) Enhanced microwave absorption in Ni/polyaniline nanocomposites by dual dielectric relaxations. Appl Phys Lett 013127(1):92–94
Liu J, Che R, Chen H et al (2012) Microwave absorption enhancement of multifunctional composite microspheres with spinel Fe3O4 cores and anatase TiO2 shells. Small 8(8):1214–1221
Chen YJ, Zhang F, Zhao G et al (2010) Synthesis, multi-nonlinear dielectric resonance, and excellent electromagnetic absorption characteristics of Fe3O4/ZnO core/shell nanorods. J Phys Chem C 114(20):9239–9244
Wang G, Chang Y, Wang L et al (2012) Synthesis, characterization and microwave absorption properties of Fe3O4/Co core/shell-type nanoparticles. Adv Powder Technol 23(6):861–865
Qiu J, Wang Y, Gu M (2007) Microwave absorption properties of substituted BaFe12O19/TiO2 nanocomposite multilayer film. J Mater Sci 42(1):166–169
Zhu J, Wei S, Haldolaarachchige N et al (2011) Electromagnetic field shielding polyurethane nanocomposites reinforced with core–shell Fe–silica nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 115(31):15304–15310
Deng YH, Wang CC, Hu JH et al (2005) Investigation of formation of silica-coated magnetite nanoparticles via sol–gel approach. Colloids Surf A 262(1):87–93
Ohlan A, Singh K, Chandra A et al (2010) Microwave absorption behavior of core–shell structured poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)–barium ferrite nanocomposites. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2(3):927–933
Huo J, Wang L, Yu H (2009) Polymeric nanocomposites for electromagnetic wave absorption. J Mater Sci 44(15):3917–3927
Liu Q, Zhang D, Fan T (2008) Electromagnetic wave absorption properties of porous carbon/Co nanocomposites. Appl Phys Lett 013110(1):93–96
Zhang B, Du Y, Zhang P et al (2013) Microwave absorption enhancement of Fe3O4/polyaniline core/shell hybrid microspheres with controlled shell thickness. J Appl Polym Sci 130(3):1909–1916
Belaabed B, Wojkiewicz JL, Lamouri S et al (2012) Synthesis and characterization of hybrid conducting composites based on polyaniline/magnetite fillers with improved microwave absorption properties. J Alloy Compd 527:137–144
Wang G, Gao Z, Tang S et al (2012) Microwave absorption properties of carbon nanocoils coated with highly controlled magnetic materials by atomic layer deposition. ACS Nano 6(12):11009–11017
Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Xu S et al (2016) Synthesis of γ-Fe2O3@SiO2@polypyrrole core/shell/shell nanospheres with flexible controllability of electromagnetic properties. RSC Adv 6(8):6623–6630
Dai T, Yang X, Lu Y (2007) Conductive composites of polypyrrole and sulfonic-functionalized silica spheres. Mater Lett 61(14):3142–3145
Stöber W, Fink A, Bohn E (1968) Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J Colloid Interface Sci 26(1):62–69
Li HY, Chang CM, Hsu KY et al (2012) Poly (lactide)-functionalized and Fe3O4 nanoparticle-decorated multiwalled carbon nanotubes for preparation of electrically-conductive and magnetic poly (lactide) films and electrospun nanofibers. J Mater Chem 22(11):4855–4860
Zhou H, Yao W, Li G et al (2013) Graphene/poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) hydrogel with excellent mechanical performance and high conductivity. Carbon 59:495–502
Kvarnström C, Neugebauer H, Blomquist S et al (1999) In situ FTIR spectroelectrochemical characterization of poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) films. Synth Met 101(1–3):66. doi:10.1016/S0379-6779(98)01133-3
Yin Y, Li Z, Jin J et al (2013) Facile synthesis of poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) by acid-assisted polycondensation of 5-bromo-2, 3-dihydro-thieno [3,4-b][1,4] dioxine. Synth Met 175:97–102
Gu J, Gao S, Xue Y et al (2016) Synthesis and characterization of PEDOT aqueous dispersions with sulfonated polyfluorene as a template and doping agent. React Funct Polym 100:83–88
Unsworth J, Kaynak A, Lunn BA et al (1993) Microwave transmission, reflection and dielectric properties of conducting and semiconducting polypyrrole films and powders. J Mater Sci 28(12):3307–3312
Liu X, Geng D, Shang P et al (2008) Fluorescence and microwave-absorption properties of multi-functional ZnO-coated α-Fe solid-solution nanocapsules. J Phys D Appl Phys 41(17):5006–5014
Zhang A, Tang M, Cao X et al (2014) The effect of polyethylenimine on the microwave absorbing properties of a hybrid microwave absorber of Fe3O4/MWNTs. J Mater Sci 49(13):4629–4635
Zhang XF, Dong XL, Huang H et al (2007) Microstructure and microwave absorption properties of carbon-coated iron nanocapsules. J Phys D Appl Phys 40(17):5383–5387
Naito Y, Suetake K (1971) Application of ferrite to electromagnetic wave absorber and its characteristics. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech 19(1):65–72
Zhang D, Cheng J, Yang X et al (2014) Electromagnetic and microwave absorbing properties of magnetite nanoparticles decorated carbon nanotubes/polyaniline multiphase heterostructures. J Mater Sci 49(20):7221–7230
Qiao M, Lei X, Ma Y et al (2016) Well-defined core–shell Fe3O4@Polypyrrole composite microspheres with tunable shell thickness: synthesis and their superior microwave absorption performance in the Ku band. Ind Eng Chem Res 55(22):6263–6275
Cao MS, Yang J, Song WL et al (2012) Ferroferric oxide/multiwalled carbon nanotube vs polyaniline/ferroferric oxide/multiwalled carbon nanotube multiheterostructures for highly effective microwave absorption. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4(12):6949–6956
Chen K, Xiang C, Li L, Qian H, Xiao Q, Xu F (2012) A novel ternary composite: fabrication, performance and application of expanded graphite/polyaniline/CoFe2O4 ferrite. J Mater Chem 22(13):6449–6455
Sun Y, Xiao F, Liu X, Feng C, Jin C (2013) Preparation and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of core–shell structured Fe3O4–Polyaniline nanoparticles. RSC Adv 3:22554–22559
He Z, Fang Y, Wang X et al (2011) Microwave absorption properties of PANI/CIP/Fe3O4 composites. Synth Met 161(5):420–425
Wang L, Zhu J, Yang H et al (2015) Fabrication of hierarchical graphene@Fe3O4@SiO2@ polyaniline quaternary composite and its improved electrochemical performance. J Alloy Compd 634:232–238
Acknowledgement
This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41476059).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, S., Zhang, Z., Jiang, X. et al. Synthesis and microwave absorbing properties of γ-Fe2O3–SiO2–poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) core–shell–shell nanocomposites. J Mater Sci 52, 12358–12369 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1337-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1337-6