Abstract
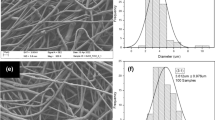
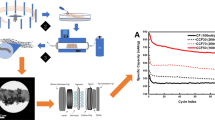
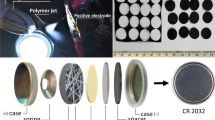
SnO2 microfibers were prepared using a newly developed centrifugal spinning technology with subsequent thermal treatment. The as-prepared SnO2 microfibers were further treated with chemical vapor deposition (CVD) of acetylene using different durations of 30, 60, and 90 min. The surfaces of the CVD-treated SnO2 microfibers are covered with thin carbon layers, and the surface nanoparticles on the SnO2 microfibers were reduced by carbon, producing nano-sized Sn/C whiskers grafted on the backbones. The X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, and cyclic voltammetry results demonstrate that longer CVD coating duration promotes the formation of Sn/C whiskers on the SnO2 microfibers. The thin carbon coating layers help stabilize the solid electrolyte interface formation while the grafted Sn/C whiskers facilitate better electrolyte–electrode contact. Hence, the CVD-treated SnO2 microfibers exhibit higher initial capacities than the pristine SnO2 microfibers, as well as enhanced capacity retentions after cycling. The results suggest that centrifugal spinning is a promising approach to produce fibrous electrode materials in a rapid and mass production fashion, and the CVD coating process is an effective method to improve the electrochemical performance of the SnO2-based electrode materials.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ji L, Lin Z, Alcoutlabi M, Zhang X (2011) Recent developments in nanostructured anode materials for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. Energy Environ Sci 4:2682–2699
Xue L, Fu K, Li Y, Xu G, Lu Y, Zhang S, Toprakci O, Zhang X (2013) Si/C composite nanofibers with stable electric conductive network for use as durable lithium-ion battery anode. Nano Energy 2:361–367
Li Y, Sun Y, Xu G, Lu Y, Zhang S, Xue L, Jur JS, Zhang X (2014) Tuning electrochemical performance of Si-based anodes for lithium-ion batteries by employing atomic layer deposition alumina coating. J Mater Chem A 2:11417
Zhang S, Lin Z, Ji L, Li Y, Xu G, Xue L, Li S, Lu Y, Toprakci O, Zhang X (2012) Cr-doped Li2MnSiO4/carbon composite nanofibers as high-energy cathodes for Li-ion batteries. J Mater Chem 22:14661–14666
Wang LP, Yu L, Wang X, Srinivasan M, Xu ZJ (2015) Recent developments in electrode materials for sodium-ion batteries. J Mater Chem A 3:9353–9378
Yabuuchi N, Kubota K, Dahbi M, Komaba S (2014) Research development on sodium-ion batteries. Chem Rev 114:11636–11682
Slater MD, Kim D, Lee E, Johnson CS (2013) Sodium-ion batteries. Adv Funct Mater 23:947–958
Ge P, Fouletier M (1988) Electrochemical intercalation of sodium in graphite. Solid State Ionics 30:1172–1175
Alcántara R, Jiménez Mateos JM, Tirado JL (2002) Negative electrodes for lithium- and sodium-ion batteries obtained by heat-treatment of petroleum cokes below 1000°C. J Electrochem Soc 149:A201–A205
Thomas P, Ghanbaja J, Billaud D, Poincare H, Nancy I (1999) Electrochemical insertion of sodium in pitch-based carbon fibres in comparison with graphite in NaClO4–ethylene carbonate electrolyte. Carbon 45:423–430
Stevens DA, Dahn JR (2001) The mechanisms of lithium and sodium insertion in carbon materials. J Electrochem Soc 148:A803–A811
Alcántara R, Jiménez-Mateos JM, Lavela P, Tirado JL (2001) Carbon black: a promising electrode material for sodium-ion batteries. Electrochem Commun 3:639–642
Wang H, Wu Z, Meng F, Ma D, Huang X, Wang L, Zhang X (2013) Nitrogen-doped porous carbon nanosheets as low-cost, high-performance anode material for sodium-ion batteries. ChemSusChem 6:56–60
Fu L, Tang K, Song K, van Aken PA, Yu Y, Maier J (2014) Nitrogen doped porous carbon fibres as anode materials for sodium ion batteries with excellent rate performance. Nanoscale 6:1384–1389
Cao Y, Xiao L, Sushko ML, Wang W, Schwenzer B, Xiao J, Nie Z, Saraf LV, Yang Z, Liu J (2012) Sodium ion insertion in hollow carbon nanowires for battery applications. Nano Lett 12:3783–3787
Chen T, Liu Y, Pan L, Lu T, Yao Y, Sun Z, Chua DHC, Chen Q (2014) Electrospun carbon nanofibers as anode materials for sodium ion batteries with excellent cycle performance. J Mater Chem A 2:4117–4121
Ge Y, Jiang H, Fu K, Zhang C, Zhu J, Chen C, Lu Y, Qiu Y, Zhang X (2014) Copper-doped Li4Ti5O12/carbon nanofiber composites as anode for high-performance sodium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 272:860–865
Pan H, Lu X, Yu X, Hu YS, Li H, Yang XQ, Chen L (2013) Sodium storage and transport properties in layered Na2Ti3O7 for room-temperature sodium-ion batteries. Adv Energy Mater 3:1186–1194
Ge Y, Jiang H, Zhu J, Lu Y, Chen C, Hu Y, Qiu Y, Zhang X (2015) High cyclability of carbon-coated TiO2 nanoparticles as anode for sodium-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 157:142–148
Xue L, Xia X, Tucker T, Fu K, Zhang S, Li S, Zhang X (2013) A simple method to encapsulate SnSb nanoparticles into hollow carbon nanofibers with superior lithium-ion storage capability. J Mater Chem A 1:13807–13813
Li Y, Guo B, Ji L, Lin Z, Xu G, Liang Y, Zhang S, Toprakci O, Hu Y, Alcoutlabi M, Zhang X (2013) Structure control and performance improvement of carbon nanofibers containing a dispersion of silicon nanoparticles for energy storage. Carbon 51:185–194
Liu Y, Zhang N, Jiao L, Tao Z, Chen J (2015) Ultrasmall Sn nanoparticles embedded in carbon as high-performance anode for sodium-ion batteries. Adv Funct Mater 25:214–220
Zhu Y, Han X, Xu Y, Liu Y, Zheng S, Xu K, Hu L, Wang C (2013) Electrospun Sb/C fibers for a stable and fast sodium-ion battery anode. ACS Nano 7:6378–6386
Chen C, Fu K, Lu Y, Zhu J, Xue L, Hu Y, Zhang X (2015) Use of a tin antimony alloy-filled porous carbon nanofiber composite for use as anode in sodium-ion batteries. RSC Adv 5:30793–30800
Fu K, Xue L, Yildiz O, Li S, Lee H, Li Y, Xu G, Zhou L, Bradford PD, Zhang X (2013) Effect of CVD carbon coatings on Si@CNF composite as anode for lithium-ion batteries. Nano Energy 22:976–986
Wang Y, Su D, Wang C, Wang G (2013) SnO2@MWCNT nanocomposite as a high capacity anode material for sodium-ion batteries. Electrochem Commun 29:8–11
Su D, Ahn HJ, Wang G (2013) SnO2@graphene nanocomposites as anode materials for Na-ion batteries with superior electrochemical performance. Chem Commun 49:3131–3133
Xie X, Su D, Zhang J, Chen S, Mondal AK, Wang G (2015) A comparative investigation on the effects of nitrogen-doping into graphene on enhancing the electrochemical performance of SnO2/graphene for sodium-ion batteries. Nanoscale 7:3164–3172
Wang YX, Lim YG, Park MS, Chou SL, Kim JH, Liu HK, Dou SX, Kim YJ (2014) Ultrafine SnO2 nanoparticle loading onto reduced graphene oxide as anodes for sodium-ion batteries with superior rate and cycling performances. J Mater Chem A 2:529–534
Zhang X, Lu Y (2014) Centrifugal spinning: an alternative approach to fabricate nanofibers at high speed and low cost. Polym Rev 54:677–701
Lu Y, Fu K, Zhang S, Li Y, Chen C, Zhu J, Yanilmaz M, Dirican M, Zhang X (2015) Centrifugal spinning: a novel approach to fabricate porous carbon fibers as binder-free electrodes for electric double-layer capacitors. J Power Sources 273:502–510
Lu Y, Li Y, Zhang S, Xu G, Fu K, Lee H, Zhang X (2013) Parameter study and characterization for polyacrylonitrile nanofibers fabricated via centrifugal spinning process. Eur Polym J 49:3834–3845
Liu Y, Xu Y, Zhu Y, Culver JN, Lundgren CA, Xu K, Wang C (2013) Tin-coated viral nanoforests as sodium-ion battery anodes. ACS Nano 7:3627–3634
Xu Y, Zhu Y, Liu Y, Wang C (2013) Electrochemical performance of porous carbon/tin composite anodes for sodium-ion and lithium-ion batteries. Adv Energy Mater 3:128–133
Su D, Wang C, Ahn H, Wang G (2013) Octahedral tin dioxide nanocrystals as high capacity anode materials for Na-ion batteries. Phys Chem Chem Phys 15:12543–12550
Li L, Kovalchuk A, Tour JM (2014) SnO2-reduced graphene oxide nanoribbons as anodes for lithium ion batteries with enhanced cycling stability. Nano Res 7:1319–1326
Zhao X, Zhang Z, Yang F, Fu Y, Lai Y, Li J (2015) Core–shell structured SnO2 hollow spheres–polyaniline composite as an anode for sodium-ion batteries. RSC Adv 5:31465–31471
Tian Q, Zhang Z, Yang L, Hirano S, Mater J (2014) Synthesis of SnO2/Sn@ carbon nanospheres dispersed in the interspaces of a three-dimensional SnO2/Sn@ carbon nanowires network, and their application as an anode material for lithium-ion batteries. J Mater Chem A 2:12881–12887
Lian P, Zhu X, Liang S, Li Z, Yang W, Wang H (2011) High reversible capacity of SnO2/graphene nanocomposite as an anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 56:4532–4539
Zhou X, Yin YX, Wan LJ, Guo YG (2012) A robust composite of SnO2 hollow nanospheres enwrapped by graphene as a high-capacity anode material for lithium-ion batteries. J Mater Chem 22:17456–17459
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by National Science Foundation under Award Number CMMI-1231287.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Y., Fu, K., Zhu, J. et al. Comparing the structures and sodium storage properties of centrifugally spun SnO2 microfiber anodes with/without chemical vapor deposition. J Mater Sci 51, 4549–4558 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-9768-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-9768-z