Abstract
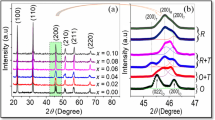
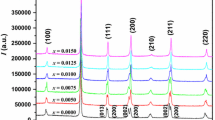
The aim of this work is to improve the electrical properties of BNKLLT ceramics with the addition of BCTZ. New binary (1 − x)BNKLLT-xBCTZ lead-free piezoelectric ceramics with different x contents between 0 and 0.10 (step 0.02) were fabricated by the solid-state combustion technique, where glycine was used as a fuel. The influences of x concentration on the phase evolution, morphology, and electrical behavior were investigated. The phase formation exhibited a coexistence of rhombohedral and tetragonal phases in all samples. With the increasing x content, the phase formation was dominated by a higher tetragonality. The average gain size continuously reduced from 1.52 to 0.96 µm when x content was increased. The maximum dielectric temperature (T SA) of these ceramics decreased with the increasing x content. The ferroelectric properties were further weakened with the increasing x content. The MPB region was obtained at x content of around 0.04 producing this sample and showed the highest dielectric constants (ε r = 2720 and ε SA = 6110) and an excellent piezoelectric constant (d 33 = 295 pC/N).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rodel J, Jo W, Seifert KTP, Anton EM, Granzow T (2009) Perspective on the development of lead-free piezoceramics. J Am Ceram Soc 92:1153–1177
Bai Y, Matousek A, Tofel P, Bijalwan V, Nan B, Hughes H, Button TW (2015) (Ba, Ca)(Zr, Ti)O3 lead-free piezoelectric ceramics-the critical role of processing on properties. J Eur Ceram Soc 35:3445–3456
Smolenskii GA, Isupov VA, Agranovskaya AI, Krainik NN (1961) New ferroelectrics of complex composition. Phys Solid State 2(11):2651–2654
Li YM, Chen W, Zhou J, Xu Q, Sun HJ, Liao MS (2005) Dielectric and ferroelectric properties of lead-free Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3–K0.5Bi0.5TiO3 ferroelectric ceramics. Ceram Int 31(1):139–142
Yang ZP, Hou YT, Pan H, Chang YF (2009) Structure, microstructure and electrical properties of (1 – x − y)Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3-xBi0.5K0.5TiO3-yBi0.5Li0.5TiO3 lead-free piezoelectric ceramics. J Alloys Compd 480:246–253
Herabut A, Safari AM (1997) Processing and electromechanical properties of (Bi0.5Na0.5)(1−1.5x)LaxTiO3 ceramics. J Am Ceram Soc 80:2954–2958
Zhou CR, Liu XY, Li WZ, Yuan CL, Chen GH (2010) Structure and electrical properties of Bi0.5(Na, K)0.5TiO3-BiGaO3 lead-free piezoelectric ceramics. Curr Appl Phys 10:93–98
Baettig P, Schelle CLF, LeSar RC, Waghmare UV, Spaldin NCA (2005) Theoretical prediction of new high-performance lead-free piezoelectrics. Chem Mater 17:1376–1380
Takenaka T, Maruyama KI, Sakata K (1991) (Bi1/2Na1/2)TiO3-BaTiO3 system for lead-free piezoelectric ceramics. Jpn J Appl Phys 30:2236–2239
Kounga AB, Zhang ST, Jo W, Granzow TT, Rödel JG (2008) Morphotropic phase boundary in lead-free piezoceramics. Appl Phys Lett 92:222902
Ji WJ, Chen YB, Zhang ST, Yang B, Zhao XN, Wang QJ (2012) Microstructure and electric properties of lead-free 0.8Bi1/2Na1/2TiO3-0.2Bi1/2K1/2TiO3 ceramics. Ceram Int 38:1683–1686
Gou Q, Wu JG, Li AG, Wu B, Xiao DG, Zhu JG (2012) Enhanced d33 value of Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3–(Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Ti0.90Zr0.10)O3 lead-free ceramics. J Alloys Comp 521:4–7
Pan H, Hou YT, Chao XL, Wei LL, Yang ZP (2011) Microstructure and electrical properties of La2O3-doped Bi0.5(Na0.68K0.22Li0.1)0.5TiO3 lead-free piezoelectric ceramics. Curr Appl Phys 11:888–892
Naderer MC, Schütz DN, Kainz TR, Reichmann K, Mittermayr FR (2012) The formation of secondary phases in Bi0.5Na0.375K0.125TiO3 ceramics. J Euro Ceram Soc 32:2399–2404
Bhupaijit P, Kornphom C, Vittayakorn N, Bongkarn T (2015) Structural, microstructure and electrical properties of La2O3-doped Bi0.5(Na0.68K0.22Li0.1)0.5TiO3 lead-free piezoelectric ceramics synthesized by the combustion technique. Ceram Int 41:81–86
Kornphom C, Vittayakorn N, Bongkarn T (2016) Low firing temperatures and high ferroelectric properties of (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Ti0.90Zr0.10)O3 lead-free ceramics synthesized by the combustion technique. Ferroelectric. doi:10.1080/00150193.2015.1070239
Kornphom C, Laowanidwatana A, Bongkarn T (2013) The effects of sintering temperature and content of x on phase formation, microstructure and dielectric properties of (1 − x)(Bi0.4871Na0.4871La0.0172TiO3)–x(BaZr0.05Ti0.95O3) ceramics prepared via the combustion technique. Ceram Int 39:421–426
Sumang R, Vittayakorn N, Bongkarn T (2013) Crystal structure, microstructure and electrical properties of (1 – x − y)Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3-xBi0.5K0.5TiO3–yBiFeO3 ceramics near MPB prepared via the combustion technique. Ceram Int 39:409–413
Julphunthong P, Bongkarn T (2014) Phase formation, microstructure and dielectric properties of Bi0.5(Na0.74K0.16Li0.10)0.5TiO3-Ba(Zr0.5Ti0.95)O3 ceramics prepared via combustion technique. Mater Res Innov 18(S2):151–156
Wattanawikkam C, Vittayakorn N, Bongkarn T (2013) Low temperature fabrication of lead-free KNN-LS-BS ceramics via the combustion method. Ceram Int 39:399–403
Razak K, Yip CJ, Sreekantan S (2011) Synthesis of (Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3 (BNT) and Pr doped BNT using the soft combustion technique and its properties. J Alloys Compd 509:2936–2941
Manoharan SS, Patil KC (1992) Combustion synthesis of metal chromite powders. J Am Ceram Soc 75:1012–1015
Kornphom C, Combustion technique synthesis and characterization of new BNKLLT-BCTZ-NKLNST system ceramics. PhD Dissertation. Naresuan University, Thailand (In progress)
Jo W, Schaab S, Sapper EA, Schmitt L, Kleebe HJ, Bell AJ, Rödel J (2011) On the phase identity and its thermal evolution of lead free (Bi1/2Na1/2)TiO3-6 mol%BaTiO3. J Appl Phys 110:074106
Dittmer R, Jo W, Daniels J, Schaab S, Rödel J (2011) Relaxor characteristics of morphotropic phase boundary (Bi1/2Na1/2)TiO3–(Bi1/2K1/2)TiO3 modified with Bi(Zn1/2Ti1/2)O3. J Am Ceram Soc 94:4283–4290
Tian HY, Wang DY, Lin DM, Zeng JT, Kwok KW, Chan HLW (2007) Diffusion phase transition and dielectric characteristics of Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3–Ba(Hf, Ti)O3 lead-free ceramics. Solid State Commun 142:10–14
Chen XY, Wu JG, Cheng XJ, Wu B, Wu WJ, Xiao DQ, Zhu JG (2012) Piezoelectric properties of [Li0.03(K0.48Na0.52)0.97](Nb0.97Sb0.03)O3-(Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Ti0.90Zr0.10)O3 lead-free piezoelectric ceramics. Curr Appl Phys 12:752–754
Xu Q, Chen M, Chen W, Liu HX, Kim BH, Ahn BK (2008) Effect of CoO additive on structure and electrical properties of (Na0.5Bi0.5)0.93Ba0.07TiO3 ceramics prepared by the citrate method. Acta Mater 56:642–650
Buessem WR, Cross LE, Goswami AK (1966) Phenomenological theory of high permittivity in fine-grained barium titanate. J Am Ceram Soc 49:33–36
Zhao XM, Chen XM, Wang J, Liang XX, Zhou JP, Liu P (2015) Effects of Ti nonstoichiometry on microstructure, dielectric, ferroelectric and piezoelectric properties of (Na0.5Bi0.5)0.94Ba0.06Ti1+xO3 lead-free ceramics. J Ceram Process Res 16:18–23
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Higher Education Research Promotion and National Research University project of Thailand, Office of the Higher Education Commission. The authors wish to thank the Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Naresuan University for the supporting facilities. Thanks are also due to Mr. Don Hindle for his help in editing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kornphom, C., Vittayakorn, N. & Bongkarn, T. Lead-free piezoelectric ceramics based on (1 − x)BNKLLT–xBCTZ binary solid solutions synthesized by the solid-state combustion technique. J Mater Sci 51, 4142–4149 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-9737-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-9737-6