Abstract
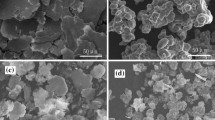
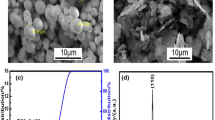
Oriented flake carbonyl iron/epoxy resin (FCI/EP) composites with enhanced microwave absorption properties were prepared by a magnetic field which was applied to make the plane of FCI parallel to each other. The morphology and the frequency-dependent electromagnetic and microwave absorption properties of the composites were investigated. The measurement results showed that the higher permeability and modest permittivity of the composites were obtained after orientation in the frequency range of 2–18 GHz. The calculated absorption properties indicated that the orientation plays an important role in decreasing the absorber thickness and broadening the absorption bandwidths. The oriented FCI/EP composites containing 75 wt% FCI show a wider absorption frequency range of 12.5 GHz from 5.5 to 18 GHz with reflection loss below −10 dB at thickness of 1.4 mm, while the bandwidth of the un-oriented one is only in a narrow frequency range of 1.4 GHz. This work offers a promising approach for the fabrication of magnetic absorbents for thin–thickness and microwave-absorbing materials with adjustable wider working frequencies range simply by magnetic field.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li G, Xie T, Yang S, Jin J, Jiang J (2012) Microwave absorption enhancement of porous carbon fibers compared with carbon nanofibers. J Phys Chem C 116:9196–9201
Bi S, Su X, Hou G, Liu C, Song W, Cao M (2013) Electrical conductivity and microwave absorption of shortened multi-walled carbon nanotube/alumina ceramic composites. Ceram Int 39:5979–5983
Kong L, Yin X, Yuan X, Zhang Y, Liu X, Cheng L, Zhang L (2014) Electromagnetic wave absorption properties of graphene modified with carbon nanotube/poly(dimethyl siloxane) composites. Carbon 73:185–193
Tong G, Wu W, Guan J, Qian H, Yuan J, Li W (2011) Synthesis and characterization of nanosized urchin-like α-Fe2O3 and Fe3O4: microwave electromagnetic and absorbing properties. J Alloys Compd 509:4320–4326
Wang A, Wang W, Long C, Li W, Guan J, Gu H, Xu G (2014) Facile preparation, formation mechanism and microwave absorption properties of porous carbonyl iron flakes. J Mater Chem C 2:3769–3776
Yu Y, Ma C, Yu K, Teng C, Tien H, Chang K, Kuo Y (2014) Preparation, morphological, and microwave absorbing properties of spongy iron powders/epoxy composites. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 45:674–680
Qing Y, Min D, Zhou Y, Luo F, Zhou W (2015) Graphene nanosheet and flake carbonyl iron particle-filled epoxy-silicone composites as thin-thickness and wide-bandwidth microwave absorber. Carbon 86:98–107
Park K, Han J, Lee S, Kim J, Yi J, Lee S (2009) Fabrication and electromagnetic characteristics of microwave absorbers containing carbon nanofibers and NiFe particles. Compos Sci Technol 69:1271–1278
Chen Y, Gao P, Zhu C, Wang R, Wang L, Cao M, Fang X (2009) Synthesis, magnetic and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of porous Fe3O4/Fe/SiO2 core/shell nanorods. J Appl Phys 106:0543031–0543034
He J, Wang W, Guan J (2012) Internal strain dependence of complex permeability of ball milled carbonyl iron powders in 2–18 GHz. J Appl Phys 111:0939241–0939245
Zhou Y, Zhou W, Qing Y, Luo F, Zhu D (2015) Temperature dependence of the electromagnetic properties and microwave absorption of carbonyl iron particles/silicone resin composites. J Magn Magn Mater 374:345–349
Zhu Z, Sun X, Xue H, Guo H, Fan X, Pan X, He J (2014) Graphene-carbonyl iron cross-linked composites with excellent electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J Mater Chem C 2:6582–6591
Xu Y, Zhang D, Cai J, Yuan L, Zhang W (2013) Microwave absorbing property of silicone rubber composites with added carbonyl iron particles and graphite platelet. J Magn Magn Mater 327:82–86
Wang B, Wei J, Yang Y, Wang T, Li F (2011) Investigation on peak frequency of the microwave absorption for carbonyl iron/epoxy resin composite. J Magn Magn Mater 323:1101–1103
Duan Y, Wu G, Gu S, Li S, Ma G (2012) Study on microwave absorbing properties of carbonyl-iron composite coating based on PVC and Al sheet. Appl Surf Sci 258:5746–5752
Liu L, Duan Y, Liu S, Chen L, Guo J (2009) Microwave absorption properties of one thin sheet employing carbonyl-iron powder and chlorinated polyethylene. J Magn Magn Mater 322:1736–1740
Chen L, Duan Y, Liu L, Guo J, Liu S (2011) Influence of SiO2 fillers on microwave absorption properties of carbonyl iron/carbon black double-layer coatings. Mater Des 32:570–574
Liu Y, Liu X, Wang X (2014) Double-layer microwave absorber based on CoFe2O4 ferrite and carbonyl iron composites. J Alloys Compd 584:249–253
Qiao M, Zhang C, Jia H (2012) Synthesis and absorbing mechanism of two-layer microwave absorbers containing flocs-like nano-BaZn1.5Co0.5Fe16O27 and carbonyl iron. Mater Chem Phys 135:604–609
Qing Y, Zhou W, Luo F, Zhu D (2011) Optimization of electromagnetic matching of carbonyl iron/BaTiO3 composites for microwave absorption. J Magn Magn Mater 323:600–606
Qing Y, Wen Q, Luo F, Zhou W, Zhu D (2016) Graphene nanosheets/BaTiO3 ceramics as highly efficient electromagnetic interference shielding materials in the X-band. J Mater Chem C 4:371–375
Qing Y, Wen Q, Luo F, Zhou W (2016) Temperature dependence of the electromagnetic properties of graphene nanosheet reinforced alumina ceramics in the X-band. J Mater Chem C 4:4853–4862
Han R, Yi H, Zuo W, Wang T, Qiao L, Li F (2012) Greatly enhanced permeability for planar anisotropy Ce2Fe17N3-δ compound with rotational orientation in various external magnetic fields. J Magn Magn Mater 324:2488–2491
Zhang Y, Wang P, Wang Y, Qiao L, Wang T, Li F (2015) Synthesis and excellent electromagnetic wave absorption properties of parallel aligned FeCo@C core-shell nanoflake composites. J Mater Chem C 3:10813–10818
Chen G, Wang H, Zhao W (2008) Fabrication of highly ordered polymer/graphite flake composite with eminent anisotropic electrical property. Polym Adv Technol 19:1113–1117
Shi D, He P, Lian J, Chaud X, Bud’ko S, Beaugnon E, Wang L, Ewing R, Tournier R (2005) Magnetic alignment of carbon nanofibers in polymer composites and anisotropy of mechanical properties. J Appl Phys 97:064312–0643125
Kimura T, Ago H, Tobita M, Ohshima S, Kyotani M, Yumura M (2002) Polymer composites of carbon nanotubes aligned by a magnetic field. Adv Mater 14:1380–1383
Cooper C, Ravich D, Lips D, Mayer J, Wagner H (2002) Distribution and alignment of carbon nanotubes and nanofibrils in a polymer matrix. Compos Sci Technol 62:1105–1112
Haggenmueller R, Gommans H, Rinzler A, Fischer J, Winey K (2000) Aligned single-wall carbon nanotubes in composites by melt processing methods. Chem Phys Lett 330:219–225
Lu J, Weng W, Chen X, Wu D, Wu C, Chen G (2005) Piezoresistive materials from directed shear-induced assembly of graphite nanosheets in polyethylene. Adv Funct Mater 15:1358–1363
Sfadi B, Andrews R, Grulke E (2002) Multiwalled carbon nanotube polymer composites: synthesis and characterization of thin films. J Appl Polym Sci 84:2660–2669
Breval E, Klimkiewicz M, Shi Y, Arakaki D, Dougherty J (2003) Magnetic alignment of particles in composite films. J Mater Sci 38:1347–1351. doi:10.1023/A:1022867400786
Kumar M, Jayanisha V, Manjari R, Prabu S, Padmanabhan K (2014) Self-assembly of carbon nanotubes using magnetic positioning and alignment by drop drying. Mater Lett 114:68–71
Yang W, Qiao L, Wei J, Zhang Z, Wang T, Li F (2010) Microwave permeability of flake-shaped FeCuNbSiB particle composite with rotational orientation. J Appl Phys 107:0339131–0339135
Li R, Wang T, Tan G, Zuo W, Wei J, Qiao L, Li F (2014) Microwave absorption properties of oriented Pr2Fe17N3-δ particles/paraffin composite with planar anisotropy. J Alloys Compd 586:239–243
Mu Y, Zhou W, Luo F, Zhu D, Qing Y, Huang Z (2014) Electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness of SiCf/SiC composites with PIP–SiC interphase after thermal oxidation in air. J Mater Sci 49:1527–1536. doi:10.1007/s10853-013-7834-3
Qing Y, Zhou W, Luo F, Zhu D (2010) Epoxy-silicone filled with multi-walled carbon nanotubes and carbonyl iron particles as a microwave absorber. Carbon 48:4074–4080
Varga Z, Filipcsei G, Zrı´nyi M (2005) Smart composites with controlled anisotropy. Polymer 46:7779–7787
Doyle W, Jacobs I (1990) EfFective cluster model of dielectric enhancement in metal-insulator composites. Phys Rev B 42:9319–9327
Song W, Cao M, Lu M, Liu J, Yuan J, Fan L (2013) Improved dielectric properties and highly efficient and broadened bandwidth electromagnetic attenuation of thickness-decreased carbon nanosheet/wax composites. J Mater Chem C 1:1846–1854
Qiao L, Han R, Wang T, Tang L, Li F (2015) Greatly enhanced microwave absorbing properties of planar anisotropy carbonyl-iron particle composites. J Magn Magn Mater 375:100–105
Kato T, Mikami H, Noguchi S (2010) Performance of Z-type hexagonal ferrite core under demagnetizing and external static fields. J Appl Phys 108:0339031–0339035
Pang H, Fan M, He Z (2012) A method for analyzing the microwave absorption properties of magnetic materials. J Magn Magn Mater 324:2492–2495
Song Z, Xie J, Zhou P, Wang X, Liu T, Deng L (2013) Toughened polymer composites with flake carbonyl iron powders and their electromagnetic/absorption properties. J Alloys Compd 551:677–681
Chen T, Deng F, Zhu J, Chen C, Sun G, Ma S, Yang X (2012) Hexagonal and cubic Ni nanocrystals grown on graphene: phase-controlled synthesis, characterization and their enhanced microwave absorption properties. J Mater Chem 22:15190–15197
Yan L, Wang J, Ye Y, Hao Z, Liu Q, Li F (2009) Broadband and thin microwave absorber of nickel-zinc ferrite/carbonyl iron composite. J Alloys Compd 487:708–711
Zou J, Liu Q, Zi Z, Dai J (2014) Enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties of planar anisotropy carbonyl-iron/Fe3O4 composites in gigahertz range. Mater Res Innov 18:304–309
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51402239), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No.3102014JCY01002), and the State Key Laboratory of Solidification Processing (NWPU), China (Grant No. KP201422).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Min, D., Zhou, W., Qing, Y. et al. Greatly enhanced microwave absorption properties of highly oriented flake carbonyl iron/epoxy resin composites under applied magnetic field. J Mater Sci 52, 2373–2383 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-0532-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-0532-1