Abstract
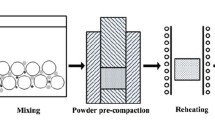
SiCp/2024 composites were fabricated by powder thixoforming, and the effects of pressure on the microstructure and mechanical properties were studied. The results indicate that the pressure applied during thixoforming affected the secondary solidification behavior by altering the solidification rate, microstructure compactness, plastic deformation, loading capacity of SiCp, and thus the fracture regimes and the mechanical properties. The tensile strengths increased as the pressure increased from 128 to 224 MPa because of the improved compactness, enhanced work hardening and loading capacity of SiCp, and increased concentration of the θ-phase and then decreased owing to the serious stress concentration and θ-phase harmfulness. The composite thixoformed under 224 MPa exhibited the largest improvements, with an ultimate tensile strength of 388 MPa, a 0.2 % offset yield strength (YS) of 297 MPa, and an elongation of 3.8 %, which were increased by 29.3 and 35 % and decreased by 63.5 %, respectively, compared with those of the 2024 alloy. The increment in the tensile strength was due to the synergetic contributions resulting from the strengthening mechanisms of load transfer, thermal mismatch, geometrically necessary dislocations, and grain refinement.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bathula S, Anandani RC, Dhar A, Srivastava AK (2012) Microstructural features and mechanical properties of Al 5083/SiCp metal matrix nanocomposites produced by high energy ball milling and spark plasma sintering. Mater Sci Eng, A 545:97–102. doi:10.1016/j.msea.2012.02.095
Torralba JM, Costa CED, Velasco F (2003) P/M aluminum matrix composites: an overview. J Mater Process Technol 133:203–206
Zhou J, Drużdżel AT, Duszczyk J (1999) The effect of extrusion parameters on the fretting wear resistance of Al-based composites produced via powder metallurgy. J Mater Sci 34:5089–5097. doi:10.1023/A:1004761116824
Zu LJ, Luo SJ (2001) Study on the powder mixing and semi-solid extrusion forming process of SiCp/2024Al composites. J Mater Process Technol 114:189–193. doi:10.1016/S0924-0136(01)00738-5
Chen CM, Yang CC, Chao CG (2004) Thixocasting of hypereutectic Al–25Si–2.5Cu–1 Mg–0.5Mn alloys using densified powder compacts. Mater Sci Eng, A 366:183–194. doi:10.1016/j.msea.2003.09.063
Fan Z (2002) Semisolid metal processing. Int Mater Rev 47:49–85
Li PB, Chen TJ, Zhang SQ, Guan RG (2015) Research on semisolid microstructural evolution of 2024 aluminum alloy prepared by powder thixoforming. Metals 5:547–564
Li PB, Chen TJ, Ma Y, Hao Y, Guan RG (2016) Microstructural evolution during partial remelting of a 2024 aluminum alloy prepared by cold pressing ball-milled alloy powders. Mater Trans 57:91–98. doi:10.2320/matertrans.M2015367
Li PB, Chen TJ, Zhan SQ, Wang YJ (2015) Effects of partial remelting on the microstructure evolution of SiCp/2024p aluminum composites prepared by alloy powder cold pressing. Spec Cast Nonferrous Alloys 35:260–264
Sukumaran K, Ravikumar KK, Pillai SGK, Rajan TPD, Ravi M, Pillai RM, Pai BC (2008) Studies on squeeze casting of Al 2124 alloy and 2124-10% SiCp metal matrix composite. Mater Sci Eng, A 490:235–241
Yong MS, Clegg AJ (2004) Process optimisation for a squeeze cast magnesium alloy. J Mater Process Technol 145:134–141
Kurnaz SC, Sevik H, Açıkgöz S, Özel A (2011) Influence of titanium and chromium addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of squeeze cast Mg–6Al alloy. J Alloys Compd 509:3190–3196
Beffort O, Long SY, Cayron C, Kuebler J, Buffat PA (2007) Alloying effects on microstructure and mechanical properties of high volume fraction SiC-particle reinforced Al-MMCs made by squeeze casting infiltration. Compos Sci Technol 67:737–745
Daoud A (2005) Microstructure and tensile properties of 2014 Al alloy reinforced with continuous carbon fibers manufactured by gas pressure infiltration. Mater Sci Eng, A 391:114–120. doi:10.1016/j.msea.2004.08.075
Manson-Whitton ED, Stone IC, Jones JR, Grant PS, Cantor B (2002) Isothermal grain coarsening of spray formed alloys in the semi-solid state. Acta Mater 50:2517–2535
Zoqui EJ, Shehata MT, Paes M, Kao V, Es-Sadiqi E (2002) Morphological evolution of SSM A356 during partial remelting. Mater Sci Eng, A 325:38–53
Chen TJ, Huang LK, Huang XF, Ma Y, Hao Y (2013) Effects of mould temperature and grain refiner amount on microstructure and tensile properties of thixoforged AZ63 magnesium alloy. J Alloys Compd 556:167–177
Martinez RA, Karma A, Flemings MC (2006) Spheroidal particle stability in semisolid processing. Metall Mater Trans A 37:2807–2815
Gallerneault M, Durrant G, Cantor B (1996) The squeeze casting of hypoeutectic binary Al-Cu. Metall Mater Trans A 27:4121–4132
Sekhar JA, Abbaschian GJ, Mehrabian R (1979) Effect of pressure on metal-die heat transfer coefficient during solidification. Mater Sci Eng 40:105–110. doi:10.1016/0025-5416(79)90014-4
Ghomashchi MR, Vikhrov A (2000) Squeeze casting: an overview. J Mater Process Technol 101:1–9
Chen TJ, Huang LK, Huang XF, Ma Y, Hao Y (2014) Effects of reheating temperature and time on microstructure and tensile properties of thixoforged AZ63 magnesium alloy. Mater Sci Technol 30:96–108
Williamson GK, Hall WH (1953) X-ray line broadening from filed aluminum and wolfram. Acta Metall 1:22–31
Smallman RE, Westmacott KH (1957) Stacking faults in face-centred cubic metals and alloys. Philos Mag 2:669–683
Cheng NP, Zeng SM, Liu ZY (2008) Preparation, microstructures and deformation behavior of SiCP/6066Al composites produced by PM route. J Mater Process Technol 202:27–40. doi:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.08.044
Arsenault RJ, Wang L, Feng CR (1991) Strengthening of composites due to microstructural changes in the matrix. Acta Metall Mater 39:47–57. doi:10.1016/0956-7151(91)90327-W
Hansen N (1977) The effect of grain size and strain on the tensile flow stress of aluminium at room temperature. Acta Metall 25:863–869. doi:10.1016/0001-6160(77)90171-7
Miller WS, Humphreys FJ (1991) Strengthening mechanisms in particulate metal matrix composites. Scr Metall Mater 25:33–38
Sekine H, Chen R (1995) A combined microstructure strengthening analysis of SiCp/Al metal matrix composites. Composites 26:183–188
Chen CP, Tsao CYA (1997) Semi-solid deformation of non-dendritic structures—I. Phenomenological behavior. Acta Mater 45:1955–1968. doi:10.1016/S1359-6454(96)00312-6
Nardone VC, Prewo KM (1986) On the strength of discontinuous silicon carbide reinforced aluminum composites. Scr Metall 20:43–48. doi:10.1016/0036-9748(86)90210-3
Wu Y, Lavernia EJ (1992) Strengthening behavior of particulate reinforced MMCs. Scr Metall Mater 27:173–178
Sekine H, Chen R (1995) A combined microstructure strengthening analysis of SiCp/Al metal matrix composites. Composites 26:183–188
Lee JC, Subramanian KN (1992) Failure behaviour of particulate-reinforced aluminium alloy composites under uniaxial tension. J Mater Sci 27:5453–5462. doi:10.1007/BF00541606
Li ZF, Dong J, Zeng XQ, Lu C, Ding WJ (2007) Influence of Mg17Al12 intermetallic compounds on the hot extruded microstructures and mechanical properties of Mg–9Al–1Zn alloy. Mater Sci Eng, A 466:134–139. doi:10.1016/j.msea.2007.02.029
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to express thanks for the financial support provided by the Basic Scientific Fund of Gansu University (Grant No. G2014-07), the Program for New Century Excellent Talents of the University of China (Grant No. NCET-10-0023), and the Program for Hongliu Outstanding Youth of the Lanzhou University of Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, P., Chen, T. & Qin, H. Effects of pressure on microstructure and mechanical properties of SiCp/2024 Al-based composites fabricated by powder thixoforming. J Mater Sci 52, 2045–2059 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-0493-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-0493-4