Abstract
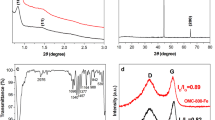
A sol–gel method has been utilized for synthesizing the wormhole-like mesoporous carbon (WMC), in which the gel skeleton can be regulated by using hydrofluoric acid and sulfuric acid. The electromagnetic characteristics of a series of WMCs with different surface areas embedded in paraffin at 15 wt% loading at 2–18 GHz were investigated. The electric conductivity of WMCs gradually increases with the decrease of surface area, leading to an increase in complex permittivity through dielectric loss. A minimum reflection loss (RL) value of −68.41 dB and a broader absorption band (reach 9.8 GHz) with RL values less than −10 dB are obtained, due to WMC’s well matching the characteristic impedance and dielectric loss, implying its great potential as a microwave absorbing material.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Qin F, Brosseau C (2012) A review and analysis of microwave absorption in polymer composites filled with carbonaceous particles. J Appl Phys 111:061301
Qing Y, Zhou W, Luo F, Zhu D (2009) Microwave-absorbing and mechanical properties of carbonyl-iron/epoxy-silicone resin coatings. J Magn Magn Mater 321:25
Wu H, Wu G, Wang L (2015) Peculiar porous α-Fe2O3, γ-Fe2O3 and Fe3O4 nanospheres: facile synthesis and electromagnetic properties. Powder Technol 269:443
Liu X, Or SW, Ho SL et al (2011) Electromagnetic wave absorption properties of mechanically mixed Nd2Fe14B/C microparticles. J Alloy Compd 509:2929
Ren Y, Yang L, Wang L, Xu T, Wu G, Wu H (2015) Facile synthesis, photoluminescence properties and microwave absorption enhancement of porous and hollow ZnO spheres. Powder Technol 281:20
Wu G, Cheng Y, Xie Q, Jia Z, Xiang F, Wu H (2015) Facile synthesis of urchin-like ZnO hollow spheres with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties. Mater Lett 144:157
Wu H, Wang L, Wang Y, Guo S, Shen Z (2012) Enhanced microwave absorbing properties of carbonyl iron-doped Ag/ordered mesoporous carbon nanocomposites. Mater Sci Eng B 177:476
Li G, Wang L, Li W, Xu Y (2015) Mesoporous Fe/C and Core-Shell Fe–Fe3C@C composites as efficient microwave absorbents. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 211:97
Wu H, Wang L, Wang Y, Guo S, Shen Z (2012) Enhanced microwave performance of highly ordered mesoporous carbon coated by Ni2O3 nanoparticles. J Alloy Compd 525:82
Wu H, Wu G, Ren Y, Yang L, Wang L, Li X (2015) Co2+/Co3+ ratio dependence of electromagnetic wave absorption in hierarchical NiCo2O4–CoNiO2 hybrids. J Mater Chem C 3:7677
Wu H, Wu Q, Wang L (2015) Design and wide range microwave absorption of porous Co–Co3O4 hybrid hollow sphere with magnetic multi-resonance mechanisms. Mater Charact 103:1
Wu Q, Wu G, Wang L, Hu W, Wu H (2015) Facile synthesis and optical properties of Prussian blue microcubes and hollow Fe2O3 microboxes. Mater Sci Semicond Process 30:476
Hu W, Wang L, Wu Q, Wu H (2014) Facile synthesis, magnetic and optical properties of double-shelled Co3O4 hollow microspheres. Adv Powder Technol 25:1780
Yonggang Xu, Zhang D, Cai J, Yuan L, Zhang W (2012) Effects of multi-walled carbon nanotubes on the electromagnetic absorbing characteristics of composites filled with carbonyl iron particles. J Mater Sci 28:34. doi:10.1016/S1005-0302(12)60020-6
Qing Y, Wang X, Zhou Y, Huang Z, Luo F, Zhou W (2014) Enhanced microwave absorption of multi-walled carbon nanotubes/epoxy composites incorporated with ceramic particles. Compos Sci Technol 102:161
Qing Y, Zhou W, Luo F, Zhu D (2010) Epoxy-silicone filled with multi-walled carbon nanotubes and carbonyl iron particles as a microwave absorber. Carbon 48:4074
Zhang Z, Zhang F, Jiang X, Liu Y, Guo Z, Leng J (2014) Electrospinning and microwave absorption of polyaniline/polyacrylonitrile/multiwalled carbon nanotubes nanocomposite fibers. Fiber Polym 15:2290
Zhang Z, Liu X, Zhang H, Li E (2015) Electromagnetic and microwave absorption properties of carbon fibers coated with carbonyl iron. J Mater Sci 26:6518. doi:10.1007/s10854-015-3247-1
Chu Z, Cheng H, Xie W, Sun L (2012) Effects of diameter and hollow structure on the microwave absorption properties of short carbon fibers. Ceram Int 38:4867
Qiang C, Xu J, Zhang Z et al (2010) Magnetic properties and microwave absorption properties of carbon fibers coated by Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J Alloy Compd 506:93
Wang L, Jia X, Li Y et al (2014) Synthesis and microwave absorption property of flexible magnetic film based on graphene oxide/carbon nanotubes and Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J Mater Chem A 2:14940
Song W-L, Cao M-S, Lu M-M et al (2014) Flexible graphene/polymer composite films in sandwich structures for effective electromagnetic interference shielding. Carbon 66:67
Xu J, Wu F, Wu H-T, Xue B, Li Y-X, Cao Y (2014) Three-dimensional ordered mesoporous carbon nitride with large mesopores: synthesis and application towards base catalysis. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 198:223
Jahel A, Darwiche A, Ghimbeu CM, Vix-Guterl C, Monconduit L (2014) High cycleability nano-GeO2/mesoporous carbon composite as enhanced energy storage anode material in Li-ion batteries. J Power Sour 269:755
Wang J, Senkovska I, Oschatz M et al (2013) Imine-linked polymer-derived nitrogen-doped microporous carbons with excellent CO2 capture properties. ACS Appl Mater Interface 5:3160
Saha D, Warren KE, Naskar AK (2014) Soft-templated mesoporous carbons as potential materials for oral drug delivery. Carbon 71:47
Fuertes AB, Lota G, Centeno TA, Frackowiak E (2005) Templated mesoporous carbons for supercapacitor application. Electrochim Acta 50:2799
Zhou H, Wang J, Zhuang J, Liu Q (2013) A covalent route for efficient surface modification of ordered mesoporous carbon as high performance microwave absorbers. Nanoscale 5:12502
Wu H, Wang L, Guo S, Shen Z (2012) Double-layer structural design of dielectric ordered mesoporous carbon/paraffin composites for microwave absorption. Appl Phys A 108:439
Wang Y, Wang L, Wu H (2013) Enhanced microwave absorption properties of α-Fe2O3-filled ordered mesoporous carbon nanorods. Materials 6:1520
Wang J, Zhou H, Zhuang J, Liu Q (2015) Magnetic γ-Fe2O3, Fe3O4, and Fe nanoparticles confined within ordered mesoporous carbons as efficient microwave absorbers. Phys Chem Chem Phys 17:3802
Wu D, Li Z, Liang Y, Yang X, Zeng X, Fu R (2009) Pore size control of worm hole like mesoporous carbons. Carbon 47:916
Kawashima D, Aihara T, Kobayashi Y, Kyotani T, Tomita A (2000) Preparation of mesoporous carbon from organic polymer/silica nanocomposite. Chem Mater 12:3397
Han BH, Zhou W, Sayari A (2003) Direct preparation of nanoporous carbon by nanocasting. J Am Chem Soc 125:3444
Du Y, Liu T, Yu B et al (2012) The electromagnetic properties and microwave absorption of mesoporous carbon. Mater Chem Phys 135:884
Chen Y, Lei Z, Wu H et al (2013) Electromagnetic absorption properties of graphene/Fe nanocomposites. Mater Res Bull 48:3362
Liu XG, Ou ZQ, Geng DY, Han Z, Xie ZG, Zhang ZD (2009) Enhanced natural resonance and attenuation properties in superparamagnetic graphite-coated FeNi3 nanocapsules. J Phys D 42:155004
Wu H, Wu G, Wu Q, Wang L (2014) Facile synthesis and microwave absorbability of C@Ni–NiO core–shell hybrid solid sphere and multi-shelled NiO hollow sphere. Mater Charact 97:18
Fu M, Jiao Q, Zhao Y (2013) Preparation of NiFe2O4 nanorod–graphene composites via an ionic liquid assisted one-step hydrothermal approach and their microwave absorbing properties. J Mater Chem A 1:5577
Wu G, Cheng Y, Ren Y, Wang Y, Wang Z, Wu H (2015) Synthesis and characterization of γ-Fe2O3@C nanorod–carbon sphere composite and its application as microwave absorbing material. J Alloy Compd 652:346
Wu H, Wang L, Wu H, Lian Q (2013) Synthesis and significantly enhanced microwave absorption properties of hematite dendrites/polyaniline nanocomposite. Appl Phys A 115:1299
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51276044 and 51302043), the Science and Technology Program of Guangdong Province of China (Grant Nos. 2016A020221031, 2015B010135011, and 2015A050502047), and the Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou City of China (Grant No. 201508030018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, H., Zhang, H., Chen, Y. et al. The electromagnetic property and microwave absorption of wormhole-like mesoporous carbons with different surface areas. J Mater Sci 51, 9723–9731 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-0206-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-0206-z