Abstract
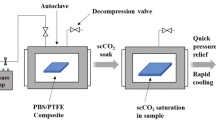
A cyclic olefin copolymer (COC) matrix was melt compounded with various amounts of fumed silica nanoparticles (1, 3 and 5 vol%) and the resulting materials were foamed through supercritical carbon dioxide. Foams were produced at four different foaming pressures (90, 110, 130, and 150 bar), keeping all other processing parameters constant. The main physical properties of both bulk and foamed samples were investigated in order to assess the role of both nanofiller content and foaming pressure. It was observed that the density values of the foamed materials decreased as the foaming pressure increased and that the presence of nanofillers leads to slightly denser materials. Both scanning and transmission electron microscopy evidenced the presence of filler aggregates on the bulk composites. These aggregates resulted to be elongated along the cell wall direction upon foaming. Dynamic mechanical thermal analysis, quasi-static tensile tests, and creep tests evidenced a positive effect played by nanosilica in improving the stiffness, the strength, and the creep stability of the polymer matrix for all foaming pressures. The application of a theoretical model for closed-cell foams highlighted how the stiffening effect provided by the nanosilica networking is mostly effective at elevated filler amounts and reduced foaming pressure values.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cooper AI (2003) Porous materials and supercritical fluids. Adv Mater 15:1049–1059
Bhattacharya S, Gupta RK, Jollands M, Bhattacharya SN (2009) Foaming behavior of high-melt strength polypropylene/clay nanocomposites. Polym Eng Sci 49:2070–2084
Deng L, Zhang J, Yu W and Zhao Y (2008) Foaming behavior of polystyrene with supercritical carbon dioxide. 11th European Meeting on Supercritical Fluids. Barcelona, Spain
Gendron R, Champagne MF, Tatibouet J, Bureau MN (2009) Foaming cyclo-olefin copolymers with carbon dioxide. Cell Polym 28:1–23
Han X, Koelling KW, Tomasko DL, Lee LJ (2002) Continuous microcellular polystyrene foam extrusion with supercritical CO2. Polym Eng Sci 42:2094–2106
Han X, Zeng C, Lee LJ, Koelling KW, Tomasko DL (2003) Extrusion of polystyrene nanocomposite foams with supercritical CO2. Polym Eng Sci 43:1261–1275
Jiang X-L, Bao J-B, Liu T, Zhao L, Xu Z-M and Yuan W-K (2009) Microcellular foaming of polypropylene/clay nanocomposites with supercritical carbon dioxide. J Cell Plast 45(6):515–538
Nam PH, Maiti P, Okamoto M et al (2002) Foam processing and cellular structure of polypropylene/clay nanocomposites. Polym Eng Sci 42:1907–1918
Otsuka T, Taki K, Ohshima M (2008) Nanocellular foams of PS/PMMA polymer blends. Macromol Mater Eng 293:78–82
Strauss W, D’Souza NA (2004) Supercritical CO2 processed polystyrene nanocomposite foams. J Cell Plast 40:229–241
Xu Z-M, Jiang X-L, Liu T et al (2007) Foaming of polypropylene with supercritical carbon dioxide. J Supercrit Fluids 41:299–310
Zosel K (1978) Praktische Anwendungen der Stofftrennung mit überkritischen Gasen. Angew Chem 90:748–755
Nalawade SP, Picchioni F, Janssen L (2006) Supercritical carbon dioxide as a green solvent for processing polymer melts: processing aspects and applications. Prog Polym Sci 31:19–43
Yeo S-D, Kiran E (2005) Formation of polymer particles with supercritical fluids: a review. J Supercrit Fluids 34:287–308
Arndt M, Beulich I (1998) C1-symmetric metallocenes for olefin polymerisation, 1. Catalytic performance of [Me2C (3-tertBuCp)(Flu)] ZrCl2 in ethene/norbornene copolymerisation. Macromol Chem Phys 199:1221–1232
Ou C-F, Hsu M-C (2007) Preparation and characterization of cyclo olefin copolymer (COC)/silica nanoparticle composites by solution blending. J Polym Res 14:373–378
Ou CF, Hsu MC (2007) Preparation and properties of cycloolefin copolymer/silica hybrids. J Appl Polym Sci 104:2542–2548
Forsyth JF, Scrivani T, Benavente R, Marestin C, Perena JM (2001) Thermal and dynamic mechanical behavior of ethylene/norbornene copolymers with medium norbornene contents. J Appl Polym Sci 82:2159–2165
Kolařík J, Pegoretti A, Fambri L, Penati A (2006) High-density polyethylene/cycloolefin copolymer blends, part 2: nonlinear tensile creep. Polym Eng Sci 46:1363–1373
Mandalia T, Bergaya F (2006) Organo clay mineral–melted polyolefin nanocomposites effect of surfactant/CEC ratio. J Phys Chem Solids 67:836–845
Ajayan PM, Schadler LS, Braun PV (2006) Nanocomposite science and technology. Wiley, Hoboken
Bondioli F, Dorigato A, Fabbri P, Messori M, Pegoretti A (2008) High-density polyethylene reinforced with submicron titania particles. Polym Eng Sci 48:448–457
Dorigato A, Pegoretti A (2012) Fracture behaviour of linear low density polyethylene–fumed silica nanocomposites. Eng Fract Mech 79:213–224
Dorigato A, Pegoretti A, Fambri L, Slouf M, Kolarik J (2011) Cycloolefin copolymer/fumed silica nanocomposites. J Appl Polym Sci 119:3393–3402
Jana SC, Jain S (2001) Dispersion of nanofillers in high performance polymers using reactive solvents as processing aids. Polymer 42:6897–6905
Dorigato A, Pegoretti A, Frache A (2012) Thermal stability of high density polyethylene–fumed silica nanocomposites. J Therm Anal Calorim 109:863–873
Chen L, Schadler LS, Ozisik R (2011) An experimental and theoretical investigation of the compressive properties of multi-walled carbon nanotube/poly (methyl methacrylate) nanocomposite foams. Polymer 52:2899–2909
Huang H-X, Wang J-K, Sun X-H (2008) Improving of cell structure of microcellular foams based on polypropylene/high-density polyethylene blends. J Cell Plast 44:69–85
Kozlowski M (2012) Lightweight plastic materials. INTECH Open Access Publisher, Rijeka
Li G, Wang J, Park C, Simha R (2007) Measurement of gas solubility in linear/branched PP melts. J Polym Sci Part B 45:2497–2508
Rachtanapun P, Selke S, Matuana L (2004) Effect of the high-density polyethylene melt index on the microcellular foaming of high-density polyethylene/polypropylene blends. J Appl Polym Sci 93:364–371
Su FH, Huang HX (2010) Rheology and melt strength of long chain branching polypropylene prepared by reactive extrusion with various peroxides. Polym Eng Sci 50:342–351
Tsivintzelis I, Angelopoulou AG, Panayiotou C (2007) Foaming of polymers with supercritical CO2: an experimental and theoretical study. Polymer 48:5928–5939
Corre Y-M, Maazouz A, Duchet J, Reignier J (2011) Batch foaming of chain extended PLA with supercritical CO2: influence of the rheological properties and the process parameters on the cellular structure. J Supercrit Fluids 58:177–188
Sun Y, Matsumoto M, Kitashima K, Haruki M, S-i Kihara, Takishima S (2014) Solubility and diffusion coefficient of supercritical-CO2 in polycarbonate and CO2 induced crystallization of polycarbonate. J Supercrit Fluids 95:35–43
D’Amato M, Dorigato A, Fambri L, Pegoretti A (2012) High performance polyethylene nanocomposite fibers. Express Polym Lett 6:954–964
S-s Hwang, Hsu PP (2013) Effects of silica particle size on the structure and properties of polypropylene/silica composites foams. J Ind Eng Chem 19:1377–1383
Pegoretti A, Dorigato A, Penati A (2007) Tensile mechanical response of polyethylene–clay nanocomposites. Express Polym Lett 1:123–131
Starkova O, Yang J, Zhang Z (2007) Application of time–stress superposition to nonlinear creep of polyamide 66 filled with nanoparticles of various sizes. Compos Sci Technol 67:2691–2698
Gibson LJ, Ashby MF (1997) Cellular solids: structure and properties. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Alvarez P, Mendizabal A, Petite M, Rodríguez-Pérez M, Echeverria A (2009) Finite element modelling of compressive mechanical behaviour of high and low density polymeric foams. Materialwiss Werkstofftech 40:126–132
De Vries D (2009) Characterization of polymeric foams. Eindhoven University of Technology, Eindhoven
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Mr. Marco Schintu for his support to the experimental work and Prof. Claudio Migliaresi, Director of the BIOtech center of Mattarello (Italy), for courtesy allowing the usage of the scCO2 plant. This research activity has been partly founded by the University of Trento through the strategic project 2014 “Mechanical and dynamical properties of disordered materials: from colloids to polymer nanocomposites.” The work at the Institute of Macromolecular Chemistry was supported by the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic within the National Sustainability Program I (NPU I), project POLYMAT LO1507.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pegoretti, A., Dorigato, A., Biani, A. et al. Cyclic olefin copolymer–silica nanocomposites foams. J Mater Sci 51, 3907–3916 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9710-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9710-9