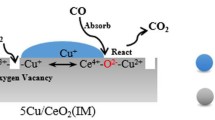
Abstract
A series of supported CuO/CeO2 catalysts with various CuO loadings (5–25 wt%) were prepared using a solvothermal method with ethylene glycol as solvent. The effects of CuO loading on physicochemical properties and catalytic activity of the prepared CuO/CeO2 catalysts have been investigated by X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, BET surface area measurement, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, temperature-programmed reduction with H2, temperature-programmed desorption of CO techniques, and low-temperature CO oxidation reaction test. The results indicate that the catalyst with 10 wt% CuO loading has the highest catalytic activity, which can be attributed to the largest amounts of well-dispersed CuO species strongly interacting with support CeO2 and oxygen vacancies caused by the incorporation of Cu2+ into CeO2 lattice, and the highest concentration of and the most active lattice oxygen. The activity for CO oxidation of the supported CuO/CeO2 catalyst prepared by the present solvothermal method was significantly higher than that of the counterparts prepared by the commonly used impregnation and deposition–precipitation methods.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kang M, Song MW, Lee CH (2003) Catalytic carbon monoxide oxidation over CoOx/CeO2 composite catalysts. Appl Catal A 251:143–156
Liotta LF, Macaluso A, Longo A et al (2003) Effects of redox treatments on the structural composition of a ceria–zirconia oxide for application in the three-way catalysis. Appl Catal A 240:295–307
Tang X, Zhang B, Li Y et al (2005) CuO/CeO2 catalysts: redox features and catalytic behaviors. Appl Catal A 288:116–125
Zimmer P, Tschöpe A, Birringer R (2002) Temperature-programmed reaction spectroscopy of ceria- and Cu/ceria-supported oxide catalyst. J Catal 205:339–345
Liu W, Flytzanistephanopoulos M (1995) Total oxidation of carbon monoxide and methane over transition metal fluorite oxide composite catalysts: I. Catalyst composition and activity. J Catal 153:304–316
Tschöpe A, Schaadt D, Birringer R et al (1997) Catalytic properties of nanostructured metal oxides synthesized by inert gas condensation. Nanostruct Mater 9:423–432
Qi L, Yu Q, Dai Y et al (2012) Influence of cerium precursors on the structure and reducibility of mesoporous CuO-CeO2 catalysts for CO oxidation. Appl Catal B 119–120:308–320
Jiang XY, Lu GL, Zhou RX et al (2001) Studies of pore structure, temperature-programmed reduction performance, and micro-structure of CuO/CeO2 catalysts. Appl Surf Sci 173:208–220
Luo MF, Zhong YJ, Yuan XX et al (1997) TPR and TPD studies of CuO/CeO2 catalysts for low temperature CO oxidation. Appl Catal A 162:121–131
Liu W, Flytzani-Stephanopoulos M (1996) Transition metal-promoted oxidation catalysis by fluorite oxides: a study of CO oxidation over Cu/CeO2. Chem Eng J 64:283–294
Sedmak G, Hočevar S, Levec J (2004) Transient kinetic model of CO oxidation over a nanostructured Cu0.1Ce0.9O2−y catalyst. J Catal 222:87–99
Jia AP, Hu GS, Meng L et al (2012) CO oxidation over CuO/Ce1−xCuxO2−δ and Ce1−xCuxO2−δ catalysts: synergetic effects and kinetic study. J Catal 289:199–209
Dow WP, Wang YP, Huang TJ (2000) TPR and XRD studies of yttria-doped ceria/γ-alumina-supported copper oxide catalyst. Appl Catal A 190:25–34
Avgouropoulos G, Ioannides T, Matralis H (2005) Influence of the preparation method on the performance of CuO–CeO2 catalysts for the selective oxidation of CO. Appl Catal B 56:87–93
Gamarra D, Munuera G, Hungría AB et al (2007) Structure − activity relationship in nanostructured copper − ceria-based preferential CO oxidation catalysts. J Phys Chem C 111:11026–11038
Sirichaiprasert K, Luengnaruemitchai A, Pongstabodee S (2007) Selective oxidation of CO over Cu–Ce–Fe–O composite oxide catalyst in hydrogen feed stream. Int J Hydrog Energy 32:915–926
Liu Z, Zhou R, Zheng X (2008) Influence of preparation methods on CuO-CeO2 catalysts in the preferential oxidation of CO in excess hydrogen. J Nat Gas Chem 17:125–129
Liu Z, Yang S, Zhou R et al (2010) Influence of pH values in the preparation of CuO-CeO2 on its catalytic performance for the preferential oxidation of CO in excess hydrogen. J Nat Gas Chem 19:313–317
Zheng XC, Wu SH, Wang SP et al (2005) The preparation and catalytic behavior of copper–cerium oxide catalysts for low-temperature carbon monoxide oxidation. Appl Catal A 283:217–223
Tang X, Zhang B, Li Y et al (2004) Carbon monoxide oxidation over CuO/CeO2 catalysts. Catal Today 93–95:191–198
Zhu J, Gao Q, Chen Z (2008) Preparation of mesoporous copper cerium bimetal oxides with high performance for catalytic oxidation of carbon monoxide. Appl Catal B 81:236–243
Luo MF, Song YP, Lu JQ et al (2007) Identification of CuO species in high surface area CuO − CeO2 catalysts and their catalytic activities for CO oxidation. J Phys Chem C 111:12686–12692
Kydd R, Teoh WY, Wong K et al (2009) Flame-synthesized ceria-supported copper dimers for preferential oxidation of CO. Adv Funct Mater 19:369–377
Pimentel A, Rodrigues J, Duarte P et al (2015) Effect of solvents on ZnO nanostructures synthesized by solvothermal method assisted by microwave radiation: a photocatalytic study. J Mater Sci 50:5777–5787. doi:10.1007/s10853-015-9125-7
Zeng SH, Liu KW, Chen TJ et al (2013) Influence of crystallite size and interface on the catalytic performance over the CeO2/CuO catalysts. Int J Hydrog Energy 38:14542–14549
Mrabet D, Abassi A, Cherizol R et al (2012) One-pot solvothermal synthesis of mixed Cu-Ce-Ox nanocatalysts and their catalytic activity for low temperature CO oxidation. Appl Catal A 447–448:60–66
Cao JL, Wang Y, Zhang TY et al (2008) Preparation, characterization and catalytic behavior of nanostructured mesoporous CuO/Ce0.8Zr0.2O2 catalysts for low-temperature CO oxidation. Appl Catal B 78:120–128
Fernández-García M, Martínez-Arias A, Iglesias-Juez A et al (2000) Structural characteristics and redox behavior of CeO2-ZrO2/Al2O3 supports. J Catal 194:385–392
Gnanakumar ES, Naik JM, Manikandan M et al (2014) Role of nanointerfaces in Cu- and Cu + Au- based near-ambient-temperature CO oxidation catalysts. ChemCatChem 6:3116–3124
Li J, Zhu P, Zuo S et al (2010) Influence of Mn doping on the performance of CuO-CeO2 catalysts for selective oxidation of CO in hydrogen-rich streams. Appl Catal A 381:261–266
Zou H, Chen S, Liu Z et al (2011) Selective CO oxidation over CuO-CeO2 catalysts doped with transition metal oxides. Powder Technol 207:238–244
Reddy LH, Reddy GK, Devaiah D et al (2012) A rapid microwave-assisted solution combustion synthesis of CuO promoted CeO2-MxOy (M = Zr, La, Pr and Sm) catalysts for CO oxidation. Appl Catal A 445–446:297–305
Cai W, Chen F, Shen X et al (2010) Enhanced catalytic degradation of AO7 in the CeO2–H2O2 system with Fe3+ doping. Appl Catal B 101:160–168
Cao JL, Shao GS, Ma TY et al (2009) Hierarchical meso–macroporous titania-supported CuO nanocatalysts: preparation, characterization and catalytic CO oxidation. J Mater Sci 44:6717–6726. doi:10.1007/s10853-009-3583-8
Kundakovic L, Flytzani-Stephanopoulos M (1998) Reduction characteristics of copper oxide in cerium and zirconium oxide systems. Appl Catal A 171:13–29
Zhu H, Shen M, Kong Y et al (2004) Characterization of copper oxide supported on ceria-modified anatase. J Mol Catal A 219:155–164
Avgouropoulos G, Ioannides T (2006) Effect of synthesis parameters on catalytic properties of CuO-CeO2. Appl Catal B 67:1–11
Wang SP, Zheng XC, Wang XY et al (2005) Comparison of CuO/Ce0.8Zr0.2O2 and CuO/CeO2 catalysts for low-temperature CO oxidation. Catal Lett 105:163–168
He C, Yu Y, Yue L et al (2014) Low-temperature removal of toluene and propanal over highly active mesoporous CuCeOx catalysts synthesized via a simple self-precipitation protocol. Appl Catal B 147:156–166
Sun SS, Mao DS, Yu J et al (2015) Low-temperature CO oxidation on CuO/CeO2 catalysts: the significant effect of copper precursor and calcination temperature. Catal Sci Technol 5:3166–3181
Yen H, Seo Y, Kaliaguine S et al (2012) Tailored mesostructured copper/ceria catalysts with enhanced performance for preferential oxidation of CO at low temperature. Angew Chem Int Ed 51:12032–12035
Zou H, Dong X, Lin W (2006) Selective CO oxidation in hydrogen-rich gas over CuO/CeO2 catalysts. Appl Surf Sci 253:2893–2898
Moretti E, Storaro L, Talon A et al (2011) Effect of thermal treatments on the catalytic behaviour in the CO preferential oxidation of a CuO–CeO2–ZrO2 catalyst with a flower-like morphology. Appl Catal B 102:627–637
Caputo T, Lisi L, Pirone R et al (2008) On the role of redox properties of CuO/CeO2 catalysts in the preferential oxidation of CO in H2-rich gases. Appl Catal A 348:42–53
Martínez-Arias A, Fernández-García M, Gálvez O et al (2000) Comparative study on redox properties and catalytic behavior for CO oxidation of CuO/CeO2 and CuO/ZrCeO4 catalysts. J Catal 195:207–216
Liu W, Flytzanistephanopoulos M (1995) Total oxidation of carbon monoxide and methane over transition metal fluorite oxide composite catalysts: II. Catalyst characterization and reaction kinetics. J Catal 153:317–332
Cao JL, Deng QF, Yuan ZY (2009) Mesoporous Ce0.8Zr0.2O2 solid solutions-supported CuO nanocatalysts for CO oxidation: a comparative study of preparation methods. J Mater Sci 44:6663–6669. doi:10.1007/s10853-009-3582-9
Fu GY, Mao DS, Sun SS et al (2015) Preparation, characterization and CO oxidation activity of Cu-Ce-Zr mixed oxide catalysts via facile dry oxalate-precursor synthesis. J Ind Eng Chem 31:283–290
Liu Y, Wen C, Guo Y et al (2010) Modulated CO oxidation activity of M-doped ceria (M = Cu, Ti, Zr, and Tb): role of the pauling electronegativity of M. J Phys Chem C 114:9889–9897
Li J, Han Y, Zhu Y et al (2011) Purification of hydrogen from carbon monoxide for fuel cell application over modified mesoporous CuO–CeO2 catalysts. Appl Catal B 108–109:72–80
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21273150) and the ‘‘ShuGuang’’ Project (10GG23) of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission and Shanghai Education Development Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, YL., Mao, DS., Sun, SS. et al. Solvothermal synthesis in ethylene glycol and catalytic activity for CO oxidation of CuO/CeO2 catalysts. J Mater Sci 51, 917–925 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9420-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9420-3