Abstract
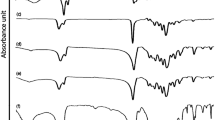
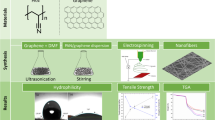
This study aims to develop a strategy to promote the mechanical properties of nanofiller/polymer composite nanofibers, i.e., nanofillers was modified with hyperbranched polyglycerol (PG) by ring-opening polymerization of glycidol. The accomplishment of grafting of PG on ND nanofiller surface was confirmed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and thermo gravimetric analysis (TGA). FITR and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) results revealed the enhanced filler–PVA interactions following PG functionalization. The improved dispersivity of PG-functionalized NDs (ND-PGs) in water and PVA matrix was verified by sedimentation tests and TEM, respectively. The grafting of PG on ND surface increased the tensile strength up to 60 %, Young’s modulus up to 51 %, and toughness up to 59 %, for 3 wt% ND/PVA composite nanofiber membranes. Therefore, the enhanced mechanical performance of ND-PG/PVA nanocomposites can be attributed to the enriched hydroxyl groups of PG which improved the dispersion of nanofillers within composite matrix and strengthened filler–matrix interactions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ramakrishna S, Fujihara K, Teo WE, Yong T, Ma Z, Ramaseshan R (2006) Electrospun nanofibers: solving global issues. Mater Today 9:40–50
Schulz S, Angarano M, Fabritius M, Mulhaupt R, Dard M, Obrecht M, Tomakidi P, Steinberg T (2014) Nonwoven-based gelatin/polycaprolactone membrane proves suitability in a preclinical assessment for treatment of soft tissue defects. Tissue Eng Part A 20:1935–1947
Croisier F, Atanasova G, Poumay Y, Jerome C (2014) Polysaccharide-coated PCL nanofibers for wound dressing applications. Adv Health Mater 3:2032–2039
Fan Z, Liu B, Wang J, Zhang S, Lin Q, Gong P, Ma L, Yang S (2014) A novel wound dressing based on Ag/graphene polymer hydrogel: effectively kill bacteria and accelerate wound healing. Adv Funct Mater 24:3933–3943
Xu J, Cai N, Xu W, Xue Y, Wang Z, Dai Q, Yu F (2013) Mechanical enhancement of nanofibrous scaffolds through polyelectrolyte complexation. Nanotechnology 24:025701
Lee SJ, Oh SH, Liu J, Soker S, Atala A, Yoo JJ (2008) The use of thermal treatments to enhance the mechanical properties of electrospun poly(epsilon-caprolactone) scaffolds. Biomaterials 29:1422–1430
Lu W, Ma M, Xu H, Zhang B, Cao X, Guo Y (2015) Gelatin nanofibers prepared by spiral-electrospinning and cross-linked by vapor and liquid-phase glutaraldehyde. Mater Lett 140:1–4
Hu JM, Jia X, Li CH, Ma ZY, Zhang GX, Sheng WB, Zhang XL, Wei Z (2014) Effect of interfacial interaction between graphene oxide derivatives and poly(vinyl chloride) upon the mechanical properties of their nanocomposites. J Mater Sci 49:2943–2951. doi:10.1007/s10853-013-8006-1
Shang SM, Gan L, Yuen CWM, Jiang SX, Luo NM (2015) The synthesis of graphene nanoribbon and its reinforcing effect on poly(vinyl alcohol). Compos Part A 68:149–154
Cai N, Dai Q, Wang Z, Luo X, Xue Y, Yu F (2015) Toughening of electrospun poly(l-lactic acid) nanofiber scaffolds with unidirectionally aligned halloysite nanotubes. J Mater Sci 50:1435–1445. doi:10.1007/s10856-005-4428-x
Schadler L, Giannaris S, Ajayan P (1998) Load transfer in carbon nanotube epoxy composites. Appl Phys Lett 73:3842–3844
Song P, Cao Z, Cai Y, Zhao L, Fang Z, Fu S (2011) Fabrication of exfoliated graphene-based polypropylene nanocomposites with enhanced mechanical and thermal properties. Polymer 52:4001–4010
Ma WS, Li J, Zhao XS (2013) Improving the thermal and mechanical properties of silicone polymer by incorporating functionalized graphene oxide. J Mater Sci 48:5287–5294. doi:10.1007/s10853-013-7320-y
Zhao L, Chano T, Morikawa S, Saito Y, Shiino A, Shimizu S, Maeda T, Irie T, Aonuma S, Okabe H (2012) Hyperbranched polyglycerol-grafted superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, functionalization, size separation, magnetic properties, and biological applications. Adv Funct Mater 22:5107–5117
Zhao L, Takimoto T, Ito M, Kitagawa N, Kimura T, Komatsu N (2011) Chromatographic separation of highly soluble diamond nanoparticles prepared by polyglycerol grafting. Angew Chem Int Ed 50:1388–1392
Potts JR, Dreyer DR, Bielawski CW, Ruoff RS (2011) Graphene-based polymer nanocomposites. Polymer 52:5–25
Krueger A, Lang D (2012) Functionality is key: recent progress in the surface modification of nanodiamond. Adv Funct Mater 22:890–906
Cai N, Hou D, Shen L, Luo X, Xue Y, Yu F (2015) Functionalization of graphene with hyperbranched polyglycerol for stable aqueous dispersion. Funct Mater Lett 8:1550068
Cai N, Dai Q, Wang Z, Luo X, Xue Y, Yu F (2015) Preparation and properties of nanodiamond/poly(lactic acid) composite nanofiber scaffolds. Fiber Polym 15:2544–2552
Salaam AD, Mishra M, Nyairo E, Dean D (2014) Electrospun polyvinyl alcohol/nanodiamond composite scaffolds: morphological, structural, and biological analysis. J Biomater Tissue Eng 4:173–180
Wang Z, Cai N, Zhao DP, Xu J, Dai Q, Xue Y, Luo X, Yang Y, Yu F (2013) Mechanical reinforcement of electrospun water-soluble polymer nanofibers using nanodiamonds. Polym Compos 34:1735–1744
Greiner A, Wendorff JH (2007) Electrospinning: a fascinating method for the preparation of ultrathin fibres. Angew Chem Int Ed 46:5670–5703
Skipa T, Lellinger D, Böhm W, Saphiannikova M, Alig I (2010) Influence of shear deformation on carbon nanotube networks in polycarbonate melts: interplay between build-up and destruction of agglomerates. Polymer 51:201–210
Qi RL, Guo R, Shen MW, Cao XY, Zhang LQ, Xu JJ, Yu JY, Shi XY (2010) Electrospun poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)/halloysite nanotube composite nanofibers for drug encapsulation and sustained release. J Mater Chem 20:10622–10629
Zong X, Kim K, Fang D, Ran S, Hsiao BS, Chu B (2002) Structure and process relationship of electrospun bioabsorbable nanofiber membranes. Polymer 43:4403–4412
Zhou C, Shi Q, Guo W, Terrell L, Qureshi AT, Hayes DJ, Wu Q (2013) Electrospun bio-nanocomposite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering by cellulose nanocrystals reinforcing maleic anhydride grafted PLA. ACS Appl Mater Interface 5:3847–3854
Zhao YQ, Lau KT, Kim JK, Xu CL, Zhao DD, Li HL (2010) Nanodiamond/poly(lactic acid) nanocomposites: effect of nanodiamond on structure and properties of poly(lactic acid). Compos Part B Eng 41:646–653
Zhou C, Chu R, Wu R, Wu Q (2011) Electrospun polyethylene oxide/cellulose nanocrystal composite nanofibrous mats with homogeneous and heterogeneous microstructures. Biomacromolecules 12:2617–2625
Chuangchote S, Sirivat A, Supaphol P (2007) Mechanical and electro-rheological properties of electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibre mats filled with carbon black nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 18:145705
Liang J, Huang Y, Zhang L, Wang Y, Ma Y, Guo T, Chen Y (2009) Molecular-level dispersion of graphene into poly(vinyl alcohol) and effective reinforcement of their nanocomposites. Adv Funct Mater 19:2297–2302
Ding W, Wei S, Zhu J, Chen X, Rutman D, Guo Z (2010) Manipulated electrospun PVA nanofibers with inexpensive salts. Macromol Mater Eng 295:958–965
Morimune S, Kotera M, Nishino T, Goto K, Hata K (2011) Poly(vinyl alcohol) nanocomposites with nanodiamond. Macromolecules 44:4415–4421
Cerezo FT, Preston CML, Shanks RA (2007) Morphology, thermal stability, and mechanical behavior of [poly(propylene)-grafted maleic anhydride]-layered expanded graphite oxide composites. Macromol Mater Eng 292:155–168
Liu L, Barber AH, Nuriel S, Wagner HD (2005) Mechanical properties of functionalized single-walled carbon-nanotube/poly(vinyl alcohol) nanocomposites. Adv Funct Mater 15:975–980
Zhang Q, Mochalin VN, Neitzel I, Knoke IY, Han J, Klug CA, Zhou JG, Lelkes PI, Gogotsi Y (2011) Fluorescent PLLA-nanodiamond composites for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 32:87–94
Alhuthali A, Low IM (2013) Water absorption, mechanical, and thermal properties of halloysite nanotube reinforced vinyl-ester nanocomposites. J Mater Sci 48:4260–4273. doi:10.1007/s10853-013-7240-x
Fu SY, Feng XQ, Lauke B, Mai YW (2008) Effects of particle size, particle/matrix interface adhesion and particle loading on mechanical properties of particulate-polymer composites. Compos Part B Eng 39:933–961
Otsuka H, Nagasaki Y, Kataoka K (2012) PEGylated nanoparticles for biological and pharmaceutical applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 64:246–255
Bao C, Guo Y, Song L, Hu Y (2011) Poly(vinyl alcohol) nanocomposites based on graphene and graphite oxide: a comparative investigation of property and mechanism. J Mater Chem 21:13942–13950
Jaggi HS, Kumar Y, Satapathy BK, Ray AR, Patnaik A (2012) Analytical interpretations of structural and mechanical response of high density polyethylene/hydroxyapatite bio-composites. Mater Design 36:757–766
Sahoo NG, Rana S, Cho JW, Li L, Chan SH (2010) Polymer nanocomposites based on functionalized carbon nanotubes. Prog Polym Sci 35:837–867
Zhou L, Gao C, Xu W, Wang X, Xu Y (2009) Enhanced biocompatibility and biostability of CdTe quantum dots by facile surface-initiated dendritic polymerization. Biomacromolecules 10:1865–1874
Nafchi AM, Nassiri R, Sheibani S, Ariffin F, Karim A (2013) Preparation and characterization of bionanocomposite films filled with nanorod-rich zinc oxide. Carbohydr Polym 96:233–239
Ayatollahi MR, Alishahi E, Doagou-R S, Shadlou S (2012) Tribological and mechanical properties of low content nanodiamond/epoxy nanocomposites. Compos Part B Eng 43:3425–3430
Qi Y, Tai Z, Sun D, Chen J, Ma H, Yan X, Liu B, Xue Q (2013) Fabrication and characterization of poly(vinyl alcohol)/graphene oxide nanofibrous biocomposite scaffolds. J Appl Polym Sci 127:1885–1894
Naebe M, Lin T, Tian W, Dai L, Wang X (2007) Effects of MWNT nanofillers on structures and properties of PVA electrospun nanofibres. Nanotechnology 18:225605
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21571147, 21206143), Innovative Team Incubation Program in High-Tech Industry of Wuhan City (2014070504020244), Innovative Team Program of the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (2014CFA011), Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (2015CFB430), Open Fund of Key Laboratory for Green Chemical Process of Ministry of Education (GCP201405), and Graduate Innovative Fund of Wuhan Institute of Technology (CX2014009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, N., Li, C., Luo, X. et al. A strategy for improving mechanical properties of composite nanofibers through surface functionalization of fillers with hyperbranched polyglycerol. J Mater Sci 51, 797–808 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9403-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9403-4