Abstract
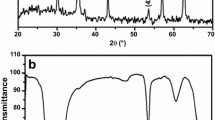
In this study, one-dimensional amino-functionalized magnetic Fe3O4 nanochains (MNCs) consisting of self-assembled Fe3O4 nanoparticles (NPs) were synthesized via a facile one-pot solvothermal route at 180 °C using FeCl3·6H2O as the iron source and ethylenediamine as the surfactant without the use of any external magnetic fields or templates. The synthesized MNCs consist of nanospheres with a diameter of 120 nm assembled from Fe3O4 NPs and have good water dispersibility with a high Brunauer–Emmett–Teller surface area (44.028 m2 g−1). The magnetic measurements revealed the superparamagnetic nature of the as-prepared MNCs with a saturation magnetization of 70.9 emu g−1 at room temperature. The nanochain formation mechanism was proposed as a magnetic dipole–dipole interaction and caused by the effects of the ethylenediamine surfactants. These MNCs were confirmed to be efficient adsorbents for chromium(VI) removal. The adsorption isotherm conformed to the Langmuir model at a Cr(VI) ion concentration higher than 40 mg L−1, and the maximum removal capacity was 60.25 mg g−1 at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:1000 g/mL.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yi DK, Lee SS, Ying JY (2006) Synthesis and applications of magnetic nanocomposite catalysts. Chem Mater 18:2459–2461
Frey NA, Peng S, Cheng K, Sun S (2009) Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, functionalization, and applications in bioimaging and magnetic energy storage. Chem Soc Rev 38:2532–2542
Gao J, Gu H, Xu B (2009) Multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles: design, synthesis, and biomedical applications. Acc Chem Res 42:1097–1107
Shen H, Chen J, Dai H, Wang L, Hu M, Xia Q (2013) New insights into the sorption and detoxification of chromium(VI) by tetraethylenepentamine functionalized nanosized magnetic polymer adsorbents: mechanism and pH effect. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:12723–12732
Gao MR, Zhang SR, Jiang J, Zheng YR, Tao DQ, Yu SH (2011) One-pot synthesis of hierarchical magnetite nanochain assemblies with complex building units and their application for water treatment. J Mater Chem 21:16888–16892
Zhu J, Wei S, Chen M, Gu H, Rapole SB, Pallavkar S, Ho TC, Hopper J, Guo Z (2013) Magnetic nanocomposites for environmental remediation. Adv Powder Technol 24:459–467
Zhang F, Shi Y, Zhao Z, Ma B, Wei L, Lu L (2014) Amino-functionalized Fe3O4/SiO2 magnetic submicron composites and In3+ ion adsorption properties. J Mater Sci 49:3478–3483. doi:10.1007/s10853-014-8060-3
Kołodyn´ska D, Kowalczyk M, Hubicki Z (2014) Evaluation of iron-based hybrid materials for heavy metal ions removal. J Mater Sci 49:2483–2495. doi:10.1007/s10853-013-7944-y
He Q, Yuan T, Zhu J, Luo Z, Haldolaarachchige N, Sun L, Khasanov A, Li Y, Young DP, Wei S, Guo Z (2012) Magnetic high density polyethylene nanocomposites reinforced with in situ synthesized Fe@FeO core-shell nanoparticles. Polymer 53:3642–3652
Dui J, Zhu G, Zhou S (2013) Facile and economical synthesis of large hollow ferrites and their applications in adsorption for As(V) and Cr(VI). ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:10081–10089
Cui S, Shen X, Lin B (2006) Surface organic modification of Fe3 O4 nanoparticles by silane-coupling agents. Rare Met 25:426–430
Liu HL, Ko SP, Wu JH, Jung MH, Min JH, Lee JH, An BH, Kim YK (2007) One-pot polyol synthesis of monosize PVP-coated sub-5 nm Fe3O4 nanoparticles for biomedical applications. J Magn Magn Mater 310:e815–e817
Takami S, Sato T, Mousavand T, Ohara S, Umetsu M, Adschiri T (2007) Hydrothermal synthesis of surface-modified iron oxide nanoparticles. Mater Lett 61:4769–4772
Liu ZL, Liu YJ, Yao KL, Ding ZH, Tao J, Wang X (2002) Synthesis and magnetic properties of Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J Mater Synth Process 10:83–87
Sun S, Zeng H, Robinson DB, Raoux S, Rice PM, Wang SX, Li G (2004) Monodisperse MFe2O4 (M) = Fe Co, Mn) Nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 126:273–279
Gan N, Jia L, Zheng L (2011) A novel sandwich electrochemical immunosensor based on the DNA-derived magnetic nanochain probes for alpha-fetoprotein. J Autom Methods Manag Chem 2011:957805
Zhou SM, Zhang XT, Gong HC, Zhang B, Wu ZS, Du ZL, Wu SX (2008) Magnetic enhancement of pure gamma Fe2O3 nanochains by chemical vapor deposition. J Phys 20:075217
Laurent S, Forge D, Port M, Roch A, Robic C, Elst LV, Muller RN (2008) Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, stabilization, vectorization, physicochemical characterizations, and biological applications. Chem Rev 108:2064–2110
Wei S, Wang Q, Zhu J, Sun L, Lin H, Guo Z (2011) Multifunctional composite core-shell nanoparticles. Nanoscale 3:4474–4502
Liu Y, Chen Q (2008) Synthesis of magnetosome chain-like structures. Nanotechnology 19:475603
Korth BD, Keng P, Shim I, Bowles SE, Tang C, Kowalewski T, Nebesny KW, Pyun J (2006) Polymer-coated ferromagnetic colloids from well-defined macromolecular surfactants and assembly into nanoparticle chains. J Am Chem Soc 128:6562–6563
He Q, Yuan T, Yan X, Luo Z, Haldolaarachchige N, Young DP, Wei S, Guo Z (2014) One-pot synthesis of size- and morphology-controlled 1-D iron oxide nanochains with manipulated magnetic properties. Chem Commun 50:201–203
He Q, Yuan T, Wei S, Haldolaarachchige N, Luo Z, Young DP, Khasanov A, Guo Z (2012) Morphology-andphase-controlled iron oxide nanoparticles stabilized with maleic anhydride grafted polypropylene. Angew Chem 51:8842–8845
Jia B, Gao L (2008) Morphological transformation of Fe3O4 spherical aggregates from solid to hollow and their self-assembly under an external magnetic field. J Phys Chem C 112:666–671
Wang H, Chen QW, Sun XL, Qi HP, Yang X, Zhou S, Xiong J (2009) Magnetic-field-induced formation of one-dimensional magnetite nanochains. Langmuir 25:7135–7139
Ma M, Zhang Q, Dou J, Zhang H, Yin D, Geng W, Zhou Y (2012) Fabrication of one-dimensional Fe3O4/P(GMA–DVB) nanochains by magnetic-field-induced precipitation polymerization. J Colloid Interface Sci 374:339–344
Zhang Y, Sun L, Fu Y, Huang ZC, Bai XJ, Zhai Y, Du J, Zhai HR (2009) The shape anisotropy in the magnetic field-assisted self-assembly chain-like structure of magnetite. J Phys Chem C 113:8152–8157
Kim Y, Choi YS, Lee HJ, Yoon H, Kim YK, Oh M (2014) Self-assembly of fluorescent and magnetic Fe3O4@coordination polymer nanochains. Chem Commun 50:7617–7620
Yu SH, Yoshimura M (2002) Ferrite/metal composites fabricated by soft solution processing. Adv Funct Mater 12:10–15
Zhang J, Wan J, Huang S, Du J, Zhu J, Zhang D, Yin Q, Wu Y (2010) Solvothermal synthesis and magnetic property of magnetic chains self-assembled by Fe3O4 microoctahedrons. Chin J Chem 28:1607–1612
Bhaumik M, Maity A, Srinivasu VV, Onyango MS (2012) Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution using polypyrrole-polyaniline nanofibers. Chem Eng J 181–182:323–333
Gu H, Rapole SB, Huang Y, Cao D, Luo Z, Wei S, Guo Z (2013) Synergistic interactions between multi-walled carbon nanotubes and toxic hexavalent chromium. J Mater Chem A 1:2011–2021
Kulkarni PS, Kalyani V, Mahajani VV (2007) Removal of hexavalent chromium by membrane-based hybrid processes. Ind Eng Chem Res 46:8176–8182
Wang J, Zhao L, Duan W, Han L, Chen Y (2012) Adsorption of aqueous Cr(VI) by novel fibrous adsorbent with amino and quaternary ammonium groups. Ind Eng Chem Res 51:13655–13662
Hu JS, Zhong LS, Song WG, Wan LJ (2008) Synthesis of hierarchically structured metal oxides and their application in heavy metal ion removal. Adv Mater 20:2977–2982
Zhao YG, Shen HY, Pan SD, Hu MQ, Xia QH (2010) Preparation and characterization of amino-functionalized nano-Fe3O4 magnetic polymer adsorbents for removal of chromium(VI) ions. J Mater Sci 45:5291–5301. doi:10.1007/s10853-010-4574-5
Ni H, Xiong Z, Ye T, Zhang Z, Ma X, Li L (2012) Biosorption of copper (II) from aqueous solutions using volcanic rock matrix-immobilized Pseudomonas putida cells with surface-displayed cyanobacterial metallothioneins. Chem Eng J 204–206:264–271
Zheng JG, Zhang Y, Zhai Y, Yang HW (2010) TEM and EBSD study of Fe3O4 particle chains grown and assembled in external magnetic field. Microsc Microanal 16:1790–1791
Descostes M, Mercier F, Thromat N, Beaucaire C, Gautier-Soyer M (2000) Use of XPS in the determination of chemical environment and oxidation state of iron and sulfur samples: constitution of a data basis in binding energies for Fe and S reference compounds and applications to the evidence of surface species of an oxidized pyrite in a carbonate medium. Appl Surf Sci 165:288–302
Rondinone AJ, Samia ACS, Zhang ZJ (1999) Superparamagnetic relaxation and magnetic anisotropy energy distribution in CoFe2O4 spinel ferrite nanocrystallites. J Phys Chem B 103:6876–6880
Yuan H, Wang Y, Zhou S, Lou S (2011) Fabrication of superparamagnetic Fe3O4 hollow microspheres with a high saturation magnetization. Chem Eng J 175:555–560
Yi Tan, Zhuang Z, Peng Q, Li Y (2008) Room-temperature soft magnetic iron oxide nanocrystals: synthesis, characterization, and size-dependent magnetic properties. Chem Mater 20:5029–5034
Wang L, Bao J, Wang L, Zhang F, Li Y (2006) One-pot synthesis and bioapplication of amine-functionalized magnetite nanoparticles and hollow nanospheres. Chem Eur J 12:6341–6347
Liu Y, Wang Y, Zhou S, Lou S, Yuan L, Gao T, Wu X, Shi X, Wang K (2012) Synthesis of high saturation magnetization superparamagnetic Fe3O4 hollow microspheres for swift chromium removal. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:4913–4920
Willard MA, Kurihara LK, Carpenter EE, Calvin S, Harris VG (2004) Chemically prepared magnetic nanoparticles. Int Mater Rev 49:125–170
Yan K, Li H, Li P, Zhu H, Shen J, Yi C, Wu S, Yeung KW, Xu Z, Xu H, Chu PK (2014) Self-assembled magnetic fluorescent polymeric micelles for magnetic resonance and optical imaging. Biomaterials 35:344–355
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledged support from a grant from the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program, No. 2012AA063508-06), the Education Department of Hubei Province of China (No. D20120101), and the Wuhan Science and Technology Bureau of China (No. 201160723217).
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflict of interest in this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ni, H., Sun, X., Li, Y. et al. Solvothermal self-assembly of magnetic Fe3O4 nanochains by ethylenediamine functionalized nanoparticles for chromium(VI) removal. J Mater Sci 50, 4270–4279 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-8979-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-8979-z