Abstract
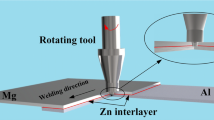
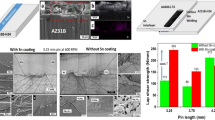
2.4-mm-thick AZ31 Mg alloy sheets were friction stir spot welded without and with the addition of Zn interlayers ranging from 0.04 to 0.16 mm in thickness. For the joints without Zn interlayers, although the loads of the joints could be increased by changing the end surface geometry and size of the shoulders, the small bonded area and hook defects limited further increase of joint loads. For the joints with Zn interlayers, the Zn interlayer reacted with the Mg substrate, forming a Mg–Zn brazed zone composed of complex Mg–Zn intermetallics and a thin strip of (α-Mg + MgZn) eutectoid structure, thereby increasing the bonded area and reducing the hook defects of joints at the same time. As a result, the maximum joint load increased from 2.7 to 5.2 kN using a 10-mm-diameter concave shoulder with a 0.12-mm-thick Zn interlayer. A thicker interlayer resulted in a significant increase in the thickness of the thin strip in the hook region, and a thinner interlayer led to the formation of more defects due to intense diffusion reactions, thereby reducing the joint loads.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lathabai S, Painter MJ, Cantin GMD, Tyagi VK (2006) Friction spot joining of an extruded Al-Mg-Si alloy. Scripta Mater 55:899
Gerlich A, Su P, North TH (2005) Tool penetration during friction stir spot welding of Al and Mg alloys. J Mater Sci 40:6473. doi:10.1007/s10853-005-1568-9
Bilici MK, Yukler AI, Kurtulmus M (2011) The optimization of welding parameters for friction stir spot welding of high density polyethylene sheets. Mater Des 32:4074
Rodrigues DM, Loureiro A, Leitao C (2009) Influence of friction stir welding parameters on the microstructural and mechanical properties of AA6016-T4 thin welds. Mater Des 30:1913
Patel VK, Bhole SD, Chen DL (2011) Influence of ultrasonic spot welding on microstructure in a magnesium alloy. Scripta Mater 65:911
Gerlich A, Su P, North TH (2005) Friction stir spot welding of Mg-alloys for automotive. In: Neelameggham NR, Kaplan HI, Powell BR (eds) Magnesium technology. TMS, Warrendale, pp 383–388
Rao HM, Jordon JB, Barkey ME, Guo YB, Su XM, Badarinarayan H (2013) Influence of structural integrity on fatigue behavior of friction stir spot welded AZ31 Mg alloy. Mater Sci Eng A 564:369
Yin YH, Sun N, North TH, Hu SS (2010) Hook formation and mechanical properties in AZ31 friction stir spot welds. J Mater Process Technol 210:2062
Su P, Gerlich A, North TH, Bendzsak GJ (2006) Material flow during friction stir spot welding. Sci Technol Weld Join 11:61
Gerlich A, Su P, Yamamoto M, North TH (2008) Material flow and intermixing during dissimilar friction stir welding. Sci Technol Weld Join 13:254
Su P, Gerlich A, North TH, Bendzsak GJ (2007) Intermixing in dissimilar friction stir spot welds. Metall Mater Trans A 38:584
Yuan W, Mishra RS, Carlson B, Verma R, Mishra RK (2012) Material flow and micro structural evolution during friction stir spot welding of AZ31 magnesium alloy. Mater Sci Eng A 543:200
Yin YH, Sun N, North TH, Hu SS (2010) Microstructures and mechanical properties in dissimilar AZ91/AZ31 spot welds. Mater Charact 61:1018
Yin YH, Sun N, North TH, Hu SS (2010) Influence of tool design on mechanical properties of AZ31 friction stir spot welds. Sci Technol Weld Join 15:81
Horie S, Shinozaki K, Yamamoto M, Kadoi K, Nakanshin H, North TH (2010) Effects of tool geometry and process conditions on material flow and strength of friction stir spot welded joints. Transact JWRI 39:28
Zhang YN, Cao X, Larose S, Wanjara P (2012) Review of tools for friction stir welding and processing. Can Metall Q 51:250
Ni YQ (2012) Study on the bonding-friction stir spot hybrid welding procedure of AZ31 Mg alloy. Dalian Jiaotong University, Dalian
Shen J, Min D, Wang D (2011) Effects of heating process on the microstructures and tensile properties of friction stir spot welded AZ31 magnesium alloy plates. Mater Des 32:5033
Dhanapal A, Boopathy SR, Balasubramanian V (2011) Developing an empirical relationship to predict the corrosion rate of friction stir welded AZ61 magnesium alloy under salt fog environment. Mater Des 32:5066
Wang DA, Lee SC (2007) Microstructures and failure mechanisms of friction stir spot welds of aluminum 6061-T6 sheets. J Mater Process Technol 186:291
Lathabai S, Painter MJ, Cantin GMD, Tyagi VK (2006) Friction spot joining of anextruded Al-Mg-Si alloy. Scripta Mater 55:899
Bozzil S, Etter AL, Baudin T, Klosek V, Kerbiguet JG, Criqui B (2010) Influence of FSSW parameters on fracture mechanisms of 5182 aluminium welds. J Mater Process Technol 210:1429
Liu LM, Wu ZH (2010) Microstructure and interfacial reactions of soldering magnesium alloy AZ31B. Mater Charact 61:13
Ma L, Long WM, Qiao PX, He DY, Li XY (2013) Development of a binary Zn-based solder alloy for joining wrought magnesium alloy AZ31B. J Mater Eng Perform 22:118
Wu H, Song G (2010) Microstructure and properties of brazing joints of magnesium alloy AZ31B. Mater Res Innov 14:160
Clark JB, Zabdyr L, Moser Z (1998) In: Nayebhashemi AA, Clark JB (eds) Phase diagrams of binary magnesium alloys. ASM International, Metals Park p353
Ni JF (2012) Precipitation and hardening in magnesium alloys metal. Metall Mater Trans A 43:3891
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National R&D Program of China under Grant No. 2011BAE22B05, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 51371179 and 51331008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, R.Z., Ni, D.R., Yang, Q. et al. Influence of Zn interlayer addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir welded AZ31 Mg alloy. J Mater Sci 50, 4160–4173 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-8841-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-8841-3