Abstract
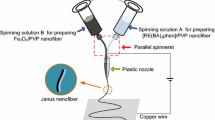
A novel nanostructure of [CoFe2O4/PVP]//[YAG:7 % Tb3+/PVP] magnetic-luminescent bifunctional Janus nanofibers has been successfully fabricated via electrospinning technology using a homemade parallel spinneret. Electrospun YAG:7 % Tb3+ luminescent nanofibers and CoFe2O4 magnetic nanofibers were respectively incorporated into polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP) matrix and electrospun into Janus nanofibers with CoFe2O4 magnetic nanofibers/PVP as one strand nanofiber and YAG:7 % Tb3+ luminescent nanofibers/PVP as another strand nanofiber. [CoFe2O4/PVP]//[YAG:7 % Tb3+/PVP] magnetic-luminescent bifunctional Janus nanofibers possess superior magnetic and luminescent properties due to their peculiar nanostructure, and the luminescent characteristics and saturation magnetizations of the Janus nanofibers can be tuned by adding various amounts of YAG:7 % Tb3+ luminescent nanofibers and CoFe2O4 magnetic nanofibers. Compared with CoFe2O4/YAG:7 % Tb3+/PVP composite nanofibers, the magnetic-luminescent bifunctional Janus nanofibers provide higher performances due to isolating YAG:7 %Tb3+ luminescent nanofibers from CoFe2O4 magnetic nanofibers. Formation mechanism of [CoFe2O4/PVP]//[YAG:7 % Tb3+/PVP] Janus nanofibers is also presented. The design conception and construction technology are of universal significance to fabricate other bifunctional Janus nanofibers.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang HG, Sun L, Li YP, Fei XL, Sun MD, Zhang CQ, Li YX, Yang QB (2011) Layer-by-Layer assembled Fe3O4@C@CdTe core/shell microspheresas separable luminescent probe for sensitive sensing of cu2+ ions. Langmuir 27:11609–11615
Zhu MY, Diao GW (2011) Synthesis of porous Fe3O4 nanospheres and its application for the catalytic degradation of xylenol orange. J Phys Cnem C 115:18923–18934
Sun P, Zhang HY, Liu C, Fang J, Wang M, Chen J, Zhang JP, Mao CB, Xu SK (2010) Preparation and characterization of Fe3O4/CdTe magnetic/fluorescent nanocomposites and their applications in immuno-labeling and fluorescent imaging of cancer cells. Langmuir 26:1278–1284
Lu P, Zhang JL, Liu YL, Sun DH, Liu GX, Hong GY, Ni JZ (2010) Synthesis and characteristic of the Fe3O4@SiO2@Eu(DBM)3·2H2O/SiO2 luminomagnetic microspheres with core-shell structure. Talanta 83:450–457
Daisuke N, Mikio Y, Noriko Y, Hideki M, Yoshio K, Mikio K (2008) Synthesis of highly monodisperse particles composed of a magnetic core and fluorescent shell. Langmuir 24:9804–9808
Wang W, Zou M, Chen KZ (2010) Novel Fe3O4@YPO4:Re (Re = Tb, Eu) multifunctional magnetic-fluorescent hybrid spheres for biomedical applications. Chem Commun 46:5100–5102
Feng J, Song SY, Deng RP, Fan WQ, Zhang HJ (2010) Novel multifunctional nanocomposites: magnetic mesoporous silica nanospheres covalently bonded with near-infrared luminescent lanthanide complexes. Langmuir 26:3596–3600
Chen HY, Daniel CC, Qi B, Thomas M, He J, Thompson Mefford O, Frank A, John CC, Jeffrey NA (2012) Magnetic and optical properties of multifunctional core-shell radioluminescence nanoparticles. J Mater Chem 22:12802–12809
Guo K, Huang ML, Chen HL, Yang XX, Zhao JT (2012) Comparative study on photoluminescence of amorphous and nano-crystalline YAG:Tb phosphors prepared by a combustion method. J Non-Cryst Solids 358:88–92
Mukherjee S, Sudarsan V, Vatsa RK, Tyagi AK (2009) Luminescence studies on lanthanide ions (Eu3+, Dy3+ and Tb3+) doped YAG: ce nano-phosphors. J Lumin 129:69–72
Wang WW, Yao JL (2009) Hydrothermal synthesis of SnO2/Fe3O4 nanocomposites and their magnetic property. J Phys Chem C 113:3070–3075
Zhu YF, Fang Y, Stefan K (2010) Folate-conjugated Fe3O4@SiO2 hollow mesoporous spheres for targeted anticancer drug delivery. J Phys Chem C 114:16382–16388
Wang L, Yu Y, Chen PC, Zhang DW, Chen CH (2008) Electrospinning synthesis of C/Fe3O4 composite nanofibers and their application for high performance lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 183:717–723
Zhang ZY, Shao CL, Sun YY, Mu JB, Zhang MY, Zhang P, Guo ZC, Liang PP, Wang CH, Liu YC (2012) Tubular nanocomposite catalysts based on size-controlled and highly dispersed silver nanoparticles assembled on electrospun silica nanotubes for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. J Mater Chem 22:1387–1395
Lu X, Wang C, Wei Y (2009) One-Dimensional composite nanomaterials: synthesis by electrospinning and their applications. Small 5:2349–2370
Song C, Dong XT (2012) Preparation and characterization of tricomponent SiO2/SnO2/TiO2 composite nanofibers by electrospinning. Optoelectron Adv Mater RC 6:225–229
Ma QL, Wang JX, Dong XT, Yu WS, Liu GX, Xu J (2012) Electrospinning preparation and properties of Fe3O4/Eu(BA)3phen/PVP magnetic-photoluminescent bifunctional composite nanofibers. Nanopart. Res. 14:1203–1209
Ma QL, Wang JX, Dong XT, Yu WS, Liu GX, Xu J (2012) Electrospinning preparation and properties of magnetic-photoluminescent bifunctional coaxial nanofibers. J Mater Chem 22:14438–14442
Ma QL, Wang JX, Dong XT, Yu WS, Liu GX, Xu J (2013) Electrospinning fabrication and properties of Fe3O4/Eu(BA)3phen/PMMA magnetic-photoluminescent bifunctional composite nanoribbons. Opt Mater 35:526–530
Lv N, Ma QL, Dong XT, Wang JX, Yu WS, Liu GX (2014) Parallel spinnerets electrospinning fabrication of novel flexible luminescent-electrical-magnetic trifunctional bistrand-aligned nanobundles. Chem Eng J 243:500–508
Ma QL, Yu WS, Dong XT, Wang JX, Liu GX (2014) Janus Nanobelts: fabrication. Structure and enhanced magnetic-fluorescent bifunctional performance, nanoscale 6:2945–2952
Lv N, Ma QL, Dong XT, Wang JX, Yu WS, Yu WS, Liu GX (2014) Flexible Janus nanofiber: facile electrospinning construct, structure and enhanced luminescent-electrical-magnetic trifunction. ChemPlusChem. doi:10.1002/cplu.201300404
Ma QL, Wang JX, Dong XT, Yu WS, Liu GX (2014) Fabrication of magnetic-fluorescent bifunctional flexible coaxial nanobelts by electrospinning using a modified coaxial spinneret. ChemPlusChem 79:290–297
Sheng SJ, Ma QL, Dong XT, Nan L, Wang JX, Yu WS, Liu GX (2014) Photoluminescence-electricity-magnetism trifunction simultaneously assembled into one flexible nanofiber. J Mater Sci:Mater Electron 25:1309–1316
Ma QL, Wang JX, Dong XT, Yu WS, Liu GX (2013) Electrospinning fabrication of high-performance magnetic@photoluminescent bifunctional coaxial nanocables. Chem Eng J 222:16–22
Nisisako T, Torii T, Takahashi T, Takizawa Y (2006) Synthesis of monodisperse bicolored janus particles with electrical anisotropy using a microfluidic co-flow system. Adv Mater 18:1152–1156
Kyung-Ho R, David CM, Joerg L (2005) Biphasic Janus particles with nanoscale anisotropy. Nat Mater 4:759–763
Isaac S, Xin Y, Emily JC, Nicholas MM, Gerald TM, Olga K, Anna CB (2013) Harnessing fluid-driven vesicles to pick up and drop off janus particles. ACS Nano 7:1224–1238
Liu ZY, Sun DD, Guo P, Leckie JO (2007) An efficient bicomponent TiO2/SnO2 nanofiber photocatalyst fabricated by electrospinning with a side-by-side dual spinneret method. Nano lett 7:1081–1085
Justin DS, Jennifer SA (2013) Janus-type bi-phasic functional nanofibers. Chem Commun 49:4151–4153
Naveen KR, Ljiljana P, Linda S, Johan B, Jan F, Christian C (2013) Metallic and bi-metallic Janus nanofibers: electrical and self-propulsion properties. J Mater Chem C 1:3646–3650
Naveen KR, Christian C (2014) Self-propelling micro-disks. Korea Aust Rheol J 26:73–79
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC 50972020, 51072026), Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (20102216110002, 20112216120003), the Science and Technology Development Planning Project of Jilin Province (Grant Nos. 20130101001JC, 20070402), the Science and Technology Research Project of the Education Department of Jilin Province during the eleventh five-year plan period (Under Grant No. 2010JYT01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bi, F., Dong, X., Wang, J. et al. Flexible Janus nanofiber to acquire tuned and enhanced simultaneous magnetism-luminescence bifunctionality. J Mater Sci 49, 7244–7252 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8431-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8431-9