Abstract
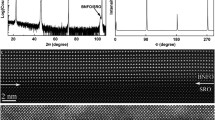
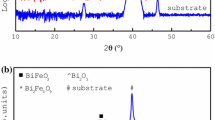
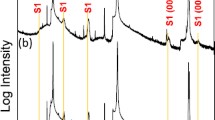
We report the observation of nano-scale precipitates corresponding to a new structure not displayed by the phase diagram of bismuth iron oxide. BiFeO3 (BFO) thin films grown on terbium scandate and strontium titanate substrates by pulsed laser deposition were investigated using high-resolution transmission and scanning transmission electron microscopy. Precipitate-like structures with a so far unknown metastable phase of bismuth, iron, and oxygen were observed in these films. They consist of well-ordered Bi2O2 layers, as they are known from bismuth oxide layered compounds. They have a pseudo-orthorhombic structure with a single perovskite-like unit (FeO6) sandwiched between Bi2O2 layers, similar to the Aurivillius phase Bi2WO6, with a chemical composition of the precipitates of Bi2FeO6−x . The structure of the new phase with its lattice constants was elucidated and the band gap of the precipitates was determined by electron energy loss spectroscopy. The results point to promising future applications for this new phase in the field of electronics, if it might be grown phase pure as an epitaxial thin film.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang J, Neaton JB, Zheng H, Nagarajan V, Ogale SB, Liu B, Viehland D, Vaithyanathan V, Schlom DG, Waghmare UV, Spaldin NA, Rabe KM, Wuttig M, Ramesh R (2003) Epitaxial BiFeO3 multiferroic thin film heterostructures. Science 299:1719–1722
Catalan G, Scott JF (2009) Physics and applications of bismuth ferrite. Adv Mater 21:2463–2485
Kubel F, Schmid H (1990) Structure of a ferroelectric and ferroelastic monodomain crystal of the perovskite BiFeO3. Acta Cryst B 46:698–702
Lebeugle D, Colson D, Forget A, Viret M (2007) Very large spontaneous electric polarization in BiFeO3 single crystals at room temperature and its evolution under cycling fields. Appl Phys Lett 91:022907
Zhang JX, He Q, Trassin M, Luo W, Yi D, Rossell MD, Yu P, You L, Wang CH, Kuo CY, Heron JT, Hu Z, Zeches RJ, Lin HJ, Tanaka A, Chen CT, Tjeng LH, Chu YH, Ramesh R (2011) Microscopic origin of the giant ferroelectric polarization in tetragonal-like BiFeO3. Phys Rev Lett 107:147602
Streiffer SK, Parker CB, Romanov AE, Lefevre MJ, Zhao L, Speck JS, Pompe W, Foster CM, Bai GR (1998) Domain patterns in epitaxial rhombohedral ferroelectric films. I. Geometry and experiments. J Appl Phys 83:2742–2753
Wang X, Zhu YL, Mi SB, Wang C, Lu HB, Ma XL (2010) Morphology and orientation of iron oxide precipitates in epitaxial BiFeO3 thin films grown under two non-optimized oxygen pressures. Phil Mag 34:4551–4567
Murakami M, Fujino S, Lim SH, Salamanca-Riba LG, Wuttig M, Takeuchi I, Varughese B, Sugaya H, Hasegawa T, Lofland SE (2006) Microstructure and phase control in Bi–Fe–O multiferroic nanocomposite thin films. Appl Phys Lett 88:112505
Arredondo M, Ramesse QM, Bogle K, Nagarajan V (2010) Chemistry of the Fe2O3/BiFeO3 interface in BiFeO3 thin film structures. Materials 3:5274–5282
Bea H, Bibes M, Barthelemy A, Bouzehouane K, Jacquet E, Khodan A, Contour JP, Fusil S, Wyczisk F, Forget A, Lebeugle D, Colson D, Viret M (2005) Influence of parasitic phases on the properties of BiFeO3 epitaxial thin films. Appl Phys Lett 87:072508
Johann F, Morelli A, Biggemann D, Arredondo M, Vrejoiu I (2011) Epitaxial strain and electric boundary condition effects on the structural and ferroelectric properties of BiFeO3 films. Phys Rev B 84:094105
Rossell MD, Erni R, Prange MP, Idrobo JC, Luo W, Zeches RJ, Pantelides ST, Ramesh R (2012) Atomic structure of highly strained BiFeO3 thin films. Phys Rev Lett 108:047601
Liu H, Yang P, Yao K, Ong KP, Wu P, Wang J (2012) Origin of a tetragonal BiFeO3 phase with a giant c/a ratio on SrTiO3 substrates. Adv Funct Mater 22:937–942
Chen Z, Luo Z, Qi Y, Yang P, Wu S, Huang C, Wu T, Wang J, Gao C, Sritharan T, Chen L (2010) Low symmetry monoclinic MC phase in epitaxial BiFeO3 thin films on LaSrAlO4 substrates. Appl Phys Lett 97:242903
Kim YH, Bhatnagar A, Pippel E, Alexe M, Hesse D (2014) Microstructure of highly strained BiFeO3 thin films: transmission electron microscopy and electron-energy loss spectroscopy studies. J Appl Phys 115:043526
Marti X, Ferrer P, Herrero-Albillos J, Narvaez J, Holy V, Barrett N, Alexe M, Catalan G (2011) Skin layer of BiFeO3 single crystals. Phys Rev Lett 106:236101
Berger A, Hesse D, Hähnel A, Arredondo M, Alexe M (2012) Regular nanodomain vertex arrays in BiFeO3 single crystals. Phys Rev B 85:064104
Nelson CT, Winchester B, Zhang Y, Kim SJ, Melville A, Adamo C, Folkman CM, Baek SH, Eom CB, Schlom DG, Chan LQ, Pan X (2011) Spontaneous vortex nanodomain arrays at ferroelectric heterointerfaces. Nano Lett 11:828–834
Wolfe RW, Newnahm RE, Kay MI (1969) Crystal structure of Bi2WO6. Solid State Commun 7:1797–1801
Ketterer J, Kraemer V (1986) Crystal structure of bismuth silicate Bi2SiO5. N Jb Miner Mh 1:13–18
Pirovano C, Islam MS, Vannier RN, Nowogrocki G, Mairesse G (2001) Modeling the crystal structure of Aurivillius phases. Solid State Ionics 140:115–123
Gujar TP, Shinde VR, Lokhande CD (2007) Nanocrystalline and highly resistive bismuth ferric oxide thin films by a simple chemical method. Mater Chem Phys 103:142–146
Ihlefeld JF, Podraza NJ, Liu ZK, Rai RC, Xu X, Heeg T, Chen YB, Li J, Collins RW, Musfeldt JL, Pan XQ, Schubert J, Ramesh R, Schlom DG (2008) Optical band gap of BiFeO3 grown by molecular-beam epitaxy. Appl Phys Lett 92:142908
Sæterli R, Selbach SM, Ravindran P, Grande T, Holmestad R (2010) Electronic structure of multiferroic BiFeO3 and related compounds: electron energy loss spectroscopy and density functional study. Phys Rev B 82:064102
Park TJ, Sambasivan S, Fischer DA, Yoon WS, Misewich JA, Wong SS (2008) Electronic structure and chemistry of iron-based metal oxide nanostructured materials: a NEXAFS investigation of BiFeO3, Bi2Fe4O9, α-Fe2O3, γ-Fe2O3, and Fe/Fe3O4. J Phys Chem C 112:10359–10369
Colliex C, Manoubi T, Ortiz C (1991) Electron-energy-loss-spectroscopy near-edge fine structures in the iron–oxygen system. Phys Rev B 44:11402–11411
de Groot FMF, Grioni M, Fuggle JC, Ghijsen J, Sawatzky GA, Petersen H (1989) Oxygen 1s X-ray absorption edges of transition-metal oxides. Phys Rev B 40:5715–5723
Wu ZY, Gota S, Jollet F, Pollak M, Gautier-Soyer M, Natoli CR (1997) Characterization of iron oxides by X-ray absorption at the oxygen K edge using a full multiple-scattering approach. Phys Rev B 55:2570–2577
Nguyen SD, Yeon J, Kim SH, Halasyamani PS (2011) BiO(IO3): a new polar iodate that exhibits an Aurivillius-type (Bi2O2)2+ layer and a large SHG response. J Am Chem Soc 133:12422–12425
Chen A, Zhou H, Bi Z, Zhu Y, Luo Z, Bayraktaroglu A, Phillips J, Choi EM, MacManus-Driscoll JL, Pennycook SJ, Narayan J, Jia Q, Zhang X, Wang H (2013) A new class of room-temperature multiferroic thin films with Bismuth-based supercell structure. Adv Mater 25:1028–1032
Noguchi Y, Murata K, Miyayama M (2006) Defect control for polarization switching in Bi2WO6-based single crystals. Appl Phys Lett 89:242916
Shang M, Wang W, Sun S, Zhou L, Zhang L (2008) Bi2WO6 nanocrystals with high photocatalytic activities under visible light. J Phys Chem C 112:10407–10411
Mao X, Wang W, Chen X, Lu Y (2009) Multiferroic properties of layer-structured Bi5Fe0.5Co0.5Ti3O15 ceramics. Appl Phys Lett 95:082901
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the EU-FP7 project IFOX for financial support for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deniz, H., Bhatnagar, A., Pippel, E. et al. Nanoscale Bi2FeO6−x precipitates in BiFeO3 thin films: a metastable Aurivillius phase. J Mater Sci 49, 6952–6960 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8400-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8400-3