Abstract
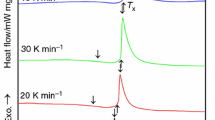
The influence of melt temperature on the glass formation, physical properties and local structure of (Fe71.2B24Y4.8)96Nb4 bulk metallic glass (BMG) was investigated through X-ray diffractometry, differential scanning calorimetry, thermal dilatation, and Mössbauer spectra tests. Amorphous alloys were formed by fast cooling of the melt from the temperature range of 1573–1773 K. BMG cast from 1623 K has lower Curie temperature and larger spontaneous volume magnetostriction, i.e., stronger Invar effect. The abnormality, which can not be eliminated by annealing, is attributed to the higher amount of Fe–Fe pairs indicated by the hyperfine field distribution. This special local structure is inherited from the melt, which has a liquid–liquid change manifested by an exothermic step region at the temperature range of 1615–1650 K. Through a slow-cooling process, the melt in the liquid–liquid change is frozen to a crystalline structure contained Y2Fe17 phase with a high intensity signal. These findings help explain the correlation between the liquid–liquid change and the structure of cooling products.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Han Z, Zhang J, Li Y (2007) Quaternary Fe-based bulk metallic glasses with a diameter of 5 mm. Intermetallics 15:1447–1452
Kim DH, Park JM, Kim WT (2007) Development of quaternary Fe–B–Y–Nb bulk glassy alloys with high glass-forming ability. J Mater Res 22:471–477
Lee S, Kato H, Kubota T, Yubuta K, Makino A, Inoue A (2008) Excellent thermal stability and bulk glass forming ability of Fe–B–Nb–Y soft magnetic metallic glass. Mater Trans 49:506–512
Stoica M, Kolesar V, Bednarcik J, Roth S, Franz H, Eckert J (2011) Thermal stability and magnetic properties of partially Co-substituted (Fe71.2B24Y4.8)96Nb4 bulk metallic glasses. J Appl Phys 109:054901
Masood A, Strom V, Belova L, Rao KV, Agren J (2013) Effect of Ni-substitution on glass forming ability, mechanical, and magnetic properties of FeBNbY bulk metallic glasses. J Appl Phys 113:013505
Tang MB, Yi J, Wang JQ, Wang WH, Zhao JT (2012) Low expansion in [(Fe0.9Co0.1)0.72B0.24Nb0.04]95.5Y4.5 bulk metallic glass. J Non-Cryst Solids 358:470–473
Li J, Yang W, Zhang M, Chen G, Shen B (2013) Thermal stability and crystallization behavior of (Fe0.75−x Dy x B0.2Si0.05)96Nb4 (x = 0–0.07) bulk metallic glasses. J Non-Cryst Solids 365:42–46
Hu Q, Zeng XR, Fu MW (2010) Invar effects of (Fe71.2B24Y4.8)96Nb4 alloy in different structural states. Appl Phys Lett 97:221907
Kumar G, Ohnuma M, Furubayashi T, Ohkubo T, Hono K (2008) Thermal embrittlement of Fe-based amorphous ribbons. J Non-Cryst Solids 354:882–888
Wei S, Yang F, Bednarcik J, Kaban I, Shuleshova O, Meyer A, Busch R (2013) Liquid–liquid transition in a strong bulk metallic glass-forming liquid. Nat Commun 4:2083–2089
Sidorov V, Popel P, Calvo-Dahlborg M, Dahlborg U, Manov V (2001) Heat treatment of iron based melts before quenching. Mater Sci Eng A 304:480–486
Zu FQ, Zhu ZG, Guo LJ, Qin XB, Yang H, Shan WJ (2002) Observation of an anomalous discontinuous liquid-structure change with temperature. Phys Rev Lett 89:125505
Li JJZ, Rhim WK, Kim CP, Samwer K, Johnson WL (2011) Evidence for a liquid–liquid phase transition in metallic fluids observed by electrostatic levitation. Acta Mater 59:2166–2171
Manov V, Popel P, Brook-Levinson E, Molokanov V, Calvo-Dahlborg M, Dahlborg U, Sidorov V, Son L, Tarakanov Y (2001) Influence of the treatment of melt on the properties of amorphous materials: ribbons, bulks and glass coated microwires. Mater Sci Eng A 304:54–60
Popel PS, Sidorov VE (1997) Microheterogeneity of liquid metallic solutions and its influence on the structure and properties of rapidly quenched alloys. Mater Sci Eng A 226–228:237–244
Curiotto S, Battezzati L, Johnson E, Palumbo M, Pryds N (2008) The liquid metastable miscibility gap in the Cu–Co–Fe system. J Mater Sci 43:3253–3258. doi:10.1007/s10853-008-2540-2
Zhu ZW, Zhang HF, Wang H, Ding BZ, Hu ZQ (2008) Influence of casting temperature on the thermal stability of Cu- and Zr-based metallic glasses: theoretical analysis and experiments. J Mater Res 23:2714–2719
Mao J, Zhang HF, Fu HM, Wang AM, Li H, Hu ZQ (2009) The effects of casting temperature on the glass formation of Zr-based metallic glasses. Adv Eng Mater 11:986–991
Mu J, Fu H, Zhu Z, Wang A, Li H, Hu Z, Zhang H (2010) The effect of melt treatment on glass forming ability and thermal stability of Al-based amorphous alloy. Adv Eng Mater 12:1127–1130
Wang Z, Zu F, Zhang Z, Cui X, Wang L, Sun G (2012) Dependence of GFA and crystallization behaviors of Al86Ni9La5 metallic glass on its original liquid state. Adv Eng Mater 14:898–901
Liu J, Guo J, Hu X, Guo S, Meng W, Xiao Q (2013) Effect of melt superheated treatment on glass forming ability and thermal expansion of Gd55Al25Cu10Co10 alloys. J Alloy Compd 581:671–674
Fan C, Liu CT, Chen G, Chen D, Yang X, Liaw PK, Yan HG (2013) Influence of the molten quenching temperature on the thermal physical behavior of quenched Zr-based metallic glasses. Intermetallics 38:19–22
Kumar G, Ohkubo T, Hono K (2009) Effect of melt temperature on the mechanical properties of bulk metallic glasses. J Mater Res 24:2353–2360
Mondal K, Ohkubo T, Toyama T, Nagai Y, Hasegawa M, Hono K (2008) The effect of nanocrystallization and free volume on the room temperature plasticity of Zr-based bulk metallic glasses. Acta Mater 56:5329–5339
Zeng X, Xie S, Hu Q, Fu D, Qian H, Fu M (2011) Influence of melt temperature on the compressive plasticity of a Zr–Cu–Ni–Al–Nb bulk metallic glass. J Mater Sci 46:951–956. doi:10.1007/s10853-010-4839-z
Zhu Z, Zhang H, Wang H, Ding B, Hu Z-Q, Huang H (2009) Influence of casting temperature on microstructures and mechanical properties of Cu50Zr45.5Ti2.5Y2 metallic glass prepared using copper mold casting. J Mater Res 24:3108–3115
Zhu ZW, Zheng SJ, Zhang HF, Ding BZ, Hu ZQ, Liaw PK, Wang YD, Ren Y (2008) Plasticity of bulk metallic glasses improved by controlling the solidification condition. J Mater Res 23:941–948
Shahri F, Beitollahi A (2008) Effect of super-heat treatment and quenching wheel speed on the structure and magnetic properties of Fe–Si–Nb–Cu–B–Al–Ge melt spun ribbons. J Non-Cryst Solids 354:1487–1493
van Schilfgaarde M, Abrikosov IA, Johansson B (1999) Origin of the Invar effect in iron–nickel alloys. Nature 400:46–49
Martin Rodriguez D, Plazaola F, Garitaonandia JS, Jimenez JA, Apinaniz E (2012) Influence of volume and Fe local environment on magnetic properties of Fe-rich Fe–Al alloys. Intermetallics 24:38–49
Lin XH, Johnson WL (1995) Formation of Ti–Zr–Cu–Ni bulk metallic glasses. J Appl Phys 78:6514–6519
Huang XM, Wang XD, He Y, Cao QP, Jiang JZ (2009) Are there two glass transitions in Fe–M–Y–B (M = Mo, W, Nb) bulk metallic glasses? Scripta Mater 60:152–155
Zeng XR, Hu Q, Fu MW, Xie SH (2012) Investigation of the free volume change of Fe41Co7Cr15Mo14C15B6Y2 bulk metallic glass using the cyclic thermal dilatation test. J Non-Cryst Solids 358:2682–2686
Hajlaoui K, Yousfi MA, Tourki Z, Vaughan G, Yavari AR (2010) On the free volume kinetics during isochronal structural relaxation of Pd-based metallic glass: effect of temperature and deformation. J Mater Sci 45:3344–3349. doi:10.1007/s10853-010-4355-1
Borrego JM, Blázquez JS, Lozano-Pérez S, Kim JS, Conde CF, Conde A (2014) Structural relaxation in Fe(Co)SiAlGaPCB amorphous alloys. J Alloy Compd 584:607–610
Olszewski J (2000) Magnetic interactions in amorphous and nanocrystalline Fe90Zr7Cu1B2 alloy. Hyperfine Interact 131:83–90
Brzozka K, Slawska-Waniewska A, Nowicki P, Jezuita K (1997) Hyperfine magnetic fields in FeZrB(Cu) alloys. Mater Sci Eng A 226–228:654–658
Kaban I, Kohler M, Ratke L, Nowak R, Sobczak N, Mattern N, Eckert J, Greer AL, Sohn SW, Kim DH (2012) Phase separation in monotectic alloys as a route for liquid state fabrication of composite materials. J Mater Sci 47:8360–8366. doi:10.1007/s10853-012-6660-3
Andreev AV, Daniš S (2009) Spontaneous magnetostriction of R2Fe13.6Si3.4 (R = U, Lu). J Alloy Compd 470:24–26
Hao YM, Gao Y, Wang BW, Qu JP, Li YX, Hu JF, Deng JC (2001) Negative thermal expansion and magnetic properties of Y2Al3Fe14−x Mn x compounds. Appl Phys Lett 78:3277–3279
Lukoyanov AV, Kokorina EE, Medvedev MV, Nekrasov IA (2009) Ab initio exchange interactions and magnetic properties of the Gd2Fe17 iron sublattice: rhombohedral versus hexagonal phases. Phys Rev B 80:104409
Tereshina EA, Andreev AV (2010) Magnetization and specific heat study of metamagnetism in Lu2Fe17-based intermetallic compounds. Intermetallics 18:1205–1210
Wang JL, Campbell SJ, Tegus O, Marquina C, Ibarra MR (2007) Magnetovolume effect and magnetic properties of Dy2Fe17−x Mn x . Phys Rev B 75:174423
Wang JL, Studer AJ, Kennedy SJ, Zeng R, Dou SX, Campbell SJ (2012) Magnetovolume effect in Ho2Fe17−x Mn x compounds. J Appl Phys 111:07A91
Mattern N, Eckert J, Kuhn U, Hermann H, Sakowski J, Herms G, Neuefeind J (2002) Structural behavior of Zr52Ti5Cu18Ni15Al10 bulk metallic glass at high temperatures. Appl Phys Lett 80:4525–4527
Mizuno A, Matsumura S, Watanabe M, Kohara S, Takata M (2005) High-energy X-ray diffraction study of liquid structure of metallic glass-forming Zr70Cu30 alloy. Mater Trans 46:2799–2802
Kordel T, Holland-Moritz D, Yang F, Peters J, Unruh T, Hansen T, Meyer A (2011) Neutron scattering experiments on liquid droplets using electrostatic levitation. Phys Rev B 83:104205
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the funding support from the Innovation and Technology Commission of Hong Kong Government under the project of ITS/228/11 and the National Natural Science Foundation of China for the Grant of No. 51201109.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Q., Sheng, H.C., Fu, M.W. et al. Influence of melt temperature on the Invar effect in (Fe71.2B24Y4.8)96Nb4 bulk metallic glass. J Mater Sci 49, 6900–6906 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8392-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8392-z