Abstract
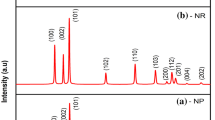
Pure and Sn-doped ZnO nanostructures have been synthesized by the microwave irradiation method. The influence of Sn loading on the morphology and microstructure was evaluated by using field emission scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), energy-dispersive spectrum analysis techniques, X-ray diffraction, and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. A change in the growth pattern, from needle-like particles for pure ZnO to agglomerated spherical crystallites for Sn-doped ZnO, has been observed. TEM observations indicated that the average particle size of the pure ZnO nano needles is in the range of 40–60 nm, whereas on addition of Sn spherical nanoassemblies size lies in the range of 10–21 nm. The pure ZnO and Sn-doped ZnO nanostructures were further characterized for their optical properties by UV–Vis reflectance spectra (DRS) and photoluminescence (PL) spectroscopy.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hu Z, Escamilla Ramirez DJ, Heredia Cervera BE, Oskam G, Searson PC (2005) Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles in 2-propanol by reaction with water. J Phys Chem B 109:11209–11214
Huang MH, Wu Y, Feick H, Tran N, Weber E, Yang P (2001) Catalytic growth of zinc oxide nanowires by vapor transport. Adv Mater 13:113–116
Yu H, Zhang Z, Han M, Hao X, Zhu F (2005) A general low-temperature route for large-scale fabrication of highly oriented ZnO nanorods/nanotube arrays. J Am Chem Soc 127:2378–2379
Ramgir NS, Late DJ, Bhise AB, Mulla IS, More MA, Joag DS, Pillai VK (2006) Field emission studies of novel ZnO nanostructures in high and low field regions. Nanotechnology 17:2730
Pan ZW, Dai ZR, Wang ZL (2001) Nanobelts of semiconducting oxides. Science 291:1947–1949
Kong XY, Ding Y, Yang RS, Wang ZL (2004) Single-crystal nanorings formed by epitaxial self-coiling of polar nanobelts. Science 303:1348–1351
Kong XY, Wang ZL (2003) Spontaneous polarization-induced nanohelixes, nanospringes, and nanorings of piezoelectric nanobelts. Nano Lett 3(12):1625–1631
Wang ZL, Kong XY, Zuo JM (2003) Induced growth of asymmetric nanocantilever arrays on polar surfaces. Phys Rev Lett 91:185502
Ryu YR, Zhu S, Han SW, White HW, Miceli PF, Chandrasehar HR (1998) ZnSe and ZnO film growth by pulsed-laser deposition. Appl Surf Sci 127–129:496–499
Wu J-J, Liu S-C (2002) Catalyst-free growth and characterization of ZnO nanorods. J Phys Chem B 106(37):9546–9551
Heo YW, Varadarajan V, Kaufman M, Kim K, Norton DP, Ren F, Fleming PH (2002) Site-specific growth of ZnO nanorods using catalysis-driven molecular-beam epitaxy. Appl Phys Lett 81:3046
Jung S-H, Oh E, Lee K-H, Yang Y, Park CG, Park W, Jeong S-H (2008) Sonochemical preparation of shape-selective ZnO nanostructures. Cryst Growth Des 8(1):265–269
Peulon S, Lincot D (1996) Cathodic electrodeposition from aqueous solution dense or open-structured zinc oxide films. Adv Mater 8:166–170
Jamali Sheini F, Mulla IS, Joag DS, More MA (2009) Influence of process variables on growth of ZnO nanowires by cathodic electrodeposition on zinc substrate. Thin Solid Films 517:6605–6611
Huang CY, Wang CY, Wang JT (2009) First-principles study of diffusion of zinc vacancies and interstitials in ZnO. Solid State Commun 149:199–204
Bigdeli F, Morsali A (2010) Synthesis ZnO nanoparticles from a new zinc(II) coordination polymer precursor. Mater Lett 64:4–5
Qiu YF, Yang SH (2007) ZnO nanotetrapods: controlled vapor-phase synthesis and application for humidity sensing. Adv Funct Mater 17:1345–1352
Sato Y, Yamamoto T (2007) Atomic structures and electrical properties of ZnO grain boundaries. J Am Ceram Soc 90:337–357
Deng SH, Duan MY, Xu M, He L (2011) Effect of La doping on the electronic structure and optical properties of ZnO. Phys B 406:2314–2318
Hou QY, Li JJ, Zhao CW, Ying C, Zhang Y (2011) First-principle study on the effect of high Li–2N co-doping on the conductivity of ZnO. Phys B 406:1956–1960
Prabakar K, Kim C, Lee C (2005) UV, violet and blue-green luminescence from RF sputter deposited ZnO:Al thin films. Cryst Res Technol 40:1150–1154
Deng R, Zhang XT, Zhang E, Liang Y, Liu Z, Xu HY, Hark SK (2007) Planar defects in Sn-doped single-crystal ZnO nanobelts. J Phys Chem C 111(35):13013–13015
Yasemin Caglar, Seval Aksoy, Saliha Ilican, Mujdat Caglar (2009) Crystalline structure and morphological properties of undoped and Sn doped ZnO thin films. Superlattice Microstruct 46:469–475
Navale SC, Mulla IS (2009) Photoluminescence and gas sensing study of nanostructured pure and Sn doped ZnO. Mater Sci Eng C 29:1317–1320
Krishnakumar T, Pinna N, Prasanna Kumari K, Perumal K, Jayaprakash R (2008) Microwave-assisted synthesis and characterization of tin oxide nanoparticles. Mater Lett 62:3437–3440
Krishnakumar T, Jayaprakash R, Parthibavarman M, Phani AR, Singh VN, Mehta BR (2009) Microwave-assisted synthesis and investigation of SnO2 nanoparticles. Mater Lett 63:896–898
Tsay CY, Cheng HC, Tung YT, Tuan WH, Lin CK (2008) Effect of Sn-doped on microstructural and optical properties of ZnO thin films deposited by sol-gel method. Thin Solid Films 517:1032–1036
Park KC, Ma DY, Kim KH (1997) The physical properties of Al-doped zinc oxide films prepared by RF magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 305:201–209
Cullity BD, Stock SR (2001) Elements of X-Ray Diffraction, 3rd edn. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River
Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards (JCPDS), Powder diffraction file, Card no: 36–1451. Swarthmore, PA
Bougrine A, El Hichou A, Addou M, Ebothe J, Kachouane A, Troyon M (2003) Structural, optical and cathodoluminescence characteristics of undoped and tin-doped ZnO thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis. Mater Chem Phys 80:438–445
Manoj PK, Benny Joseph, Vaidyan VK, Sumangala Devi Amma D (2007) Preparation and characterization of indium-doped tin oxide thin films. Ceram Int 33:273–278
Liang Z, Yong-ping Z (2012) Preparation and characterization of Sn-doped ZnO particles with low infrared emissivity. Chin J Process Eng 12:516–521
Tauc J, Grigorovici R, Vancu A (1966) Optical properties and electronic structure of amorphous germanium. Phys Status Solidi 15:627–637
Sernelius BE, Berggren KF, Jin ZC, Hamberg I, Granqvist CG (1988) Band-gap tailoring of ZnO by means of heavy Al doping. Phys Rev B 37:10244–10248
Dakhel AA (2009) Transparent conducting properties of samarium-doped CdO. J Alloy Compd 475:51–54
Dakhel AA (2011) Effect of cerium doping on the structural and optoelectrical properties of CdO nanocrystallite thin films. Mater Chem Phys 130:398–402
Camassel J, Auvergne D, Mathieu H (1975) Temperature dependence of the band gap comparision with the threshold frequency of pure GaAs lasers. J Appl Phys 46:2683
Matsumoto T, Kato H, Miyamoto K, Sano M, Zhukov EA, Yao T (2002) Correlation between grain size and optical properties in zinc oxide thin films. Appl Phys Lett 81:1231–1235
Sadia A, Shaheer Akhtar M, Seo H-K, Kim YS, Shin HS (2012) Influence of Sn doping on ZnO nanostructures from nanoparticles to spindle shape and their photoelectrochemical properties for dye sensitized solar cells. Chem Eng J 187:351–356
Duan JX, Huang XT, Wang H, Zhong Q, Sun FL, He X (2007) Synthesis of porous ZnO micro-flakes via an integrated autoclave and pyrolysis process. Mater Chem Phys 106:181–186
Deng R, Zhang XT (2008) Effect of Sn concentration on structural and optical properties of zinc oxide nanobelts. J Lumin 128:1442–1446
Ghosh M, Raychaudhuri AK (2008) Shape transition in ZnO nanostructures and its effect on blue-green photo luminescence. Nanotechnology 19:445704
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prakash, T., Jayaprakash, R., Espro, C. et al. Effect of Sn doping on microstructural and optical properties of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by microwave irradiation method. J Mater Sci 49, 1776–1784 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-013-7865-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-013-7865-9