Abstract
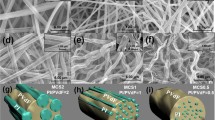
Battery separators based on electrospun membranes of poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) have been prepared in order to study the effect of fiber alignment on the performance and characteristics of the membrane. The prepared membranes show an average fiber diameter of ~272 nm and a degree of porosity of ~87 %. The gel polymer electrolytes are prepared by soaking the membranes in the electrolyte solution. The alignment of the fibers improves the mechanical properties for the electrospun membranes. Further, the microstructure of the membrane also plays an important role in the ionic conductivity, being higher for the random electrospun membrane due to the lower tortuosity value. Independently of the microstructure, both membranes show good electrochemical stability up to 5.0 V versus Li/Li+. These results show that electrospun membranes based on PVDF are appropriate for battery separators in lithium-ion battery applications, the random membranes showing a better overall performance.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pistoia G, Nazri G-A (eds) (2003) Lithium batteries, science and technology. Springer Science, New York
Scrosati B, Garche J (2010) J Power Sources 195(9):2419
Rydh CJ, Sandén BA (2005) Energy Convers Manag 46(11–12):1957
Kang B, Ceder G (2009) Nature 458(7853):190
Yoshio M, Brodd RJ, Kozawa A (2009) Lithium-ion batteries: science and technologies. Springer, New York
Arico AS, Bruce P, Scrosati B, Tarascon J-M, van Schalkwijk W (2005) Nat Mater 4(5):366
Yang M, Hou J (2012) Membranes 2(3):367
Cheng F, Liang J, Tao Z, Chen J (2011) Adv Mater 23(15):1695
Missan HPS, Sekhon SS (2005) J Mater Sci 40(14):3771. doi:10.1007/s10853-005-3317-5
Balbuena PB, Wang Y (eds) (2004) Lithium-ion batteries: solid–electrolyte interphase. Imperial College Press, London
Hikmet RAM (2001) In: Buschow KHJ, Cahn Robert W, Merton CF et al (eds) Encyclopedia of materials: science and technology. Elsevier, Oxford, p 6534
Arora P, Zhang Z (2004) Chem Rev 104(10):4419
Xu K (2004) Chem Rev 104(10):4303
Park M, Zhang X, Chung M, Less GB, Sastry AM (2010) J Power Sources 195(24):7904
Stephen AM (2006) Eur Polym J 42(1):21
Millet P, Andolfatto F, Durand R (1995) J Appl Electrochem 25(3):233
Chung YS, Yoo SH, Kim CK (2009) Ind Eng Chem Res 48(9):4346
Venugopal G, Moore J, Howard J, Pendalwar S (1999) J Power Sources 77(1):34
Costa CM, Tamano Machiavello MN, Gomez Ribelles JL et al (2013) J Mater Sci 48(9):3494. doi:10.1007/s10853-013-7141-z
Kang Y, Kim HJ, Kim E, Oh B, Cho JH (2001) J Power Sources 92(1–2):255
Costa CM, Silva MM, Lanceros-Mendez S (2013) RSC Adv. doi:10.1039/C3RA40732B
Costa CM, Rodrigues LC, Sencadas V, Silva MM, Rocha G, Lanceros-Méndez S (2012) J Membr Sci 407–408(8):193
Yang XQ, Lee HS, Hanson L, McBreen J, Okamoto Y (1995) J Power Sources 54(2):198
Nishikawa O, Sugimoto T, Nomura S, Doyama K, Miyatake K, Uchida H, Watanabe M (2004) Electrochim Acta 50(2–3):667
Kim JR, Choi SW, Jo SM, Lee WS, Kim BC (2004) Electrochim Acta 50(1):69
Li Z, Shan F, Wei J, Yang J, Li X, Wang X (2008) J Solid State Electrochem 12(12):1629
Abraham KM, Jiang Z, Carroll B (1997) Chem Mater 9(9):1978
Sylla S, Sanchez JY, Armand M (1992) Electrochim Acta 37(9):1699
Cui W-W, Tang D-Y, Gong Z-l, Guo Y-D (2012) J Mater Sci 47(17):6276. doi:10.1007/s10853-012-6547-3
Srinivasan G, Reneker DH (1995) Polym Int 36(2):195
Saunier J, Alloin F, Sanchez JY, Maniguet L (2004) J Polym Sci B 42(12):2308
Nakajima T, Groult H (2005) Fluorinated materials for energy conversion. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Kim JR, Choi SW, Jo SM, Lee WS, Kim BC (2005) J Electrochem Soc 152(2):A295
Gao K, Hu X, Dai C, Yi T (2006) Mater Sci Eng B 131(1–3):100
Ding Y, Zhang P, Long Z, Jiang Y, Xu F, Di W (2008) Sci Technol Adv Mater 9(1):015005
Alcoutlabi M, Lee H, Watson JV et al (2013) J Mater Sci 48(6):2690. doi:10.1007/s10853-012-7064-0
Choi SW, Kim JR, Ahn YR, Jo SM, Cairns EJ (2006) Chem Mater 19(1):104
Croce F, Focarete ML, Hassoun J, Meschini I, Scrosati B (2011) Energy Environ Sci 4(3):921
Ribeiro C, Sencadas V, Ribelles JLG, Lanceros-Méndez S (2010) Soft Mater 8(3):274
California A, Cardoso VF, Costa CM, Sencadas V, Botelho G, Gómez-Ribelles JL, Lanceros-Mendez S (2011) Eur Polym J 47(12):2442
Brett AMCFO, Brett CMA (1996) Electroquímica: princípios, métodos e aplicações. Livraria Almedina, Coimbra
Raghavan P, Manuel J, Zhao X, Kim D-S, Ahn J-H, Nah C (2011) J Power Sources 196(16):6742
Karabelli D, Leprêtre JC, Alloin F, Sanchez JY (2011) Electrochim Acta 57(1):98
Quartarone E, Mustarelli P, Magistris A (2002) J Phys Chem B 106(42):10828
Sheidaei A, Xiao X, Huang X, Hitt J (2011) J Power Sources 196(20):8728
Kim CS, Oh SM (2001) Electrochim Acta 46(9):1323
Krevelen DW, Te Nijenhuis K (2009) Properties of polymers: their correlation with chemical structure; their numerical estimation and prediction from additive group contributions. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Chang B-Y, Park S-M (2010) Annu Rev Anal Chem 3(1):207
Cole K (1941) J Chem Phys 9(4):341
Saunier J, Alloin F, Sanchez JY, Caillon G (2003) J Power Sources 119–121(1–2):454
Rajendran S, Sivakumar P (2008) Physica B 403(4):509
Gray FM (1997) Polymer electrolytes. Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge
Aurbach D, Daroux M, Faguy P, Yeager E (1991) J Electroanal Chem 297(1):225
Bard AJ, Faulkner LR (2001) Electrochemical methods: fundamentals and applications. Wiley, New York
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by FEDER funds through the “Programa Operacional Factores de Competitividade – COMPETE” and by national funds by FCT—Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, project references Project PTDC/CTM/69316/2006, NANO/NMed-SD/0156/2007 and Pest-C/QUI/UIO686/2011 and Grant SFRH/BD/68499/2010 (C.M.C) and SFRH/BD/66930/2009 (J.N.P.) SFRH/BPD/63148/2009 (V.S). The authors also thank Celgard, LLC for kindly supplying their high quality membranes.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Costa, C.M., Nunes-Pereira, J., Sencadas, V. et al. Effect of fiber orientation in gelled poly(vinylidene fluoride) electrospun membranes for Li-ion battery applications. J Mater Sci 48, 6833–6840 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-013-7489-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-013-7489-0