Abstract
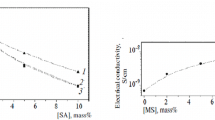
In this paper, the feasibility of fabricating polypropylene (PP) nanofibres was investigated using conductive additives such as sodium oleate (SO) and sodium chloride (NaCl) during melt-electrospinning. PP of high melt flow index (MFI = 2000) was used with varying amounts of additives. The effects of amount of additives on the fibre diameter and morphology were investigated. The lowest fibre diameters of 0.371 ± 0.106 and 0.310 ± 0.102 μm were achieved with 7 % SO and 5 % NaCl, respectively. The fabrication of nanofibres was attributed to the increase in the electrical conductivity with the introduction of the additives. The increase in the electrical conductivity was greater in the case of NaCl, due to the smaller ionic size of NaCl. Differential scanning calorimetry results showed complex melting behaviour during the heating cycles for the fibres containing SO; and double melting peaks during the second heating cycle for the fibres containing NaCl. X-ray diffraction studies showed the fibres fabricated with the additives contained lower degrees of crystallinity compared to the as-spun fibre and the crystallinity was increased after annealing. The fibres fabricated with the additives contained α-form crystals only which did not change after annealing. The fibres fabricated from pure polymer and with the additives were hydrophobic in nature. The hydrophobicity was marginally decreased with the addition of SO and NaCl.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ramakrishna S (2005) An introduction to electrospinning and nanofibers. World Scientific Pub Co Inc, Singapore
Nayak R, Padhye R, Kyratzis IL, Truong Y, Arnold L (2011) Textile Res J. doi:10.1177/0040517511424524
Liu Y, Deng R, Hao M, Yan H, Yang W (2010) Polym Eng Sci 50(10):2074. doi:10.1002/pen.21753
Larrondo L, St John Manley R (1981) J Polym Sci 19(6):909
Larrondo L, St John Manley R (1981) J Polym Sci 19(6):921
Larrondo L, St John Manley R (1981) J Polym Sci 19(6):933
Ogata N, Lu G, Iwata T, Yamaguchi S, Nakane K, Ogihara T (2007) J Appl Polym Sci 104:1368
Ogata N, Yamaguchi S, Shimada N, Lu G, Iwata T, Nakane K, Ogihara T (2007) J Appl Polym Sci 104(3):1640
Zhou H, Green T, Joo Y (2006) Polymer 47(21):7497
Lin T, Wang H, Wang X (2004) Nanotechnology 15:1375
Zong X, Kim K, Fang D, Ran S, Hsiao BS, Chu B (2002) Polymer 43(16):4403
Inai R, Kotaki M, Ramakrishna S (2005) Nanotechnology 16:208
Liang S, Hu D, Zhu C, Yu A (2002) Chem Eng Technol 25(4):401
Ferrer-Balas D, Maspoch ML, Martinez A, Santana O (2001) Polymer 42(4):1697
Kirshenbaum I, Wilchinsky Z, Groten B (1964) J Appl Polym Sci 8(6):2723
Krupa I, Luyt A (2001) Polym Degrad Stab 72(3):505
Wochowicz A, Eder M (1984) Polymer 25(9):1268
Scholte TG, Meijerink N, Schoffeleers H, Brands A (1984) J Appl Polym Sci 29(12):3763
Frost K, Kaminski D, Kirwan G, Lascaris E, Shanks R (2009) Carbohydr Polym 78(3):543
Farrow G, Preston D (1960) Br J Appl Phys 11:353
Hutmacher DW, Dalton PD (2011) Chem Asian J 6(1):44
Góra A, Sahay R, Thavasi V, Ramakrishna S (2011) Polym Rev 51(3):265
Kim D, Yoshino K (2000) J Phys D Appl Phys 33:464
Tandon P, Neubert R, Wartewig S (2000) J Mol Struct 526(1):49
Broda J, Wochowicz A (2000) Eur Polymer J 36(6):1283
Machado G, Denardin E, Kinast E, Gonçalves M, De Luca M, Teixeira S, Samios D (2005) Eur Polymer J 41(1):129
Chung T, Lee S (1997) J Appl Polym Sci 64(3):567
Cho D, Zhou H, Cho Y, Audus D, Joo YL (2010) Polymer 51(25):6005
Acknowledgements
The technical support from Muthu Pannirselvam and Mike Allan (Rheology and Materials Processing Centre, School of Civil, Environmental & Chemical Engineering, RMIT University); Phil Francis, Peter Rummel, Matthew Field and Frank Antolasic (School of Applied Sciences, RMIT University); Gary Peeters and Lance Nichols (MSE, CSIRO, Clayton); Mark Greaves and John Ward (Scanning Electron Microscopy, Digital Imaging & Surface Analysis Facility of MSE, CSIRO, Clayton); Birendra Singh, Mark Hickey, Jacinta Poole, Tim Hughes, Russell Varley and Wendy Tian (MSE, CSIRO, Clayton); Liz Goodall and Winston Liew (Materials Characterisation Services of MSE, CSIRO, Clayton); and David Sutton and Peter Kouwenoord (Lyondellbasell) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nayak, R., Kyratzis, I.L., Truong, Y.B. et al. Melt-electrospinning of polypropylene with conductive additives. J Mater Sci 47, 6387–6396 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-012-6563-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-012-6563-3