Abstract
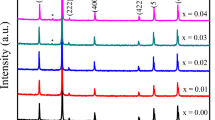
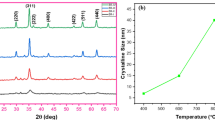
In order to improve the frequency range operation of Ni–Zn ferrites with the Ni0.7Zn0.3Fe2O4 stoichiometry in this study, they were doped with V2O3 at different concentrations (0, 0.25, 0.50, and 0.75 wt%). The samples were prepared by the solid-state reaction at 1250 °C for 24 h. The content and location of Vanadium in these ferrites allow us to determine its influence on their microstructure and magnetic properties. A single cubic spinel phase with lattice parameter variation was determined by the refinement of X-ray diffraction patterns. This refinement was achieved using the Rietveld method. The lattice parameter presents a slight enhancement with increasing Vanadium content up to 0.50 wt% of V2O3. The increase of intragrain porosity and the segregation of Vanadium at the grain boundary in samples with higher concentration of Vanadium show a narrow grain-size distribution that leads to a resonant character of the magnetic domain wall. A wide grain-size distribution determined in lower concentration of Vanadium results in a mixed resonant-relaxation dispersion. The use of V2O3 as a dopant in Ni–Zn ferrites increases the frequency operation and coercivity, H c, without abruptly degrading the saturation magnetization, M s. We, therefore conclude, that Vanadium may be used as a strong dopant for the preparation of ferrites for any particular high-frequency application.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Valenzuela R (1994) Magnetic ceramics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Chen CW (1977) Magnetism and metallurgy of soft magnetic materials. North Holland, Amsterdam
Nakamura T (1997) J Magn Magn Mater 168:285
Zhang L, Liu X, Guo X, Su M, Xu T, Song X (2010) Chem Eng J. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2011.08.041
Lima UR, Nasar MC, Nasar RS, Rezende MC, Araújo V (2008) J Magn Magn Mater 320:1666
Buswell M (1989) Microwave Theory Tech 37:860
Srinivasan TT, Ravindranathan P, Cross LE, Roy R, Newnham RE, Sankar SG, Patil KC (1988) J Appl Phys 63:3789
Kavas H, Baykal A, Toprak MS, Köseoğlu Y, Sertkol M, Aktas B (2009) J Alloys Compds 479:49
Sertkol M, Köseoğlu Y, Baykal A, Kavas H, Toprak MS (2010) J Magn Magn Mater 322:866
Atkher Hossain AKM, Mahmud ST, Seki M, Kawai T, Tabata H (2007) J Magn Magn Mater 312:210
Sertkol M, Köseoğlu Y, Baykal A, Kavas H, Bozkurt A, Toprak MS (2009) J Alloys Compds 486:325
Drofenik M, Žnidaršič A, Makovec D (1998) J Am Ceram Soc 81(11):2841
Chen SH, Chang SC, Tsay CY, Liu KS, Lin IN (2001) J Eur Ceram Soc 21:1931
Janghorban AK, Shokrollahi H (2007) J Magn Magn Mater 308:238
Rodriguez-Carvajal J (1990) FULLPROF: a program for rietveld refinement and pattern matching analysis abstracts of the satellite meeting on powder diffraction of the XV congress of the IUCr, Toulouse, France, p 127
Rodriguez-Carvajal J, Roisnel T (1998) Newsletter 20:35
Cedillo E, Ocampo J, Rivera V, Valenzuela R (1980) J Phys E Sci Instrum 13:383
Kasapoğlu N, Baykal A, Toprak MS, Koseoğlu Y, Bayrakdar H (2007) Turk J Chem 31:659
Baykal A, Kasapoğlu N, Koseoğlu Y, Toprak MS, Bayrakdar H (2008) J Alloys Compds 464:514
Akther S, Choudhury MDA, Rahman J (2009) J Bangladesh Acad Sci 33(2):145
Hsu J-Y, Ko W-S, Chen C-J (1995) IEEE Trans Magn 31(6):3994
Jean J-H, Lee C-H (2001) Jpn J Appl Phys 40:2232
Hu J, Yan M, Luo W (2005) Phys B 368:251
Shokrollahi H (2008) J Magn Magn Mater 320:463
Herrera G, Rosales Escárcega IEA, Montiel H, Valenzuela R (2004) Study of the resonance-relaxation phenomena of Ni–Zn ferrites doped with V2O3 by high-frequency impedance spectroscopy, vol 1. Magnetic Materials, Singapore, Works Scientific eProceedings of PFAM XII, p 377
Arcos D, Vázquez M, Valenzuela R, Vallet-Regí M (1999) J Mater Res 14(3):861
Narayan R, Tripathi RB, Das BK, Jain GC (1983) J Mater Sci 18(6):1583. doi:10.1007/BF00542050
Mirzaee O, Golozar MA, Shafyei A (2008) Mater Charact 59:638
Mirzaee O, Shafyei A, Golozar MA, Shokrollahi H (2008) J Alloys Compds 461:312
Sun J, Li J, Sun G (2002) J Magn Magn Mater 250:20
Shichijo Y, Tsuya N, Suzuki K (1961) J Appl Phys 32(3):386s
Lebourgeois R, Duguey S, Ganne J-P, Heintz J-M (2007) J Magn Magn Mater 312:328
Jain GC, Das BK, Tripathi RB, Narayan Ram (1982) IEEE Trans Magn 18(2):776
Rasband W (2010) ImageJ version 1.43u. National Institute of Health, USA
Jankovskis J (2002) In: Scientific proceedings of RTU series 7, telecommunications and electronics, vol 2. Institute of Radioelectronics, Riga, Latvia, pp 68–77
Azadmanjiri J (2008) Mater Chem Phys 109:109
Rao BP, Rao KH, Sankaranarayana G, Paduraru A, Caltun OF (2005) J Optoelectron Adv Mater 7(2):697
Chikazumi S (1977) Physics of ferromagnetism. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Herrera M, Montiel H, Valenzuela R (2005) In: Proceedings of the 9th international conference on ferrites ICF9, 2004 edn, San Francisco, USA, August
Herrera G (2005) Master′s Thesis, Instituto de Investigaciones en Materiales, UNAM
Rao BP, Kim C-O, Kim C-G, Caltun OF (2007) J Optoelectron Adv Mater 9(4):1151
Herrera G (2010) J Appl Phys 108:103901
Snoek JL (1948) Physica 14(4):207
Acknowledgements
The authors thank CONACyT for the student fellowships, Grant No. 170588, 129569, and PAPPIT No. IN116903. The authors would like to thank especially to MSc. Leticia Baños, MSc Adriana Tejeda-Cruz, Dr. José Guzmán, and Dr. Gabriel Lara for their assistance in XRD and SEM characterization; and the Instituto de Investigaciones en Materiales-UNAM for the facilities to achieve this research, and the Instituto de Ciencias Nucleares-UNAM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herrera, G., Pérez-Moreno, M.M. Microstructure dependence of the magnetic properties of sintered Ni–Zn ferrites by solid-state reaction doped with V2O3 . J Mater Sci 47, 1758–1766 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-011-5956-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-011-5956-z