Abstract
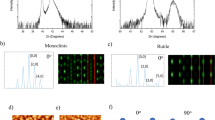
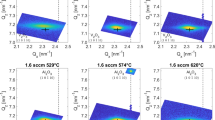
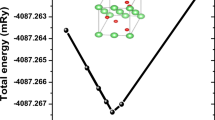
Vanadium dioxide (VO2) thin films have been shown to undergo a rapid electronic phase transition near 70 °C from a semiconductor to a metal, making it an interesting candidate for exploring potential application in high speed electronic devices such as optical switches, tunable capacitors, and field effect transistors. A critical aspect of lithographic fabrication in devices utilizing electric field effects in VO2 is the ability to grow VO2 over thin dielectric films. In this article, we study the properties of VO2 grown on thin films of Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia (YSZ). Near room temperature, YSZ is a good insulator with a high dielectric constant (\(\epsilon _{\rm r} > 25\)). We demonstrate the sputter growth of polycrystalline VO2 on YSZ thin films, showing a three order resistivity transition near 70 °C with transition and hysteresis widths of approximately 7 °C each. We examine the relationship between chemical composition and transition characteristics of mixed phase vanadium oxide films. We investigate changes in composition induced by low temperature post-deposition annealing in oxidizing and reducing atmospheres, and report their effects on electronic properties.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berglund CN, Guggenheim HJ (1969) Phys Rev 185:1022
Goodenough JB (1971) J Solid State Chem 3:490
Morin FJ (1959) Phys Rev Lett 3:34
Zylbersztejn A, Mott NF (1975) Phys Rev 11:4383
Cavalleri A et al. (2001) Phys Rev Lett 87:237401
Qazilbash MM et al. (2007) Science 318:1750
Sakai J et al. (2008) Phys Rev B 78:033106
Stefanovich G et al. (2000) J Phys Condens Matter 12:8837
Kim HT et al. (2004) New J Phys 6:52
Okimura K, Sakai J (2007) Jpn J Appl Phys 46:813
Ko C, Ramanathan S (2008) Appl Phys Lett 93:252101
Ruzmetov D et al. (2009) J Appl Phys 106:083702
Ruzmetov D et al. (2007) J Appl Phys 102:113715
Ruzmetov D et al. (2010) J Appl Phys 107:114516
Lee JS et al. (2007) Appl Phys Lett 90:015907
Lee JS et al. (2007) Appl Phys Lett 91:133509
Gopalakrishnan G et al. (2009) J Mater Sci 44:5345. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-3442-7
Gupta A et al. (2009) Appl Phys Lett 95:111915
Chae BG et al. (2004) J Korean Phys Soc 44:884
Zhu J, Liu JG (2003) Mater Lett 57:4297
Norian KH, Hazell LB (1978) Thin Solid Films 54:L9
Krishna MG et al. (1997) Thin Solid Films 312:116
Sawatzky GA, Post D (1979) Phys Rev B 20:1546
Demeter M et al. (2000) Surf Sci 454:41
Youn DH et al. (2004) J Vac Sci Technol A 22:719
Youn DH et al. (2004) J Appl Phys 95:1407
Yun SJ et al. (2008) Electrochem Solid State Lett 1:H173
Yang Z et al. (2010) Phys Rev B 82:205101
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Yanjie Cui and Kian Kerman for technical assistance as well as Zheng Yang for valuable discussions. We acknowledge NSF supplement PHY-0601184 for financial support. Device fabrication was performed, in part, at the Harvard University Center for Nanoscale Systems (CNS), a member of the National Nanotechnology Infrastructure Network (NNIN) which is supported by NSF Award No. ECS-0335765.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gopalakrishnan, G., Ramanathan, S. Compositional and metal-insulator transition characteristics of sputtered vanadium oxide thin films on yttria-stabilized zirconia. J Mater Sci 46, 5768–5774 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-011-5532-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-011-5532-6