Abstract
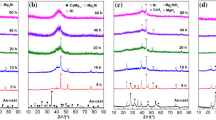
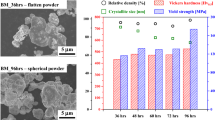
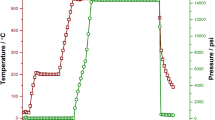
A study was carried out into the possibility of employing ECAP processing in lieu of mechanical milling for the purpose of developing powder-based hydrogen storage alloys. Mg and Mg–Ti powder compacts were encapsulated in a copper block and were subjected to ECAP deformation to an apparent strain of ε = 4. This resulted in the consolidation of the compacts as well as in the refinement of their structures. The values of coherently diffracting volume size were as small as 70–80 nm, quite comparable to those achieved with mechanical milling. It is, therefore, concluded that ECAP processing can be employed successfully for the purpose of structural refinement. As for material synthesis, however, the ECAP is less efficient in expanding the interfacial area. Therefore, it is necessary to impose relatively heavy strains to able to achieve comparable expansion in the interfacial area. It appears that an advantage of ECAP deformation is the development of structures which have improved ability for milling. It is, therefore, recommended that in the processing of hydrogen storage alloys, the powder mixtures may be first processed with ECAP in open atmosphere and then by mechanical milling of a short duration carried out under protective atmosphere.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Suryanarayana C (2001) Prog Mater Sci 46:1
Pedneault S, Huot J, Roue L (2008) J Power Sour 185:566
Segal VM (1999) Mater Sci Eng A 271:322
Güvendiren M, Baybörü E, Öztürk T (2004) Int J Hydrogen Energy 29:491
Mandzhukova T, Bobet J-L, Khrussanova M, Peshev P (2009) Mater Res Bull 44:1968
Huang JY, Wu YK, Ye HQ (1995) Mater Sci Eng A 199:165
Çakmak G, Károly Z, Mohai I, Öztürk T, Szépvölgyi J (2010) Int J Hydrogen Energy 35:10412
Zaluska A, Zaluski L, Ström–Olsen JO (1999) J Alloy Compd 288:217
Wieczorek AK, Krystian M, Zehetbauer MJ (2006) Solid State Phenom 114:177
Ivey DG, Northwood DO (1983) J Mater Sci 18:321. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00560621
Valiev RZ, Langdon TG (2006) Prog Mater Sci 51:881
Komura S, Horita Z, Nemoto M, Langdon TG (1999) J Mat Res 14:4044
Pushin VG, Stolyarov VV, Valiev RZ, Kourov NI, Kuranova NN, Prokofiev EA, Yurchenko LI (2002) Ann Chim Sci Mater 27:77
Zehetbauer M, Grössinger R, Krenn H, Krystian M, Pippan R, Rogl P, Waitz T, Würschum R (2010) Adv Eng Mater 12:692
Skripnyuk VM, Rabkin E, Estrin Y, Lapovok R (2004) Acta Mater 52:405
Skripnyuk V, Buchman E, Rabkin E, Estrin Y, Popov M, Jorgensen S (2007) J Alloy Compd 436:99
Çakmak G, Bobet J-L, Ölmez R, Öztürk T (2007) In: Proceedings International Hydrogen Energy Congress and Exhibition IHEC, Istanbul, Turkey
Loken S, Solberg JK, Maehlen JP, Denys RV, Lototsky MV, Tarasov BP, Yartys VA (2007) J Alloy Compd 446–447:114
Sprinyuk VM, Rabkin E, Estrin Y, Lapovok R (2009) Int J Hydrogen Energy 34:6320
Leiva DR, Fruchart D, Bacia M, Girard G, Skryabina N, Villela ACS, Miraglia S, Santos DS, Botta WJ (2009) Int J Mater Res 100:1739
Iwahashi Y, Wang J, Horita Z, Nemoto M, Langdon TG (1996) Scr Mater 35:143
Furukawa M, Iwahashi Y, Horita Z, Nemoto M, Langdon TG (1998) Mater Sci Eng A 257:328
Raab GI (2005) Mater Sci Eng A 410–411:230
Dinkel M, Pyczak F, May J, Höppel HW, Göken M (2008) J Mater Sci 43:7481. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-2859-8
Máthis K, Gubicza J, Nam NH (2005) J Alloy Compd 394:194
Wu HM, Hung SS, Lee PY (2007) J Alloy Compd 434–435:386
Moss M, Lapovok R, Bettles CJ (2007) JOM 59:54
Xia K, Wu X (2005) Scr Mater 53:1225
Quang P, Jeong YG, Yoon SC, Hong SH, Kim HS (2007) J Mater Process Technol 187–188:318
Öztürk T, Mirmesdagh J, Ediz T (1994) Mater Sci Eng A 175:125
Shingu PH, Ishihara KN, Otsuki A, Daigo I (2001) Mater Sci Eng A 304–306:399
Acknowledgements
Support for this study was provided by DPT with project number BAP-03-08-DPT.200305K120920-20 and by the FP6 program of the European Commission project (FP6-200-3-518-271), NESSHY, which we gratefully acknowledge.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Çakmak, G., Öztürk, T. ECAP processing and mechanical milling of Mg and Mg–Ti powders: a comparative study. J Mater Sci 46, 5559–5567 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-011-5506-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-011-5506-8