Abstract
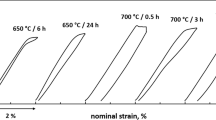
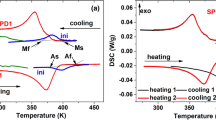
Ni–Mn–Ga Heusler-type ferromagnetic shape memory alloys are attractive materials for micro-actuator, but the relatively poor ductility and low strength of Ni–Mn–Ga alloys have triggered a great deal of interest. In this study, we attempt to introduce some ductile second phase in the alloy by partially substituting Ti for Ga and constraint aging treatment. The results show that the martensitic transformation temperature first decreases and then increases slightly with the increasing of constraint-aging temperature, which can be attributed to the decrease of Ni content in the matrix and strengthening effect of the second particles. It is found that the amount of the Ni-rich precipitates by constraint-aged samples is more and the size of the second phase particle is smaller than that of the free-aged samples. The compressive stress and ductility can be significantly improved by the constraint-aging treatment, and the maximum compressive stress for constraint-aging alloy is about 1400 MPa, which is the highest value up to date compared with the 400 MPa in solution-treated Ni–Mn–Ga–Ti alloy and about 900 MPa in Ni–Mn–Ga–Ti alloy free-aged at 1073 K for 3 h. Scanning electron microscopy observations of fracture surfaces confirm that the Ni-rich second phase play a key role in improving the compression stress and ductility of Ni–Mn–Ga–Ti alloy.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ullakko K, Huang JK, Kanter C, Kokorin VV, O’Handley RC (1996) Appl Phys Lett 69:1966
Wuttig M, Liu L, Tsuchiya K, James RD (2000) J Appl Phys 87(9):4707
O’Handley RC, Murray SJ, Marioni M, Nembach H, Allen SM (1998) J Appl Phys 83(6):3263
Mullner P, Chernenko VA, Kostorz G (2004) J Appl Phys 95:1531
Hosoda H, Wakashima K, Sugimoto T, Miyazaki S (2002) Mater Trans 43:852
Murray SJ, Marioni M, Allen SM, O’Handley RC, Lograsso TA (2000) Appl Phys Lett 77:886
Sozinov A, Likhachev AA, Ullakko K (2002) IEEE Trans Magn 38:2814
Gao L, Cai W, Liu AL, Zhao LC (2006) J Alloy Compd 425:314
Tsuchiya K, Tsutsumi A, Ohtsuka H, Umemoto M (2004) Mater Sci Eng A 378:370
Nakanishi N, Mori T, Miura S, Murakami Y, Kachi S (1973) Philos Mag 28:277
Khan M, Dubenko I, Stadler S, ALi N (2004) J Phys Condens Matter 16:5259
Stadle S, Khan M, Mitchell J, Ali N, Gomes AM, Dubenko I, Takeuchi AY, Guimaraes AP (2006) Appl Phys Lett 88:192511
Wang HB, Chen F, Gao ZY, Cai W, Zhao LC (2006) Mater Sci Eng A 438–440:990
Cong DY, Wang S, Wang YD, Ren Y, Zuo L, Esling C (2007) Mater Sci Eng A 473:213
Glavatskyy I, Glavatska N, Dobrinsky A, Hoffmann J-U, Söderberg O, Hannula S-P (2007) Scripta Mater 56:565
Khan M, Dubenko I, Stadler S, Ali N (2005) J Appl Phys 97:10M304-1
Dong GF, Cai W, Gao ZY, Sui JH (2008) Scripta Mater 58:647
Dong GF, Tan CL, Gao ZY, Feng Y, Cai W, Sui JH (2008) Scripta Mater 59:268
Gao ZY, Dong GF, Cai W, Sui JH, Feng Y, Li XH (2009) J Alloy Compd 481:44
Dong GF, Gao ZY, Tan CL, Cai W, Sui JH (2010) J Mater Sci 45:5490. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-4606-1
Scanchez-Alarcos V, Perez-Landazabal JI, Recarte V, Gomez-polo C, Rodriguez-Velamazan JA (2008) Acta Mater 56:5370
Chen XQ, Lu X, Wang DY, Qin ZX (2008) Smart Mater Struct 17:065030
Cong DY, Wang S, Wang YD, Ren Y, Zuo L, Esling C (2008) Mater Sci Eng A 473:213
Hae-Min Lee, Anthony JK, Rotermund F et al (2009) J Mater Sci 44:3731. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-3498-4
Coughlin JP, Williams JJ, Chawla N (2009) J Mater Sci 44:700. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-3188-7
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 20100481218) and Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 50601006, 20973028).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, G.F., Gao, Z.Y., Zhang, X.L. et al. Phase transition and mechanical properties of constraint-aged Ni–Mn–Ga–Ti magnetic shape memory alloy. J Mater Sci 46, 4562–4567 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-011-5354-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-011-5354-6