Abstract
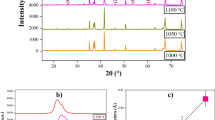
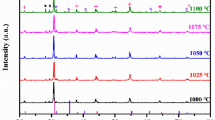
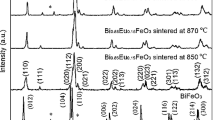
Ho3Fe5O12 ceramics were fabricated by the solid-state reaction method. The results revealed an increase of the grain size, dielectric constant, and dielectric loss, while a decrease of the remnant magnetization and coercive field with increasing sintering temperature. A dielectric relaxation behavior was observed, which might be associated with the charge carrier hopping between Fe2+ and Fe3+. A cole–cole fitting to loss peaks revealed a dependence of the activation energy and the broaden factor on the relative density of the samples. Furthermore, at appropriate frequencies, the 1250 °C-sintered samples showed high dielectric constant, low dispassion, and good temperature stability around room temperature.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Larsen PK, Metselaar R (1976) Phys Rev B 14:2520
Kidoh H, Morimoto A, Shimizu T (2007) Appl Phys Lett 59:237
Legg GJ, Lanchester PC (1980) J Phys C 13:6547
Takano S, Kita E, Tasaki A, Furukawa K, Kohn K, Siratori K, Kimura S (1989) Ferroelectrics 96:251
Larsen PK, Metselaar R (1973) Phys Rev B 8:2016
Fechine PBA, Pereira FMM, Santos MRP, Fihiho FP, de Menezes AS, de Oliveira RS, Gòes JC, Cardoso LP, Sombra ASB (2009) J Phys Chem Solids 70:804
Yamasaki Y, Kohara Y, TokuraPhys Y (2009) Phys Rev B 80:140412
Jawahar K, Choudhary RNP (2007) Solid State Commun 142:449
Wu XB, Wang XF, Liu YF, Cai W, Peng S, Huang FZ, Lu XM, Zhu JS (2009) Appl Phys Lett 95:182903
Wu YJ, Gao Y, Chen XM (2007) Appl Phys Lett 91:092912
Guillot M, Marchand A (1982) J Appl Phys 53:2719
Ostoréro J, Guillot M (1997) J Appl Phys 81:4797
Goodshaw HJ, Forrester JS, Suang GJ, Kisi EH (2007) J Mate Sci 42:337. doi:10.1007/s10853-006-1031-6
Thongbai P, Yamwong T, Maensiri S (2008) J Appl Phys 104:074109
Ahmed MA, Ateia E, El-Dek SI, Salem FM (2003) J Mater Sci 38:1087. doi:10.1023/A:1022314301113
Popa PD, Rezlescu E, Doroftei C, Rezlescu N (2005) J Optoelectron Adv Mater 7:1553
Hussain S, Maqsood A (2007) J Magn Magn Mater 316:73
Lee JW, Cho YS, Amarakoon VRW (1999) J Appl Phys 85:5696
Tǒpfer J, Schwarzer S, Senz S, Hesse D (2005) J Eur Ceram Soc 25:1681
Costantini JM, Salvetat JP, Brisard F (1997) J Appl Phys 82:5063
Cole KS, Cole RH (1941) J Chem Phys 9:341
Li W, Chen K, Yao YY, Zhu JS, Wang YN (2004) Appl Phys Lett 85:4717
Wang XF, Lu XM, Zhang C, Wu XB, Cai W, Peng S, Bo HF, Kan Y, Huang FZ, Zhu JS (2010) J Appl Phys 107:114101
Ngai KL, Wang YN, Magalass LB (1994) J Alloys Compd 212:327
Homes CC, vogt T, Shapiro SM, Wakimoto S, Ramirez AP (2001) Science 293:673
Wang CM, Lin SY, Kao KS, Chen YC, Wang SC (2010) J Alloys Compd 491:423
Kim BG, Cho SM, Kim TY, Jang HM (2001) Phys Rev Lett 86:3404
Fujii I, Ugorek M, Trolier-McKinstry S (2010) J Appl Phys 107:104116
Cross LE (1987) Ferroelectrics 76:241
Sarkar S, Jana PK, Chaudhui BK, Sakata H (2006) Appl Phys Lett 89:212905
Thongbai P, Yamwong T, Maensiri S (2008) Solid State Commun 147:385
Deng GC, Muralt P (2010) Phys Rev B 81:224111
Shri-Prakash B, Varma KBR (2007) J Mater Sci 42:7467. doi:10.1007/s10853-006-1251-9
Wu J, Nan CW, Lin Y, Deng Y (2002) Phys Rev Lett 89:217601
Hsiao YJ, Chang YS, Fang TH, Chai YL, Chung CY, Chang YH (2007) J Phys D 40:863
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Science Foundation (no. 50672034 and 50972056), and 973 Project of MOST (Grant no. 2009CB623303 and 2009CB929501).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, J., Lu, X., Zhang, C. et al. The effect of sintering temperature on magnetic and dielectric properties of Ho3Fe5O12 ceramics. J Mater Sci 46, 3488–3492 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-011-5254-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-011-5254-9