Abstract
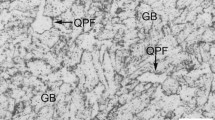
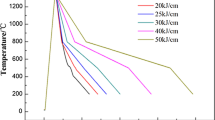
The microstructures and mechanical properties of coarse grain heat-affected zone (CGHAZ) of domestic X70 pipeline were investigated. The weld CGHAZ thermal cycles having different cooling time Δt 8/5 were simulated with the Gleeble-1500 thermal/mechanical simulator. The Charpy impact absorbed energy for toughness was measured, and the corresponding fractographs, optical micrographs, and electron micrographs were systematically investigated to study the effect of cooling time on microstructure, impact toughness, and fracture morphology in the CGHAZ of domestic X70 pipeline steel during in-service welding. The results of simulated experiment show that the microstructure of CGHAZ of domestic X70 pipeline steel during in-service welding mainly consists of granular bainite and lath bainite. Martensite–austenite (M–A) constituents are observed at the lath boundaries. With increase in cooling time, the M–A constituents change from elongated shape to massive shape. The reduction of toughness may be affected by not only the M–A constituents but also the coarse bainite sheaves. Accelerating cooling with cooling time Δt 8/5 of 8 s can be chosen in the field in-service welding X70 pipeline to control microstructures and improve toughness.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ouchi C (2001) ISIT Int 41(6):542
Wang W, Shan Y, Yang K (2009) Mater Sci Eng A 502(1–2):38
Yu H (2008) J Univ Sci Technol Beijing 15(6):683
Zhao Z, Wang Z, Zhang H, Qiao L (2007) J Univ Sci Technol Beijing 14(5):410
Avazkonandeh-Gharavol M, Haddad-Sabzevar M, Haerian A (2009) J Mater Sci 44(1):186. doi:10.1007/s10853-008-3103-2
Chiou C, Yang J, Huang C (2001) Mater Chem Phys 69(1–3):113
Li Y, Crowther DN, Green MJW, Mitchell PS, Baker TN (2001) ISIJ Int 41(1):46
Wahab MA, Sabapathy PN, Painter MJ (2005) J Mater Process Technol 168(3):414
Sathiya P, Aravindan S, Soundararajan R, Noorul Haq A (2009) J Mater Sci 44(1):114. doi:10.1007/s10853-008-3098-8
Kitagawa Y, Ikeuchi K, Kuroda T, Matsushita Y, Suenaga K, Hidaka T, Takauchi H (2008) J Mater Sci 43(1):12. doi:10.1007/s10853-007-2150-4
Weertman JR (1993) Mater Sci Eng A 166(1–2):161
Qiu H, Mori H, Enoki M, Kishi T (2000) Metall Mater Trans A 31(11):2785
Ikawa H, Oshige H, Tanoue T (1980) Trans Jpn Weld Soc 11(2):3
Raj B, Saroja S, Laha K, Karthikeyan T, Vijayalakshmi M, Bhanu Sankara Rao K (2009) J Mater Sci 44(9):2239. doi:10.1007/s10853-008-3199-4
Wang S-C, Yang J-R (1992) Mater Sci Eng A 154(1):43
Shi Y, Han Z (2008) J Mater Process Technol 207(1–3):30. doi:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.12.049
Taban E (2008) J Mater Sci 43(12):4309. doi:10.1007/s10853-008-2632-z
Shibata K, Asakura K (1995) ISIJ Int 35(8):982
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the supports of Innovation Fund for Doctors of China University of Petroleum (B2009-13).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Wang, Y., Han, T. et al. Microstructure and toughness of coarse grain heat-affected zone of domestic X70 pipeline steel during in-service welding. J Mater Sci 46, 727–733 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-4803-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-4803-y