Abstract
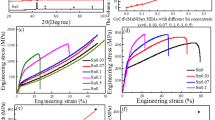
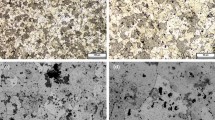
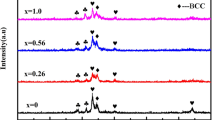
This article presents a study of solidification behavior and the corresponding microstructure of Co–Cr–W and Co–Cr–Mo alloy systems using the differential scanning calorimetry technique. The influence of main constituents on the solidification behavior and associate microstructures of these alloys are investigated. It is found that chemical composition influences significantly the solidification behavior of cobalt-based alloys. Solution-strengthened alloy has the highest solidification temperature and narrowest solidification range. Presence of carbon decreases the solidification temperature and increases the solidification range. Addition of boron greatly decreases the solidification temperature. Carbon content dominates the solidification behavior of cobalt-based alloys when the contents of the solution-strengthening elements Mo and Ni are within their saturation in the solution matrix. However, as these contents reach a certain level, formation of intermetallic compounds changes the solidification behavior of these alloys remarkably. Increase in the contents of solution-strengthening elements reduces the solid solution transformation temperature and the eutectic temperature when carbon content is constant.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davis JR (2000) Nickel, cobalt and their alloys. ASM International, Materials Park
Betteridge W (1982) Cobalt and its alloys. Halsted Press, Chichester
Yu LX, Zhao YT, Yang SL, Sun WR, Guo SR, Sun XF, Hu ZQ (2010) J Mater Sci 45(13):3448. doi:10.1007/s10853-010-4372-0
Curiotto S, Battezzati L, Johnson E, Palumbo M, Pryds N (2008) J Mater Sci 43(9):3253. doi:10.1007/s10853-008-2540-2
Zuo M, Liu XF, Sun QQ (2009) J Mater Sci 44(8):1952. doi:10.1007/s10853-009-3287-0
Sidhu RK, Ojo OA, Chaturvedi MC (2008) J Mater Sci 43(10):3612. doi:10.1007/s10853-008-2575-4
Huang P, Liu R, Wu XJ, Yao MX (2007) J Eng Mater Technol 129(4):523
Ando K, Omori T, Sato J, Sutou Y, Oikawa K, Kainuma R, Ishida K (2006) Mater Trans 47(9):2381
Riddihough M (1970) Tribology 3(4):211
Ashworth MA, Bryar JC, Jacobs MH, Davies S (1999) Powder Metall 42(3):243
Liu R, Yao MX, Wu XJ (2004) J Eng Mater Technol 126:204
Cameron CB, Ferriss DP (1975) Anti-Corrosion Method Mater 22(4):5
Mason SE, Rawlings RD (1985) J Mater Sci 20(4):1248. doi:10.1007/BF01026320
Raghu D, Wu JB (1977) Mater Perform 36(11):27
Campos I, Ramirez G, Figueroa U, Velazquez C (2007) Surf Eng 23(3):216
Campos I, Ramirez G, Figueroa U, Martinez J, Morales O (2007) Appl Surf Sci 253(7):3469
Liu YN, Yang H, Tan G, Miyazaki S, Jiang BH, Liu Y (2004) J Alloys Compd 368(14):157
Frenk A, Kurz W (1994) Wear 174:81
Schneibel JH, Ritchie RO, Kruzic JJ, Tortorelli PF (2005) Metall Mater Trans A 36:525
Maroef IS, Rowe MD, Edwards GR (2005) In: Bollinghaus Th, Herold H (eds) Hot crack phenomena in welds. Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg
Baker H (1992) In: ASM handbook, vol 3. ASM International, Materials Park
Davis JR (1998) Metals handbook. ASM International, Materials Park
Liu R, Xu W, Yao MX, Patnaik PC, Wu XJ (2005) Scr Mater 53(12):1351
Xu W, Liu R, Patnaik PC, Yao MX, Wu XJ (2007) Mater Sci Eng A 452–453:427
Acknowledgement
The authors are grateful for financial support from the Natural Science & Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC), and both financial and in-kind support from Deloro Stellite Group.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, R., Xi, S.Q., Kapoor, S. et al. Investigation of solidification behavior and associate microstructures of Co–Cr–W and Co–Cr–Mo alloy systems using DSC technique. J Mater Sci 45, 6225–6234 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-4717-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-4717-8