Abstract
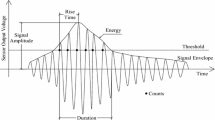
In the petroleum industry, it is known that equipments which operate in wet hydrogen sulfide (H2S) media can be subjected to damages like Hydrogen Induced Cracking (HIC) and Sulfide Stress Cracking (SSC). In this study, Acoustic Emission (AE) technique is used to monitor the cracking of steels immersed in sour media. The aim is to establish a methodology for HIC and SSC detection by AE and therefore to get more detailed information on the cracking mechanisms in steels during standard tests. The main focus of this article is the preliminary identification of the different AE sources involved during the tests performed in sour media. The methodology of identification of the different AE signals and the monitoring of HIC and SSC tests performed on different steel grades are described. The results indicate that AE can provide an early detection of cracking (HIC and SSC) when the various AE sources are identified.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
NACE (2003) MR0175/ISO 15156-2
NACE (1996) International Standard Test Method NACE TM0284-96. NACE
Eliassen S, Smith L, Jackman P (2002) In: Oil and gas production, 2nd edn. European Federation of Corrosion (EFC number16)
NACE (1996) International Standard Test Method NACE TM0177-96. NACE
Mazille H, Rothéa R (1994) In: Tretheway KR, Roberge PR (eds) Modelling aqueous corrosion. Kluwer Academic, Netherlands, p 103
Yuyama S, Kishi T, Hisamatsu Y (1983) J Acoust Emission 2(1/2):71
Pollock WJ, Hardie D, Holroyd NJH (1982) Brit Corros J 17(3):103
Gerberich WW, Jones RH, Friesel MA, Nozue N (1988) Mater Sci Eng 103:185
Ferrer F, Idrissi H, Mazille H, Fleischmann P, Labeeuw P (1999) Wear 231:108
Jones RH, Friesel MA (1992) Corrosion 48(9):751
Mazille H, Rothea R, Tronel C (1995) Corros Sci 37(9):1365
Fregonese M, Idrissi H, Mazille H, Renaud L, Cetre Y (2001) J Mater Sci 36:557. doi:10.1023/A:1004891514836
Fregonese M, Idrissi H, Mazille H, Renaud L, Cetre Y (2001) Corros Sci 43(4):627
Kim YP, Fregonese M, Mazille H, Féron D, Santarini G (2003) NDT&E Int 36:553
Kim YP, Fregonese M, Mazille H, Féron D, Santarini G (2006) Corros Sci 48(12):3945
Bellanger F, Mazille H, Idrissi H (2002) NDT&E Int 35:385
Jaubert L, Fregonese M, Caron D, Ferrer F, Franck C, Gravy E, Labeeuw P, Mazille H, Renaud L (2005) Insight 47(8):465
Weng C-C, Chen R-T (1993) J Chinese Inst Eng 16(4):489
Weng C-C, Chen R-T (1993) J Chinese Inst Eng 16(2):195
Cayard MS, Kane RD (1997) Evaluation of various methods of reducing the duration of SSC qualification testing. NACE International, Paper no. 57
Tsai SY, Shih HC (1998) J Electrochem Soc 145(6):1968
Gingell ADB, Garat X (1999) Observations of damage modes as a function of microstructure during NACE TM0177-96 tensile testing of API 5L grade X60 linepipe steel. NACE International, Paper no. 600
Amami S, Marchand P, Duval S, Longaygue X, Fregonese M, Mazille H, Millet JP (2003) Early detection and monitoring of sulfide stress cracking (SSC) of steels by an acoustic emission method. Environmental Degradation of Engineering Materials, Bordeaux, France
Galland J, Sojka J, Jerome M (2004) In: Normand B, Pebere N, Richard C, Wery M (eds) Prévention et lutte contre la corrosion. Presses polytechniques et Universitaires Romandes, Lausanne, pp 273–309
Rawlings RD (1987) In: Kuhn AT (ed) Techniques in electrochemistry, corrosion and metal finishing. A handbook. Wiley, Brisbane, p 351
Kittel J, Smanio V, Fregonese M, Garnier L, Lefebvre X (2010) Corros Sci 52(4):1386
Liu ZY, Dong CF, Li XG, Zhi Q, Cheng YF (2009) J Mater Sci 44(16):4228. doi:10.1007/s10853-009-3520-x
Abelev E, Sellberg J, Ramanarayanan TA, Bernasek SL (2009) J Mater Sci 44:6167. doi:10.1007/s10853-009-3854-4
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank M. Boinet (Euro-Physical Acoustics), for his help in the analysis of AE data, and G. Parrain for his technical support. H. Marchebois (Vallourec) is also acknowledged for helpful discussions on H2S cracking mechanisms.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smanio, V., Fregonese, M., Kittel, J. et al. Wet hydrogen sulfide cracking of steel monitoring by acoustic emission: discrimination of AE sources. J Mater Sci 45, 5534–5542 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-4613-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-4613-2