Abstract
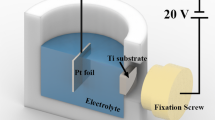
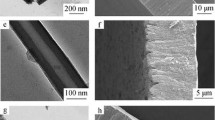
Nanotubular oxide layer formation on biomedical grade α + β type Ti–13Nb–13Zr alloy was investigated using anodization technique as a function of applied dc potential (10–40 V) and anodizing time (30–180 min) in 1 M H3PO4 + 0.5 wt% NaF at room temperature. The as-formed and crystallized nanotubes were characterized using SEM, XRD, and TEM. There was a bimodal size distribution of nanotubes with diameters at the range of 25–110 nm. Nanotubes nucleated on β matrix exhibited uniform surface appearance with circular morphology, whereas those nucleated on α phase yielded parabolic shape. TEM/EDS analysis detected the three component elements of the alloy in the nanotube. Heat treatment significantly altered the distinct interface between the nanotubes and the barrier oxide layer.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kubota S, Johkura K, Asanuma K, Okouchi Y, Ogiwara N, Sasaki K, Kasuga T (2004) J Mater Sci Mater Med 15:1031
Oh SH, Finõnes RR, Daraio C, Chen LH, Jin S (2005) Biomaterials 26:4938
Masuda H, Fukuda K (1995) Science 268:1466
Gong D, Grimes CA, Varghese OK, Hu WC, Sing RS, Chen Z, Dickey EC (2001) J Mater Res 16:3331
Macak JM, Tsuchiya H, Ghicov A, Yasuda K, Hahn R, Bauer S, Schmuki P (2007) Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci 11:3
Elsanousi A, Zhang J, Fadlalla HMH, Zhang F, Wang H, Ding X, Huang Z, Tang C (2008) J Mater Sci 43:7219. doi:10.1007/s10853-008-2947-9
Tian T, Xiao XF, Liu RF, She HD, Hu XF (2007) J Mater Sci 42:5539. doi:10.1007/s10853-006-1104-6
Allam NK, Feng XJ, Grimes CA (2008) Chem Mater 20:6477
Jakubowics J (2008) Electrochem Commun 10:735
Popat KC, Leoni L, Grimes CA, Desai TA (2007) Biomaterials 28:3188
Uchida M, Kim HM, Kokubo T, Fujibayashi S, Nakamura T (2003) J Biomed Mater Res 64:164
Davidson JA, Kovacs P (1992) US Patent 4,169,597
Long M, Rack RJ (1998) Biomaterials 19:1621
Sumner DR, Galante JO (1992) Clin Orthoped Rel Res 274:202
Tsuchiya H, Macak JM, Ghicov A, Tang YC, Fujimoto S, Niinomi M, Noda T, Schmuki P (2006) Electrochim Acta 52:94
Mor GK, Varghese OK, Paulose M, Shankar K, Grimes CA (2006) Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 90:2011
Zwilling V, Ceretti ED, Forveille AB (1999) Electrochim Acta 45:921
Jäger M, Zilkens C, Zanger K, Krauspe R (2007) J Biomed Biotechnol 2007:1
Bai J, Zhou B, Li L, Liu Y, Zheng Q, Shao J, Zhu X, Cai W, Liao J, Zou L (2008) J Mater Sci 43:1880. doi:10.1007/s10853-007-2418-8
Saji VS, Choe HC (2009) Corros Sci. doi:10.1016/j.corsci.2009.04.013
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saji, V.S., Choe, H.C. & Brantley, W.A. Nanotubular oxide layer formation on Ti–13Nb–13Zr alloy as a function of applied potential. J Mater Sci 44, 3975–3982 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-3542-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-3542-4