Abstract
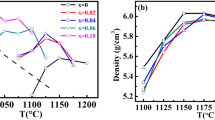
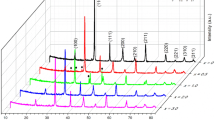
In this work, the effects of Nb2O5 addition on the dielectric properties and phase formation of BaTiO3 were investigated. A core–shell structure was formed for Nb-doped BaTiO3 resulted from a low diffusivity of Nb5+ ions into BaTiO3 when grain growth was inhibited. In the case of 0.3–4.8 mol% Nb2O5 additions, two dielectric constant peaks were observed. The Curie dielectric peak was determined by the ferroelectric-paraelectric transition of grain core, whereas the secondary broad peak at lower temperature was due to strong chemical inhomogeneity in Nb-doped BaTiO3 ceramics. The dielectric constant peak at Curie temperature was markedly depressed with the addition of Nb2O5. On the other hand, the secondary dielectric constant peak was enhanced when sintered above 1280 °C for higher Nb2O5 concentrations (≥1.2 mol%). The Curie temperature was shifted to higher temperatures, whereas the transition temperature corresponding to the secondary peak moved to lower temperatures as increasing the amount of Nb2O5 more than 1.2 mol%. The decrease of this lower transition temperature was assumed to be closely related with the secondary phase formation when Nb concentration greater than 1.2 mol%. From XRD analyses, a large amount of secondary phases was observed when Nb2O5 amount exceeded 1.2 mol%. The coefficients of thermal expansion of Nb-doped BaTiO3 were increased with increasing Nb2O5 contents, resulting in large internal stress between cores and shells. Therefore, the shift of Curie temperature to higher temperatures was attributed to internal stress resulting from the formation of a core–shell structure and a large amount of secondary phase grains.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Merz WJ (1953) Phys Rev 91:513
Lin JN, Wu TB (1990) J Appl Phys 68:985
Hennings D, Rosenstein G (1984) J Am Ceram Soc 67:249
Tang B, Zhang SR, Yuan Y. J Mater Sci Mater Electron. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-007-9477-0
Jung YS, Na ES, Paik U (2002) Mater Res Bull 37:1633
Arlt G, Hennings D, de With G (1985) J Appl Phys 58:1619
Uchino K, Sadanaga E, Hirose T (1989) J Am Ceram Soc 72:1555
Begg BD, Vance ER, Nowotny J (1994) J Am Ceram Soc 77:3186
Albertsen K, Hennings D, Steigelmann O (1998) J Electroceram 2(3):193
Lee S et al (2007) J Appl Phys 101:054119
Sato S, Fujikawa Y, Nomura T (2000) Am Ceram Soc Bull 79:155
Song YH, Hwang JH, Han YH (2005) Jpn J Appl Phys 44:1310
Kahn M (1971) J Am Ceram Soc 54:455
Cui B, Yu PF, Tian J (2007) Mater Sci Eng A 454–455:667
Sahu P, Pradhan SK, De M (2004) J Alloys Compd 377:103
Cont L et al (2002) Ferroelectrics 267:323
Iverson BJ, Jones JL, Bowman KJ (2006) Phys B Condens Matter 385–386:581
Brzozowski E, Castro MS, Foschini CR (2002) Ceram Int 28:773
Chiang SK, Lee WE, Readey DW (1987) Am Ceram Soc Bull 66:1230
Thomas NW (1990) J Phys Chem Solids 51:1419
Chazono H, Kishi H (2000) J Am Ceram Soc 83:101
Hwang JH, Choi SK, Han YH (2001) Jpn J Appl Phys 40:4952
Samara GA (1966) Phys Rev 151:378
Armstrong TR, Buchanan RC (1990) J Am Ceram Soc 73:1268
Buessem WR, Cross LE, Goswami AK (1966) J Am Ceram Soc 49:33
Buessem WR, Cross LE, Goswami AK (1966) J Am Ceram Soc 49:36
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, Y., Zhang, S.R., Zhou, X.H. et al. Effects of Nb2O5 doping on the microstructure and the dielectric temperature characteristics of barium titanate ceramics. J Mater Sci 44, 3751–3757 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-3502-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-3502-z