Abstract
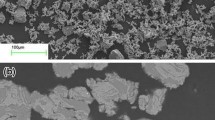
Porous NiTi shape memory alloys (SMAs) were successfully fabricated by low-pressure sintering (LPS), and the pore features have been controlled by adjusting the processing parameters. The porous NiTi SMAs with high porosity (45%) and large pore size (200–350 μm) can be prepared by LPS using TiH1.5 as pore-forming agent. These alloys exhibit isotropic pore structure with three-dimensional interconnected pores. The porous NiTi SMA produced by LPS exhibits superelasticity and mechanical properties superior to that by conventional sintering.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bansiddhi A, Sargeant TD, Stupp SI et al (2008) Acta Biomater 4:773
Zhao Y, Taya M, Izui H (2006) Int J Solid Struct 43:497
Zhou JB, Gao LP, Wang KS (2005) J Rare Earth 23:449
Levine B (2008) Adv Eng Mater 10:788
Green SM, Grant DM, Kelly NR (1997) Powder Metall 40:43
Li BY, Rong LJ, Li YY (1998) J Mater Res 13:2847
Otaguchi M, Kaieda Y, Oguro N (1990) J Japan Inst Metals 54:214
Li BY, Rong LJ, Li YY, Gjunter VE (2000) J Mater Res 15:10
Zhao Y, Taya M, Kang YS, Kawasaki A (2005) Acta Mater 53:337
Vandygriff EC, Lagoudas DC, Thangarai JK, Chen YC (2000) Proceedings of ASC 15th annual technical conference. Technomic Publishing Co Inc., Lancaster, p 239
Yuan B, Chung CY, Zhu M (2004) Mater Sci Eng A 382:181
Bansiddhi A, Dunand D (1612) Intermetallics 15:1612
Zhang YP, Yuan B, Zeng MQ, Chung CY, Zhang XP (2007) J Mater Process Technol 192:439
Yuan B, Zhu M, Gao Y, Chung CY (2008) Smart Mater Struct 17:025013
Li BY, Rong LJ, Li YY, Gjunter VE (2000) Metall Mater Trans A 31:1867
Ayers RA, Simske SJ, Bateman TA (1999) J Biomed Mater Res 45:42
Barin I (1989) Thermochemical data of pure substances. Weinheim, Federal Republic of Germany; VCH, New York
Bataillard L, Bidaux E, Gotthardt R (1998) Philos Magn 78:327
Miyazaki S, Otsuka K, Wayman CM (1989) Acta Metall 37:1873
Su PC, Wu SK (2004) Acta Mater 52:1117
Wu SL, Liu XM, Chu PK (2008) J Alloy Compd 449:139
Carroll MC, Somsen CH, Eggler G (2004) Scr Mater 50:187
Filip P, Mazanec K (2001) Scr Mater 45:701
Allafi JK, Dlouhy A, Eggeler G (2002) Acta Mater 50:4255
Porter DA, Easterling KE (1997) Phase transformations in metals and alloys. Reprinted 2nd edn. Chapman and Hall, London
Zhou YM, Zhang J, Fan GL et al (2005) Acta Mater 53:5365
Wu SL, Chung CY, Liu XM et al (2007) Acta Mater 55:3437
Li BY, Rong LJ, Li YY (2000) Intermetallics 8:643
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the support from National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.50701019), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 20060390199), the Ministry of Education (Project No IRT0551), Guangdong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (2005 Team project), and City University of Hong Kong Grant (Project No.7002215).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Yuan, B., Gao, Y. et al. High-porosity NiTi superelastic alloys fabricated by low-pressure sintering using titanium hydride as pore-forming agent. J Mater Sci 44, 875–881 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-3193-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-3193-x