Abstract
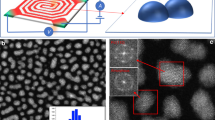
The diffusion and coalescence of Au–Cu alloy nanoparticles was studied at high magnification using in situ transmission electron microscopy. The particles prepared by physical vapor deposition onto amorphous-C support films had an average composition of Cu–43 at% Au and diameters of 15–50 nm. In the case analyzed, the larger of two nanoparticles remained stationary throughout the coalescence process while a smaller nanoparticle moved toward the larger particle at a temperature of ~573 K. The surface of the small nanoparticle was observed to fluctuate while approaching the larger particle, demonstrating that collective atom process occurs along the particle periphery. The particle also decreased in size during the process, indicating that it was losing mass as well as migrating. Direct evidence of a diffusional flux between particles was observed before the coalescence process. The small nanoparticle coalesced into the large one at a highly accelerated rate compared to its prior migration.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Datye AK (2003) J Catal 216:144
Lifshitz IM, Slyozov VV (1961) Phys Chem Solids 19:35
Voorhees PW (1985) J Stat Phys 38:231
Wynblatt P, Gjostein NA (1976) Acta Mater 24:1165
Zinke-Allmang M, Feldman LC, Grabow MH (1992) Surf Sci Rep 16:377
Morgenstern K, Rosenfeld G, Comsa G (1996) Phys Rev Lett 761:2113
Wen J-M, Chang S-L, Burnett JW et al (1994) Phys Rev Lett 73:2591
Morgenstern K, Rosenfeld G, Poelsema B et al (1995) Phys Rev Lett 74:2058
Reiss H (1968) J Appl Phys 39:5045
Bardotti L, Jensen P, Hoareau A et al (1995) Phys Rev Lett 74:4694
Ajayan PM, Marks LD (1988) Phys Rev Lett 60:585
Smith DJ, Petfordlong AK, Wallenberg LR et al (1986) Science 233:872
Jensen P, Clement A, Lewis LJ (2004) Comput Mater Sci 30:137
Yang W-C, Zeman M, Ade H et al (2003) Phys Rev Lett 90:136102
Sholl DS, Skodje RT (1996) Physica A 231:631
Zhu H, Averback RS (1996) Philos Mag Lett 73:27
Sinclair R, Itoh T, Chin R (2002) Microsc Microanal 8:288
Thune E, Carpene E, Sauthoff K, Seibt M, Reinke P (2005) J Appl Phys 98:034304
Chatterjee K, Howe JM, Johnson WC et al (2004) Acta Mater 52:2923
Lee JG, Mori H (2007) Solid State Phenom 127:135
Wallenberg R, Smith DJ, Bovin JO (1985) Ultramicroscopy 17(2):182
Jensen P (1999) Rev Mod Phys 71:1695
Wanner M, Werner R, Gerthsen D (2006) Surf Sci 600:632
Hwang HJ, Kwon O, Kang JW (2004) Solid State Commun 129:687
Lewis LJ, Jensen P, Combe N et al (2000) Phys Rev B 61:16084
Foiles SM, Baskes MI, Daw MS (1986) Phys Rev B 33:7983
Acknowledgement
This research was supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant DMR-0554792.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gautam, A.R.S., Howe, J.M. In situ TEM study of Au–Cu alloy nanoparticle migration and coalescence. J Mater Sci 44, 601–607 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-3080-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-3080-5