Abstract
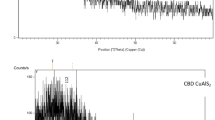
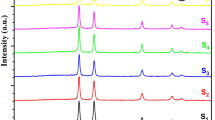
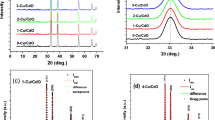
Copper indium diselenide (CuInSe2) compound was synthesized by reacting its elemental components, i.e., copper, indium, and selenium, in stoichiometric proportions (i.e., 1:1:2 with 5% excess selenium) in an evacuated quartz ampoule. Structural and compositional characterization of synthesized pulverized material confirms the polycrystalline nature of tetragonal phase and stoichiometry. CuInSe2 thin films were deposited on soda lime glass substrates kept at different temperatures (300–573 K) using flash evaporation technique. The effect of substrate temperature on structural, morphological, optical, and electrical properties of CuInSe2 thin films were investigated using X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD), atomic force microscopy (AFM), optical measurements (transmission and reflection), and Hall effect characterization techniques. XRD analysis revealed that CuInSe2 thin films deposited above 473 K exhibit (112) preferred orientation of grains. Transmission and reflectance measurements analysis suggests that CuInSe2 thin films deposited at different substrate temperatures have high absorption coefficient (~104 cm−1) and optical energy band gap in the range 0.93–1.02 eV. Results of electrical characterization showed that CuInSe2 thin films deposited at different substrate temperatures have p-type conductivity and hole mobility value in the range 19–136 cm2/Vs. Variation of energy band gap and resistivity of CuInSe2 thin films deposited at 523 K with thickness was also studied. The temperature dependence of electrical conductivity measurements showed that CuInSe2 film deposited at 523 K has an activation energy of ~30 meV.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Repins I, Contreras MA, Egaas B, DeHart C, Scharf J, Perkins CL, To B, Noufi R (2008) Prog Photovolt Res Appl 16(3):235
Akl AAS, Ashour A, Ramadan AA, Abd El Hady K (2001) Vacuum 61:75
Klenk M, Schenker O, Alberts V, Bucher E (2001) Thin Solid Films 387:47
Joseph CM, Menon CS (2001) J Phys D Appl Phys 34:1143
Martill I, Santamaria J, Gonzalez-Diaz G, Sanchez-Quesada F (1987) J Appl Phys 62:4163
Abernathy CR, Bates CW, Anani AA, Haba B, Smestad G (1984) Appl Phys Lett 45:890
Huang CJ, Meen TH, Lai MY, Chen WR (2004) Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 82:553
Hodes G, Engelhard T, Cahen D, Kazmerski LL, Herington C R (1985) Thin Solid Films 128:93
Ashour A (2006) J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 17:625
Merino JM, Leon M, Rueda F, Diaz R (2000) Thin Solid Films 361–362:22
Barett CS (1953) Structure of Metals, Crystallographic methods, Principles and Data. McGraw-Hill, New York, p 156
Noufi R, Axton R, Herrington C, Deb SK (1984) Appl Phys Lett 45(6):668
Dhanam M, Balsundarprabhu R, Jayakumar S, Gopalkrishnan P, Kanan MD (2002) Phys Stat Sol (a) 191:149
Demichelis F, Kaniadakis G, Tagliferro A, Tresso E (1987) J Appl Opt 26:1737
Schmidt J, Roscher HH, Labusch R (1994) Thin Solid Films 251:116
Yamaguchi T, Matsufusa J, Yoshida A (1992) Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 27:25
Castaneda SI, Rueda F (2000) Thin Solid Films 361:145
Petritz RL (1956) Phys Rev 104(6):1508
Wu F, Chiou BS (1993) Appl Surf Sci 68:497
Moulson AJ (1990) Electroceramics. Wiley, New York, p 26
Aissaoui O, Mehdaoui S, Bechiri L, Benebdeslem M, Benslim N, Amara A, Mahdjoubi L, Nouet G (2007) J Phys D Appl Phys 40:5663
Acknowledgements
N. M. Shah is grateful to University Grants Commission (UGC) (Western Region Office, Pune, India) for the award of teacher fellowship under “Faculty Improvement Program” in X plan. The authors also wish to thank UGC (New Delhi, India) for providing financial assistance through major research project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shah, N.M., Ray, J.R., Kheraj, V.A. et al. Structural, optical, and electrical properties of flash-evaporated copper indium diselenide thin films. J Mater Sci 44, 316–322 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-3046-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-3046-7