Abstract
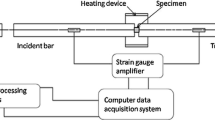
In this work, we have processed commercial purity tungsten (W) via different routes of equal-channel angular extrusion (ECAE) at temperatures as low as 600 °C. We have systematically evaluated the quasi-static and dynamic compressive behaviors of the processed W. Quasi-static compression tests were performed using an MTS hydro-servo system at room temperature. It is observed that samples ECAE processed at 800 °C show higher yield and flow stresses than those processed at other temperatures; no obvious strain hardening is observed in the quasi-static stress–strain curves. Quasi-static strain rate jump tests show that the strain rate sensitivity of ECAE W is in the range of 0.02 to 0.03, smaller than that of coarse-grained W. Uni-axial dynamic compressive tests were performed using the Kolsky bar (or split-Hopkinson pressure bar, SHPB) system. Post-loading SEM observations revealed that under dynamic compression, the competition between cracking at pre-existing extrinsic surface defects, grain boundaries, and uniform plastic deformation of the individual grains control the overall plastic deformation of the ECAE W. The existence of flow softening under dynamic loading has been established for all of the ECAE W specimens.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krasko GL (1993–1994) Int J Refract Met Hard Mater 12:251
Dummer T, Lasalvia JC, Ravichandran G, Meyers MA (1998) Acta Mater 46:6267. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6454(98)00255-9
Lennon AM, Ramesh KT (2000) Mater Sci Eng A 276:9. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(99)00517-1
Wei Q, Jiao T, Ramesh KT, Ma E, Kecskes LJ, Magness L et al (2006) Acta Mater 54:77. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2005.08.031
Kecskes LJ, Cho KC, Dowding RJ, Schuster BE, Valiev RZ, Wei Q (2007) Mater Sci Eng A 467:33. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2007.02.099
Lu K (2008) Int Mater Rev 53:21. doi:https://doi.org/10.1179/174328008X254358
Valiev RZ, Estrin Y, Horita Z, Langdon TG, Zehetbauer M, Zhu YT (2006) JOM-US 58:33
Wei Q, Ramesh KT, Kecskes LJ, Mathaudhu SN, Hartwig KT (2008) Mater Sci Forum 579:75
Bechtold JH (1956) J Met Trans AIME 206:142
Farrell K, Schaffhauser AC, Stiegler JO (1967) J Less Common Met 13:141. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-5088(67)90177-4
Wei Q, Zhang H, Schuster BE, Ramesh KT, Valiev RZ, Kecskes LJ et al (2006) Acta Mater 54:4079. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2006.05.005
Wei Q, Ramesh KT, Ma E, Kesckes LJ, Dowding RJ, Kazykhanov VU et al (2005) Appl Phys Lett 86:101907. doi:https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1875754
Barber RE, Dudo T, Yasskin PB, Hartwig KT (2004) Scripta Mater 51:373. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2004.05.022
Follansbee PS (1985) In ASM metals handbook. American Society of Metals. p 190
Hall EO (1951) P Phys Soc B 64:747
Petch NJ (1953) J Iron Steel I 174:25
Wei Q (2007) J Mater Sci 42:1709. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0700-9
Wei Q, Cheng S, Ramesh KT, Ma E (2004) Mater Sci Eng A 381:71. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2004.03.064
Wei Q, Kecskes LJ (2008) Mater Sci Eng A. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2008.01.013
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by the U.S. Army Research Laboratory under contract # W911QX-06-C-0124. The authors would like to thank Ms. Xueran Liu (University of North Carolina at Charlotte) for assistance with SEM operations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, Z., Guo, Y.Z., Mathaudhu, S.N. et al. Quasi-static and dynamic mechanical properties of commercial-purity tungsten processed by ECAE at low temperatures. J Mater Sci 43, 7379–7384 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-2788-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-2788-6