Abstract
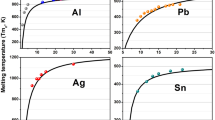
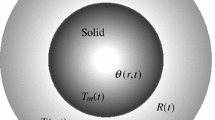
The melting behavior of nanometer-sized Sn particles with radius in the range between 5 and 50 nm is analyzed within the conceptual framework of classical thermodynamics. Experimentally observed size-dependent melting points and latent heats of fusion are exploited to point out the occurrence of pre-melting phenomena at the particle surface. The size-dependent values of the thermodynamic state functions associated with the solid–liquid interface are estimated together with the thickness of the interface layer.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alivisatos P (1996) Science 271:933
Moriarty P (2001) Rep Prog Phys 64:297
Jortner J, Rao CNR (2002) Pure Appl Chem 74:1491
Schmidt M, Kusche R, Von Issendorf B, Haberland H (1998) Nature 393:238
Thomson W (1871) Phil Mag 42:448
Pawlow P (1909) Z Phys Chem (Munich) 65:1
Hollomon TH, Turnbull D (1953) Progress in Metal Physics 4:333
Wronski CRM (1967) Brit J Appl Phys 18:1731
Coombes CJ (1972) J Phys F: Metal Phys 2:441
Baletto F, Ferrando R (2005) Rev Mod Phys 77:371
Buffat PH, Borel J-P (1976) Phys Rev A 13:2287
Couchman PR, Jesser WA (1977) Nature 269:481
Reiss H, Mirabel P, Whetten RL (1988) J Phys Chem 92:7241
Sakai H (1996) Surf Sci 351:285
Peters KF, Cohen JB, Chung Y-W (1998) Phys Rev B 57:13430
Tartaglino U, Zykova-Timan T, Ercolessi F, Tosatti E (2005) Phys Rep 411:291
Lai S, Guo JY, Petrova V, Ramanath G, Allen LH (1996) Phys Rev Lett 77:99
Efremov MYu, Schiettekatte F, Zhang M, Olson EA, Kwan AT, Berry LS, Allen LH (2000) Phys Rev Lett 85:3560
Zhang M, Efremov MYu, Schiettekatte F, Olson EA, Kwan AT, Lai SL, Greene JE, Allen LH (2000) Phys Rev B 62:10548
Olson EA, Efremov MYu, Zhang M, Zhang Z, Allen LH (2005) J Appl Phys 97:034304
Delogu F (2005) J Phys Chem B 109:21938
Brandes EA, Brook GB (eds) (1992) Smithells metals reference handbook, 7th edn. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford
Porter DA, Easterling KE (1992) Phase transformations in metals and alloys, 2nd edn. Chapman & Hall, London
Kauzmann W (1948) Chem Rev 43:219
Kleinert H (1989) Gauge theory in condensed matter. World Scientific, Singapore
Acknowledgements
Prof. L. H. Allen is acknowledged for having authorized the use of experimental data collected by his group at the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. Financial support has been given by the University of Cagliari.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Delogu, F. A thermodynamic description of the melting process in nanometer-sized particles. J Mater Sci 43, 2611–2617 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-2470-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-2470-z