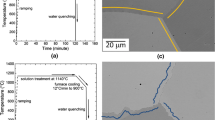
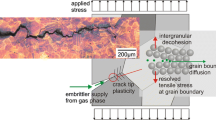
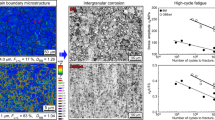
Abstract
Failure of structural components operating under high mechanical loading and/or in aggressive environments can often be attributed to intergranular degradation, e.g. by creep, corrosion, fatigue or brittle cracking. The present article is focussed on oxygen-diffusion-controlled grain-boundary attack, for example, of a nickel-based superalloy leading to intercrystalline oxidation or rapid cracking by dynamic embrittlement. Since grain-boundary diffusion depends on the crystallographic orientation relationship between adjacent grains, the grain-boundary-engineering approach was applied to reduce the susceptibility to grain-boundary attack. The relevant mechanisms are discussed in terms of modifying the network of general high-angle and so-called special grain boundaries taking the results of cracking experiments on bicrystals into account.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pugh SF (1991) An introduction to grain boundary fracture of metals. The Institute of Metals, London
Carpenter W, Kang BSJ, Chang KM (1997) In: Loria EA (ed) Proceedings superalloys 718, 625,706 and various derivatives, (TMS 1997). p 679
Bika D (1992) Dynamic embrittlement in metallic alloys. PhD thesis, Univ. of Pennsylvania
Krupp U (2005) Int Mater Rev 50:83
Krupp U, Wagenhuber PE-G, Kane WM, McMahon CJ Jr (2005) Mater Sci Tech 21:1247
Randle V (2005) Int Mater Rev 49:1
Watanabe T (1984) Res Mech 11:47
Shimada M, Kokawa H, Wang ZJ, Sato YS, Karibe I (2002) Acta Mater 50:2331
Lin P, Palumbo G, Erb U, Aust KT (1995) Scripta Metall Mater 33:1387
Yamaura S, Tsurekawa S, Watanabe T (2003) Mater Trans 44:1494
Davé VR, Cola MJ, Kumar M, Schwartz AJ, Hussen GNA (2004) Suppl Weld J 1:1
Zhou Y, Aust KT, Erb U, Palumbo G (2001) In: Proceedings processing and fabrication of advanced materials 10 (ASM Intern.). p 438
Furuhara T and Maki T (2005) Mater J Sci 40:919
Alexandreanu B, Spencer BH, Thaveeprungsriporn V, Was GS (2003) Acta Mater 51:3831
Lehockey EM, Palumbo G (1997) Mater Sci Eng A237:168
Gao Y, Kumar M, Nalla RK, Ritchie RO (2005) Metall Mater Trans A 36A:3325
Watanabe T, Tsurekawa S (eds) (2005) J Mater Sci 40:817
Kumar M, Schuh C (eds) (2006) Scripta Mater 54:961
Watanabe T, Tsurekawa S, Zhao X, Zuo L (2006) Scripta Mater 54:969
Winning M (2006) Scripta Mater 54:987
Furukawa M, Horita Z, Langdon TG (2005) J Mater Sci 40:909
Randle V (2006) Scripta Mater 54:1005
Kim C-S, Rollett AD, Rohrer GS (2006) Scripta Mater 54:1011
Randle V (1993) The measurement of grain boundary geometry. Institute of Physics Publ., Bristol
Brandon DG (1966) Acta Met 14:1479
Palumbo G, Aust KT (1990) Acta Met Mater 11:2343
Krupp U (2007) Fatigue crack propagation in metals and alloys. Wiley VCH, Weinheim
Pfaendtner JA, McMahon CJ Jr (2001) Acta Mater 49:3369
Birks N, Meier GH, Pettit FS (2006) Introduction to the high-temperature oxidation of metals. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Bika D, Pfaendtner JA, Menyhard M, Mc Mahon CJ Jr (1995) Acta Metall Mater 43:1895
Mishin Y, Herzig C (1999) Mater Sci Eng A260:55
Kaur I, Gust W (1989) Fundamentals of grain and interphase boundary diffusion. Ziegler-Press, Stuttgart
Lejcek P, Hofmann S (1993) Interface Sci 1:163
Muthiah RC, Pfaendtner JA, Ishikawa S, McMahon CJ Jr (1999) Acta Mater 47:2797
Kane WM (2005) Dynamic embrittlement of nickel-based alloys. PhD thesis, Univ. of Pennsylvania
Krupp U, Kane WM, Liu X, Laird C, McMahon CJ Jr (2003) Mater Sci Eng A349:213
Palumbo G, Lehockey EM, Lin P (1998) J Mater 2:40
Randle V, Owen G (2006) Acta Mater 54:1777
Schuh C, Kumar M, King WE (2006) Acta Mater 51:687
Chen Y, Schuh C (2006) Acta Mater 54:4709
Yun Bi H, Kokawa H, Wang ZJ, Shimada M, Sato YS (2003) Scripta Mater 49:219
Xu Y, Bassani JL (1998) Mater Sci Eng A260:48
Klinger L, Rabkin E (2007) Acta Mater (in press) (doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.200704.039)
Tan L, Sridharan K, Allen TR (2006) J Nuclear Mater 348:263
Acknowledgements
The financial support by the U.S. Air Force Office of Scientific Research under grant no. 538532, by the U.S. Department of Energy, Basic Energy Sciences, under grant no. DE-FGO-OIER 45924, the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG), under grant no. KR1999/7-1 and by the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation through a Feodor Lynen fellowship to the author is gratefully acknowledged. Furthermore, the author acknowledges the experimental contribution by Dr. William M. Kane, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA and Dr. Vicente Braz da Trinade Filho, University of Siegen, Germany, and the many useful discussions with Professor Charles J. MacMahon Jr. and Professor Campbell Laird, both University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krupp, U. Improving the resistance to intergranular cracking and corrosion at elevated temperatures by grain-boundary-engineering-type processing. J Mater Sci 43, 3908–3916 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-007-2363-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-007-2363-6