Abstract
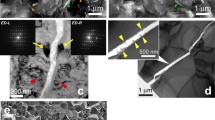
The active fracture modes in glass-ceramics, produced by controlled crystallization from three starting vitreous products containing PbO and SiO2, were studied and compared. The goal was to examine the active fracture modes in PbO-rich glass-ceramic materials, where the main glass former was PbO, and compare these results with those reported in the literature, where the main glass former was SiO2. The influence of composition, shape and mean size of the ceramic phase on the active fracture modes of the glass-ceramics was also examined. It was observed that the microhardness and fracture toughness of the starting vitreous products decrease with increasing PbO content. Increase in the relative amount of SiO2 resulted in a decrease of the percentage of the ceramic phase. Glass-ceramics with higher PbO content showed typical behaviour of high toughness material, i.e. intergranular fracture mode, with lower microhardness value. Glass-ceramics with lower PbO content showed typical behaviour of high-strength material, i.e. transgranular fracture mode, with higher microhardness value.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hölland W, Beal G (2002) Glass-ceramic technology. ACS, Westerville, p 4
Kavouras P, Charitidis C, Karakostas Th (2006) J Non-Cryst Sol 352:5515
Kriven EM, Lee SJ (2005) Am J Ceram Soc 88:1521
Zhai H, Huang Y, Wang C, Wu X (2000) J Am Ceram Soc 83:2006
Charitidis C, Karakasides TE, Kavouras P, Karakostas Th (2007) J Phys Condens Mat 19:266
Shelby JE (1997) Introduction to glass science and technology. RSC Paperbacks, Cambridge, p 78
Wang PW, Zhang L (1996) J Non-Cryst Sol 194:129
Anstis GR, Chantikul P, Lawn BR, Marshall DB (1981) J Am Ceram Soc 64:533
Amin KA (2000) Engineered materials handbook: ceramics and glasses. ASM International, p 599
Marshall DB, Noma T, Evans AG (1982) J Am Ceram Soc 65:C175
Cook RF, Pharr GM (1990) J Am Ceram Soc 73:787
Vogel W (1994) Glass chemistry, 2nd edn. Springer-Verlag, p 158
Strnad Z (1986) Glass-ceramic materials. Elsevier, Amsterdam, p 230
Hrubý A (1972) Czech J Phys B 22:1187
Shrikhande VK, Sudarsan V, Kothiyal GP, Kulshreshtha SK (2001) J Non-Cryst Sol 283:18
Doremus RH (1994) Glass science and technology. John Wiley and Sons, New York, p 163
Salama SN, El-Batal HA (1994) J Non-Cryst Solids 168:179
Li H, Bradt RC (1996) J Mater Sci 31:1065
Chai H, Lawn BR (2007) Acta Mater 55:2555
Acknowledgement
This work was co-funded by the European Social Fund and National resources, through the “PYTHAGORAS II” program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kavouras, P., Kehagias, T., Komninou, P. et al. Interface controlled active fracture modes in glass-ceramics. J Mater Sci 43, 3954–3959 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-007-2221-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-007-2221-6